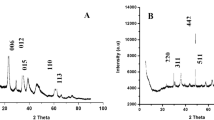
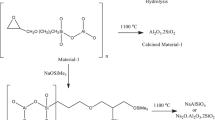
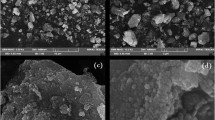
Abstract
Today, the excessive and increasing use of phenoxy family herbicides such as 2-methyl-4-chlorophenoxyacetic acid (MCPA) and (2,4- dichlorophenoxy) acetic acid (2,4-DCPA) for reasons such as indestructibility and pollution of groundwater resources is one of the most important environmental problems. Pesticide adsorbents like layered double hydroxides (LDHs) are commonly utilized due to their straightforward synthesis, substantial specific surface area resulting from their layered structure, and the potential for surface modification. These natural minerals serve as effective options for adsorption. In this study, a co-precipitation approach was used to create an MgAl-LDH@Fe3O4 magnetic adsorbent for the simultaneous removal of MCPA and 2,4-DCPA herbicides from aqueous solution. Using different techniques such as TGA, XRD, FESEM, EDS and zeta potential, we investigated the properties of the prepared adsorbent. The partial least squares method measures the concentration of each herbicide in their mixture. The optimization of MCPA and 2,4-DCPA simultaneous adsorption by LDH was achieved through Doehlert experimental design and the response surface method. The optimal conditions for absorption were determined to be an adsorbent dose of 40.20 mg L-1, a pH of 6.8, and an initial concentration of 28.35 mg L-1. In this work, the equilibrium, kinetic, and thermodynamic absorption data of the absorption process were studied, and the obtained results were well described by the Freundlich model, and the pseudo-second-order model, respectively, and showed the spontaneity of the absorption process in this research. The highest absorption capacities of MCPA and 2.4-DCPA herbicides on the prepared adsorbent were 134.50 and 131.30 mg g-1, respectively.
Graphical abstract























Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availability
The authors confirm that the data supporting the findings of this study are available within the article or its supplementary materials.
References
Amenyogbe E, Huang JS, Chen G, Wang Z. An overview of the pesticides’ impacts on fishes and humans. Int J Aquat Biol. 2021;9(1):55–65. https://doi.org/10.22034/ijab.v9i1.972.
Kumar V, Kumar P. Pesticides in agriculture and environment: impacts on human health. Contam Agric Environ: Health Risks Remediation. 2019;1:76–95.
Esrafily A, Farzadkia M, Jonidi Jafari A, Izanloo M. Removal of 2, 4-Dichlorophenoxyacetic acid herbicide from aqueous solutions by functionalization nanoparticles magnetic: equilibrium, kinetic and thermodynamic studies. J North Khorasan Univ Med Sci. 2018;9(4):1–8.
Reade JP, Cobb AH. Herbicides: modes of action and metabolism. Weed Manage Handb. 2002;9:134–70.
Chávez-Moreno C, Ferrer L, Hinojosa-Reyes L, Hernández-Ramírez A, Cerdà V, Guzmán-Mar J. On-line monitoring of the photocatalytic degradation of 2, 4-D and dicamba using a solid-phase extraction-multisyringe flow injection system. J Environ Manage. 2013;129:377–83.
CrespÍn MA, Gallego M, Valcárcel M, González JL. Study of the degradation of the herbicides 2, 4-D and MCPA at different depths in contaminated agricultural soil. Environ Sci Technol. 2001;35(21):4265–70.
Norsworthy JK, Ward SM, Shaw DR, Llewellyn RS, Nichols RL, Webster TM, Barrett M. Reducing the risks of herbicide resistance: best management practices and recommendations. Weed Sci. 2012;60(SP1):31–62. https://doi.org/10.1614/WS-D-11-00155.1.
Pandiarajan A, Kamaraj R, Vasudevan S, Vasudevan S. OPAC (orange peel activated carbon) derived from waste orange peel for the adsorption of chlorophenoxyacetic acid herbicides from water: adsorption isotherm, kinetic modelling and thermodynamic studies. Bioresour Technol. 2018;261:329–41.
