Abstract
Purpose
Several cases have been reported in which central nervous system (CNS) metastases of non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) resistant to gefitinib were improved by erlotinib. However, there has been no study in which cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) concentrations of gefitinib and erlotinib are directly compared. Thus, we aimed to compare them.
Methods
We examined 15 Japanese patients with NSCLC and CNS metastases with epidermal growth factor receptor gene mutations who received CSF examinations during epidermal growth factor receptor-tyrosine kinase inhibitors treatment (250 mg daily gefitinib or 150 mg daily erlotinib). Plasma and CSF concentrations were determined using high-performance liquid chromatography with tandem mass spectrometry.
Results
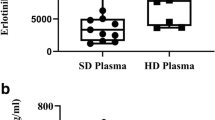
The concentration and penetration rate of gefitinib (mean ± standard deviation) in the CSF were 3.7 ± 1.9 ng/mL (8.2 ± 4.3 nM) and 1.13 ± 0.36 %, respectively. The concentration and penetration rate of erlotinib in the CSF were 28.7 ± 16.8 ng/mL (66.9 ± 39.0 nM) and 2.77 ± 0.45 %, respectively. The CSF concentration and penetration rate of erlotinib were significantly higher than those of gefitinib (P = 0.0008 and <0.0001, respectively). The CNS response rates of patients with erlotinib treatment were preferentially (but not significantly) higher than those with gefitinib treatment. (1/3 vs. 4/7, respectively). Leptomeningeal metastases in one patient, which were refractory to gefitinib, dramatically responded to erlotinib.
Conclusions
This study suggested that higher CSF concentration could be achieved with erlotinib and that erlotinib could be more effective for the treatment for CNS metastases, especially leptomeningeal metastases, than gefitinib.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Paez JG, Jänne PA, Lee JC, Tracy S, Greulich H, Gabriel S, Herman P, Kaye FJ, Lindeman N, Boggon TJ, Naoki K, Sasaki H, Fujii Y, Eck MJ, Sellers WR, Johnson BE, Meyerson M (2004) EGFR mutations in lung cancer: correlation with clinical response to gefitinib therapy. Science 304:1497–1500
Lynch TJ, Bell DW, Sordella R, Gurubhagavatula S, Okimoto RA, Brannigan BW, Harris PL, Haserlat SM, Supko JG, Haluska FG, Louis DN, Christiani DC, Settleman J, Haber DA (2004) Activating mutations in the epidermal growth factor receptor underlying responsiveness of non-small-cell lung cancer to gefitinib. N Engl J Med 350:2129–2139
Omuro AM, Kris MG, Miller VA, Franceschi E, Shah N, Milton DT, Abrey LE (2005) High incidence of disease recurrence in the brain and leptomeninges in patients with nonsmall cell lung carcinoma after response to gefitinib. Cancer 103:2344–2348
Lee YJ, Choi HJ, Kim SK, Chang J, Moon JW, Park IK, Kim JH, Cho BC (2010) Frequent central nervous system failure after clinical benefit with epidermal growth factor receptor tyrosine kinase inhibitors in Korean patients with nonsmall-cell lung cancer. Cancer 116:1336–1343
Jackman DM, Holmes AJ, Lindeman N, Wen PY, Kesari S, Borras AM, Bailey C, de Jong F, Janne PA, Johnson BE (2006) Response and resistance in a non-small-cell lung cancer patient with an epidermal growth factor receptor mutation and leptomeningeal metastases treated with high-dose gefitinib. J Clin Oncol 24:4517–4520
Dhruva N, Socinski MA (2009) Carcinomatous meningitis in non-small-cell lung cancer: response to high-dose erlotinib. J Clin Oncol 27:31–32
Clarke JL, Pao W, Wu N, Miller VA, Lassman AB (2010) High dose weekly erlotinib achieves therapeutic concentrations in CSF and is effective in leptomeningeal metastases from epidermal growth factor receptor mutant lung cancer. J Neurooncol 99:283–286
Hata A, Kaji R, Fujita S, Katakami N (2011) High-dose erlotinib for refractory brain metastases in a patient with relapsed non-small cell lung cancer. J Thorac Oncol 6:653–654