Aksu Z, Kabasakal E. Batch adsorption of 2, 4-dichlorophenoxy-acetic acid (2, 4-D) from aqueous solution by granular activated carbon. Sep Purif Technol. 2004;35(3):223–40.
Kuśmierek K, Sankowska M, Świątkowski A. Kinetic and equilibrium studies of simultaneous adsorption of monochlorophenols and chlorophenoxy herbicides on activated carbon. Desalination Water Treat. 2014;52(1–3):178–83.
Derylo-Marczewska A, Blachnio M, Marczewski A, Swiatkowski A, Tarasiuk B. Adsorption of selected herbicides from aqueous solutions on activated carbon. J Therm Anal Calorim. 2010;101(2):785–94.
Loomis D, Guyton K, Grosse Y, El Ghissasi F, Bouvard V, Benbrahim-Tallaa L, Guha N, Mattock H, Straif K. Carcinogenicity of lindane, DDT, and 2, 4-dichlorophenoxyacetic acid. Lancet Oncol. 2015;16(8):891–2.
Tanaka K, Reddy KSN. Photodegradation of phenoxyacetic acid and carbamate pesticides on TiO2. Appl Catal B. 2002;39(4):305–10.
Abdullah AH, Mun LK, Zainal Z, Hussein MZ. Photo-degradation of chlorophenoxyacetic acids by ZnO/γ-Fe2O3 nanocatalysts: a comparative study. Int J Chem. 2013;5:56–65. https://doi.org/10.5539/ijc.v5n4p56.
Costa C, Maia S, Silva P, Garrido J, Borges F, Garrido EM. Photostabilization of phenoxyacetic acid herbicides MCPA and mecoprop by hydroxypropyl-β-cyclodextrin. Int J Photoenergy. 2013.
Rahemi V, Garrido JMPJ, Borges F, Brett CMA, Garrido EMPJ. Electrochemical sensor for simultaneous determination of herbicide MCPA and its metabolite 4-chloro-2-methylphenol. Application to photodegradation environmental monitoring. Environ Sci Pollut Res. 2015;22(6):4491–9.
Mostafa GA. Electrochemical biosensors for the detection of pesticides. Open Electrochem J. 2010;2(1). https://doi.org/10.2174/1876505X01002010022.
Hemmett RB, Faust SD. Biodegradation kinetics of 2, 4-dichlorophenoxyacetic acid by aquatic microorganisms. Decontamination Pesticide Residues Environ. 1969;191–207. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-4615-8455-1_13.
Kuhlmann B, Kaczmarzcyk B. Biodegradation of the herbicides 2, 4-dichlorophenoxyacetic acid, 2, 4, 5‐trichlorophenoxyacetic acid, and 2‐methyl‐4‐chlorophenoxyacetic acid in a sulfate‐reducing aquifer. Environ Toxicol Water Qual. 1995;10(2):119–25.
Belmouden M, Assabbane A, Ichou YA. Adsorption characteristics of a phenoxy acetic acid herbicide on activated carbon. J Environ Monit. 2000;2(3):257–60.
Bailey GW, White JL, Rothberg T. Adsorption of organic herbicides by montmorillonite: role of pH and chemical character of adsorbate. Soil Sci Soc Am J. 1968;32(2):222–34.
Ward TM, Getzen FM. Influence of pH on the adsorption of aromatic acids on activated carbon. Environ Sci Technol. 1970;4(1):64–7.
Ahmad T, Rafatullah M, Ghazali A, Sulaiman O, Hashim R, Ahmad A. Removal of pesticides from water and wastewater by different adsorbents: a review. J Environ Sci Health Part C. 2010;28(4):231–71.
Castro CS, Guerreiro MC, Gonçalves M, Oliveira LC, Anastácio AS. Activated carbon/iron oxide composites for the removal of atrazine from aqueous medium. J Hazard Mater. 2009;164(2–3):609–14.
Chang CF, Chang CY, Hsu KE, Lee SC, Höll W. Adsorptive removal of the pesticide methomyl using hypercrosslinked polymers. J Hazard Mater. 2008;155(1–2):295–304.
Singh N. Adsorption of herbicides on coal fly ash from aqueous solutions. J Hazard Mater. 2009;168(1):233–7.
Ghosh S, Das SK, Guha AK, Sanyal AK. Adsorption behavior of lindane on Rhizopus oryzae biomass: Physico-chemical studies. J Hazard Mater. 2009;172(1):485–90.
Pavlovic I, Barriga C, Hermosín MC, Cornejo J, Ulibarri MA. Adsorption of acidic pesticides 2, 4-D, Clopyralid and Picloram on calcined hydrotalcite. Appl Clay Sci. 2005;30(2):125–33.
Akçay G, Akçay M, Yurdakoç K. Removal of 2, 4-dichlorophenoxyacetic acid from aqueous solutions by partially characterized organophilic sepiolite: thermodynamic and kinetic calculations. J Colloid Interface Sci. 2005;281(1):27–32.
Xi Y, Mallavarapu M, Naidu R. Adsorption of the herbicide 2, 4-D on organo-palygorskite. Appl Clay Sci. 2010;49(3):255–61.
Mahramanlioglu M. Removal of MCPA (4-Chloro-2-Methylphenoxy-Acetic acid) from aqueous solutions using adsorbent produced from elutrilithe. Energy Sources. 2003;25(1):1–13.
Tang S, Lee HK. Application of dissolvable layered double hydroxides as sorbent in dispersive solid-phase extraction and extraction by co-precipitation for the determination of aromatic acid anions. Anal Chem. 2013;85(15):7426–33.
Ramakrishna KR, Viraraghavan T. Dye removal using low cost adsorbents. Water Sci Technol. 1997;36(2–3):189–96.
Inacio J, Taviot-Gueho C, Forano C, Besse JP. Adsorption of MCPA pesticide by MgAl-layered double hydroxides. Appl Clay Sci. 2001;18(5–6):255–64.
Bruna F, Celis R, Pavlovic I, Barriga C, Cornejo J, Ulibarri MA. Layered double hydroxides as adsorbents and carriers of the herbicide (4-chloro-2-methylphenoxy) acetic acid (MCPA): systems Mg–Al, Mg–Fe and Mg–Al–Fe. J Hazard Mater. 2009;168(2–3):1476–81.
Chaara D, Pavlovic I, Bruna F, Ulibarri MA, Draoui K, Barriga C. Removal of nitrophenol pesticides from aqueous solutions by layered double hydroxides and their calcined products. Appl Clay Sci. 2010;50(3):292–8.
Li F, Wang Y, Yang Q, Evans DG, Forano C, Duan X. Study on adsorption of glyphosate (N-phosphonomethyl glycine) pesticide on MgAl-layered double hydroxides in aqueous solution. J Hazard Mater. 2005;125(1–3):89–95.
Zhang X, Wang Y, Yang S. Simultaneous removal of Co (II) and 1-naphthol by core–shell structured Fe3O4@ cyclodextrin magnetic nanoparticles. Carbohydr Polym. 2014;114:521–9. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbpol.2014.08.072.
Zhao LX, Xiao H, Li MH, Xie M, Li N, Zhao RS. Effectively removing indole-3-butyric acid from aqueous solution with magnetic layered double hydroxide-based adsorbents. J Hazard Mater. 2021;408: 124446.
Koilraj P, Sasaki K. Fe3O4/MgAl-NO3 layered double hydroxide as a magnetically separable sorbent for the remediation of aqueous phosphate. J Environ Chem Eng. 2016;4(1):984–91.
Di X, Wang H, Guo X, Wang X, Liu Y. Magnetic layered double hydroxide/zeolitic imidazolate framework-8 nanocomposite as a novel adsorbent for enrichment of four endocrine disrupting compounds in milk samples. J Hazard Mater. 2022;421: 126753.
Chen CL, Wang XK, Nagatsu M. Europium adsorption on multiwall carbon nanotube/iron oxide magnetic composite in the presence of polyacrylic acid. Environ Sci Technol. 2009;43(7):2362–7.