Grommes C, Oxnard GR, Kris MG, Miller VA, Pao W, Holodny AI, Clarke JL, Lassman AB (2011) “Pulsatile” high-dose weekly erlotinib for CNS metastases from EGFR mutant non-small cell lung cancer. Neuro Oncol 13:1364–1369
Katayama T, Shimizu J, Suda K, Onozato R, Fukui T, Ito S, Hatooka S, Sueda T, Hida T, Yatabe Y, Mitsudomi T (2009) Efficacy of erlotinib for brain and leptomeningeal metastases in patients with lung adenocarcinoma who showed initial good response to gefitinib. J Thorac Oncol 4:1415–1419
Fukuhara T, Saijo Y, Sakakibara T, Inoue A, Morikawa N, Kanamori M, Nakashima I, Nukiwa T (2008) Successful treatment of carcinomatous meningitis with gefitinib in a patient with lung adenocarcinoma harboring a mutated EGF receptor gene. Tohoku J Exp Med 214:359–363
Togashi Y, Masago K, Fukudo M, Terada T, Fujita S, Irisa K, Sakamori Y, Kim YH, Mio T, Inui K, Mishima M (2010) Cerebrospinal fluid concentration of erlotinib and its active metabolite OSI-420 in patients with central nervous system metastases of non-small cell lung cancer. J Thorac Oncol 5:950–955
Masuda T, Hattori N, Hamada A, Iwamoto H, Ohshimo S, Kanehara M, Ishikawa N, Fujitaka K, Haruta Y, Murai H, Kohno N (2011) Erlotinib efficacy and cerebrospinal fluid concentration in patients with lung adenocarcinoma developing leptomeningeal metastases during gefitinib therapy. Cancer Chemother Pharmacol 67:1465–1469
Togashi Y, Masago K, Fukudo M, Tsuchido Y, Okuda C, Kim YH, Ikemi Y, Sakamori Y, Mio T, Katsura T, Mishima M (2011) Efficacy of increased-dose erlotinib for central nervous system metastases in non-small cell lung cancer patients with epidermal growth factor receptor mutation. Cancer Chemother Pharmacol 68:1089–1092
Jones HK, Stafford LE, Swaisland HC, Payne R (2002) A sensitive assay for ZD1839 (Iressa) in human plasma by liquid–liquid extraction and high performance liquid chromatography with mass spectrometric detection: validation and use in Phase I clinical trials. J Pharm Biomed Anal 29:221–228
Zhao M, Hartke C, Jimeno A, Li J, He P, Zabelina Y, Hidalgo M, Baker SD (2005) Specific method for determination of gefitinib in human plasma, mouse plasma and tissues using high performance liquid chromatography coupled to tandem mass spectrometry. J Chromatogr, B: Anal Technol Biomed Life Sci 819:73–80
Zhao M, He P, Rudek MA, Hidalgo M, Baker SD (2003) Specific method for determination of OSI-774 and its metabolite OSI-420 in human plasma by using liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry. J Chromatogr, B: Anal Technol Biomed Life Sci 793:413–420
Masters AR, Sweeney CJ, Jones DR (2007) The quantification of erlotinib (OSI-774) and OSI-420 in human plasma by liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry. J Chromatogr, B: Anal Technol Biomed Life Sci 848:379–383
Nagai Y, Miyazawa H, Huqun, Tanaka T, Udagawa K, Kato M, Fukuyama S, Yokote A, Kobayashi K, Kanazawa M, Hagiwara K (2005) Genetic heterogeneity of the epidermal growth factor receptor in non-small cell lung cancer cell lines revealed by a rapid and sensitive detection system, the peptide nucleic acid-locked nucleic acid PCR clamp. Cancer Res 65:7276–7282
Kosaka T, Yatabe Y, Endoh H, Kuwano H, Takahashi T, Mitsudomi T (2004) Mutations of the epidermal growth factor receptor gene in lung cancer: biological and clinical implications. Cancer Res 64:8919–8923
Eisenhauer EA, Therasse P, Bogaerts J, Schwartz LH, Sargent D, Ford R, Dancey J, Arbuck S, Gwyther S, Mooney M, Rubinstein L, Shankar L, Dodd L, Kaplan R, Lacombe D, Verweij J (2009) New response evaluation criteria in solid tumours: revised RECIST guideline (version 1.1). Eur J Cancer 45:228–247
Langer CJ, Mehta MP (2005) Current management of brain metastases, with a focus on systemic options. J Clin Oncol 23:6207–6219