Chen C, Gunawan P, Xu R. Self-assembled Fe 3 O 4-layered double hydroxide colloidal nanohybrids with excellent performance for treatment of organic dyes in water. J Mater Chem. 2011;21(4):1218–25.
Gutierrez AM, Dziubla TD, Hilt JZ. Recent advances on iron oxide magnetic nanoparticles as sorbents of organic pollutants in water and wastewater treatment. Rev Environ Health. 2017;32(1–2):111–7.
Zhang X, Niu H, Pan Y, Shi Y, Cai Y. Chitosan-coated octadecyl-functionalized magnetite nanoparticles: preparation and application in extraction of trace pollutants from environmental water samples. Anal Chem. 2010;82(6):2363–71.
Shrivas K, Ghosale A, Nirmalkar N, Srivastava A, Singh SK, Shinde SS. Removal of endrin and dieldrin isomeric pesticides through stereoselective adsorption behavior on the graphene oxide-magnetic nanoparticles. Environ Sci Pollut Res. 2017;24(32):24980–8.
Zhou Q, Lei M, Li J, Zhao K, Liu Y. Sensitive determination of bisphenol A, 4-nonylphenol and 4-octylphenol by magnetic solid phase extraction with Fe@ MgAl-LDH magnetic nanoparticles from environmental water samples. Sep Purif Technol. 2017;182:78–86.
Saien J, Nasri M, Pourehie O. Enhanced activation of persulfate by magnetic CuFe-layered double hydroxide nanocomposites under visible light irradiation for degradation of quinoline. J Iran Chem Soc. 2022;19(4):1515–26. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13738-021-02400-y.
Guo X, Li Y, Zhang B, Yang L, Di X. Development of dispersive solid phase extraction based on dissolvable Fe3O4-layered double hydroxide for high-performance liquid chromatographic determination of phenoxy acid herbicides in water samples. Microchem J. 2020;152:104443.
Slutsky B, By DL, Massart BGM, Vandeginste LMC, Buydens S, De Jong PJ, Lewi J, Smeyers-Verbeke. Data Handling in Science and Technology Volume 20A. Elsevier: Amsterdam. Xvii + 867 pp. ISBN 0-444-89724-0. $293.25. J Chem Inf Comput Sci. 1997;38(6):1254–1254.
Mou RX, Chen MX, Cao ZY, Zhu ZW. Simultaneous determination of triazine herbicides in rice by high-performance liquid chromatography coupled with high resolution and high mass accuracy hybrid linear ion trap-orbitrap mass spectrometry. Anal Chim Acta. 2011;706(1):149–56.
Bodur S, Bakırdere EG. Simultaneous determination of selected herbicides in dam lake, river and well water samples by gas chromatography mass spectrometry after vortex assisted binary solvent liquid phase microextraction. Microchem J. 2019;145:168–72.
Li H, Wu J, Chen C, Xin W, Zhang W. Simultaneous determination of 74 pesticide residues in Panax notoginseng by QuEChERS coupled with gas chromatography tandem mass spectrometry. Food Sci Hum Wellness. 2021;10(2):241–50.
de Matos Morawski F, Winiarski JP, de Campos CEM, Parize AL, Jost CL. Sensitive simultaneous voltammetric determination of the herbicides diuron and isoproturon at a platinum/chitosan bio-based sensing platform. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf. 2020;206:111181.
Olivieri AC, Goicoechea HC, Iñón FA. MVC1: an integrated MatLab toolbox for first-order multivariate calibration. Chemometr Intell Lab Syst. 2004;73(2):189–97.
Pourfaraj R, Fatemi SJ, Kazemi SY, Biparva P. Synthesis of hexagonal mesoporous MgAl LDH nanoplatelets adsorbent for the effective adsorption of Brilliant Yellow. J Colloid Interface Sci. 2017;508:65–74.
Hariani PL, Faizal M, Ridwan R, Marsi M, Setiabudidaya D. Synthesis and properties of Fe3O4 nanoparticles by co-precipitation method to removal procion dye. Int J Environ Sci Dev. 2013;4(3):336–40.
Zhang H, Zou K, Sun H, Duan X. A magnetic organic–inorganic composite: synthesis and characterization of magnetic 5-aminosalicylic acid intercalated layered double hydroxides. J Solid State Chem. 2005;178(11):3485–93.
Nikou M, Samadi-Maybodi A. Application of chemometrics into simultaneous monitoring removal efficiency of two food dyes by an amine-functionalized metal–organic framework. J Iran Chem Soc. 2020;17(7):1671–93. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13738-020-01886-2.
Nde DB, Boldor D, Astete C. Optimization of microwave assisted extraction parameters of neem (Azadirachta indica A. Juss) oil using the Doehlert’s experimental design. Ind Crops Prod. 2015;65:233–40.
Tabaraki R, Heidarizadi E. Simultaneous biosorption of Arsenic (III) and Arsenic (V): application of multiple response optimizations. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf. 2018;166:35–41.
Liu RS, Tang YJ. Tuber melanosporum fermentation medium optimization by plackett–burman design coupled with Draper–Lin small composite design and desirability function. Bioresour Technol. 2010;101(9):3139–46.
Nekouei F, Nekouei S, Tyagi I, Gupta VK. Kinetic, thermodynamic and isotherm studies for acid blue 129 removal from liquids using copper oxide nanoparticle-modified activated carbon as a novel adsorbent. J Mol Liq. 2015;201:124–33.
Samadi-Maybodi A, Ghezel-Sofla H, BiParva P. Co/Ni/Al-LTH layered Triple Hydroxides with Zeolitic Imidazolate Frameworks (ZIF-8) as high efficient removal of Diazinon from Aqueous Solution. J Inorg Organomet Polym Mater. 2023;33:10–29. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10904-022-02469-9.
Ahmad R, Kumar R. Adsorption of amaranth dye onto alumina reinforced polystyrene. Clean–Soil Air Water. 2011;39(1):74–82.
Salem ANM, Ahmed MA, El-Shahat MF. Selective adsorption of amaranth dye on Fe3O4/MgO nanoparticles. J Mol Liq. 2016;219:780–8.
Johnson RD, Arnold FH. The Temkin isotherm describes heterogeneous protein adsorption. Biochim et Biophys Acta (BBA)-Protein Struct Mol Enzymol. 1995;1247(2):293–7.
Ghaedi M. Comparison of cadmium hydroxide nanowires and silver nanoparticles loaded on activated carbon as new adsorbents for efficient removal of Sunset yellow: kinetics and equilibrium study. Spectrochim Acta Part A Mol Biomol Spectrosc. 2012;94:346–51.
Rao MM, Reddy BR, Jayalakshmi M, Jaya VS, Sridhar B. Hydrothermal synthesis of Mg–Al hydrotalcites by urea hydrolysis. Mater Res Bull. 2005;40(2):347–59.
Barnabas MJ, Parambadath S, Nagappan S, Ha CS. Sulfamerazine Schiff-base complex intercalated layered double hydroxide: synthesis, characterization, and antimicrobial activity. Heliyon. 2019;5(4): e01521.
Chinchole AN, Dubey AV, Kumar AV. Bioinspired palladium nanoparticles supported on soil-derived humic acid coated iron-oxide nanoparticles as catalyst for C–C cross-coupling and reduction reactions. Catal Lett. 2019;149(5):1224–36.
Raghu MS, Kumar KY, Prashanth MK, Prasanna BP, Vinuth R, Kumar CP. Adsorption and antimicrobial studies of chemically bonded magnetic graphene oxide-Fe3O4 nanocomposite for water purification. J Water Process Eng. 2017;17:22–31.
Marangoni R, Bouhent M, Taviot-Guého C, Wypych F, Leroux F. Zn2Al layered double hydroxides intercalated and adsorbed with anionic blue dyes: a physico-chemical characterization. J Colloid Interface Sci. 2009;333(1):120–7.
Costa FR, Leuteritz A, Wagenknecht U, Jehnichen D, Haeussler L, Heinrich G. Intercalation of Mg–Al layered double hydroxide by anionic surfactants: preparation and characterization. Appl Clay Sci. 2008;38(3–4):153–64.