Paz-Ares L, Soulières D, Melezínek I, Moecks J, Keil L, Mok T, Rosell R, Klughammer B (2010) Clinical outcomes in non-small-cell lung cancer patients with EGFR mutations: pooled analysis. J Cell Mol Med 14:51–69
Fabian MA, Biggs WH 3rd, Treiber DK, Atteridge CE, Azimioara MD, Benedetti MG, Carter TA, Ciceri P, Edeen PT, Floyd M, Ford JM, Galvin M, Gerlach JL, Grotzfeld RM, Herrgard S, Insko DE, Insko MA, Lai AG, Lelias JM, Mehta SA, Milanov ZV, Velasco AM, Wodicka LM, Patel HK, Zarrinkar PP, Lockhart DJ (2005) A small molecule-kinase interaction map for clinical kinase inhibitors. Nat Biotechnol 23:329–336
Nakagawa K, Tamura T, Negoro S, Kudoh S, Yamamoto N, Takeda K, Swaisland H, Nakatani I, Hirose M, Dong RP, Fukuoka M (2003) Phase I pharmacokinetic trial of the selective oral epidermal growth factor receptor tyrosine kinase inhibitor gefitinib (‘Iressa’, ZD1839) in Japanese patients with solid malignant tumors. Ann Oncol 14:922–930
Cohen MH, Williams GA, Sridhara R, Chen G, Pazdur R (2003) FDA drug approval summary: gefitinib (ZD1839) (Iressa) tablets. Oncologist 8:303–306
Yamamoto N, Horiike A, Fujisaka Y, Murakami H, Shimoyama T, Yamada Y, Tamura T (2008) Phase I dose-finding and pharmacokinetic study of the oral epidermal growth factor receptor tyrosine kinase inhibitor Ro50–8231 (erlotinib) in Japanese patients with solid tumors. Cancer Chemother Pharmacol 61:489–496
Cohen MH, Johnson JR, Chen YF, Sridhara R, Pazdur R (2005) FDA drug approval summary: erlotinib (Tarceva) tablets. Oncologist 10:461–466
Gerstner ER, Fine RL (2007) Increased permeability of the blood-brain barrier to chemotherapy in metastatic brain tumors: establishing a treatment paradigm. J Clin Oncol 25:2306–2312
Elmeliegy MA, Carcaboso AM, Tagen M, Bai F, Stewart CF (2011) Role of ATP-binding cassette and solute carrier transporters in erlotinib CNS penetration and intracellular accumulation. Clin Cancer Res 17:89–99
Mukohara T, Engelman JA, Hanna NH, Yeap BY, Kobayashi S, Lindeman N, Halmos B, Pearlberg J, Tsuchihashi Z, Cantley LC, Tenen DG, Johnson BE, Janne PA (2005) Differential effects of gefitinib and cetuximab on non-small-cell lung cancers bearing epidermal growth factor receptor mutations. J Natl Cancer Inst 97:1185–1194
Zhang RD, Price JE, Fujimaki T, Bucana CD, Fidler IJ (1992) Differential permeability of the blood-brain barrier in experimental brain metastases produced by human neoplasms implanted into nude mice. Am J Pathol 141:1115–1124
Stewart DJ (1994) A critique of the role of the blood-brain barrier in the chemotherapy of human brain tumors. J Neurooncol 20:121–139
Davey P (2002) Brain metastases: treatment options to improve outcomes. CNS Drugs 16:325–338
Weber B, Winterdahl M, Memon A, Sorensen BS, Keiding S, Sorensen L, Nexo E, Meldgaard P (2011) Erlotinib accumulation in brain metastases from non-small cell lung cancer: visualization by positron emission tomography in a patient harboring a mutation in the epidermal growth factor receptor. J Thorac Oncol 6:1287–1289
Gleissner B, Chamberlain MC (2006) Neoplastic meningitis. Lancet Neurol 5:443–452
Lombardi G, Zustovich F, Farina P, Della Puppa A, Manara R, Cecchin D, Brunello A, Cappetta A, Zagonel V (2011) Neoplastic meningitis from solid tumors: new diagnostic and therapeutic approaches. Oncologist 16:1175–1188
Acknowledgments
This research was partially supported by Funding Program for Next Generation World-Leading Researchers (NEXT Program; LS073).
Conflict of interest
The authors have no conflict of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Togashi, Y., Masago, K., Masuda, S. et al. Cerebrospinal fluid concentration of gefitinib and erlotinib in patients with non-small cell lung cancer. Cancer Chemother Pharmacol 70, 399–405 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00280-012-1929-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00280-012-1929-4