Hernandez-Moreno MJ, Ulibarri MA, Rendon JL, Serna CJ. IR characteristics of hydrotalcite-like compounds. Phys Chem Miner. 1985;12(1):34–8. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00348744.
Ai L, Zhang C, Meng L. Adsorption of methyl orange from aqueous solution on hydrothermal synthesized Mg–Al layered double hydroxide. J Chem Eng Data. 2011;56(11):4217–25.
Abdelkader NBH, Bentouami A, Derriche Z, Bettahar N, De Menorval LC. Synthesis and characterization of Mg–Fe layer double hydroxides and its application on adsorption of Orange G from aqueous solution. Chem Eng J. 2011;169(1–3):231–8.
Răcuciu M. Synthesis protocol influence on aqueous magnetic fluid properties. Curr Appl Phys. 2009;9(5):1062–6.
Novillo C, Guaya D, Avendaño AAP, Armijos C, Cortina JL, Cota I. Evaluation of phosphate removal capacity of Mg/Al layered double hydroxides from aqueous solutions. Fuel. 2014;138:72–9.
Samuei S, Fakkar J, Rezvani Z, Shomali A, Habibi B. Synthesis and characterization of graphene quantum dots/CoNiAl-layered double-hydroxide nanocomposite: application as a glucose sensor. Anal Biochem. 2017;521:31–9.
Theiss FL, Ayoko GA, Frost RL. Thermogravimetric analysis of selected layered double hydroxides. J Therm Anal Calorim. 2013;112(2):649–57.
Timko M, Kopčanský P, Antalik M, Simsikova M, Valusova E, Molcan M, Kováč J. Physical Properties of Magnetite Nanoparticles Covered by 11-Mercaptoundecanoic Acid. Acta Physica Polonica. 2012;A:121.
Samadi-Maybodi A, Nikou M. Removal of sarafloxacin from aqueous solution by a magnetized metal-organic framework; Artificial neural network modeling. Polyhedron. 2020;179: 114342.
Cessna AJ, Grover R. Spectrophotometric determination of dissociation constants of selected acidic herbicides. J Agric Food Chem. 1978;26(1):289–92.
Wang B, Zhang H, Evans DG, Duan X. Surface modification of layered double hydroxides and incorporation of hydrophobic organic compounds. Mater Chem Phys. 2005;92(1):190–6.
Dehghani M, Nasseri S, Karamimanesh M. Removal of 2, 4-Dichlorophenolyxacetic acid (2, 4-D) herbicide in the aqueous phase using modified granular activated carbon. J Environ Health Sci Eng. 2014;12(1):1–10. https://doi.org/10.1186/2052-336X-12-28.
Salman JM, Njoku VO, Hameed BH. Adsorption of pesticides from aqueous solution onto banana stalk activated carbon. Chem Eng J. 2011;174(1):41–8.
Cengiz S, Cavas L. Removal of methylene blue by invasive marine seaweed: Caulerpa racemosa var. Cylindracea. Bioresour Technol. 2008;99(7):2357–63.
SenthilKumar P, Ramalingam S, Sathyaselvabala V, Kirupha SD, Sivanesan S. Removal of copper (II) ions from aqueous solution by adsorption using cashew nut shell. Desalination. 2011;266(1–3):63–71.
Li Y, Wang JD, Wang XJ, Wang JF. Adsorption–desorption of cd (II) and pb (II) on Ca-montmorillonite. Ind Eng Chem Res. 2012;51(18):6520–8.
Belhachemi M, Addoun F. Comparative adsorption isotherms and modeling of methylene blue onto activated carbons. Appl Water Sci. 2011;1(3):111–7.
Nejati K, Davary S, Saati M. Study of 2, 4-dichlorophenoxyacetic acid (2, 4-D) removal by Cu-Fe-layered double hydroxide from aqueous solution. Appl Surf Sci. 2013;280:67–73.
Ni ZM, Xia SJ, Wang LG, Xing FF, Pan GX. Treatment of methyl orange by calcined layered double hydroxides in aqueous solution: adsorption property and kinetic studies. J Colloid Interface Sci. 2007;316(2):284–91.
Zhu MX, Li YP, Xie M, Xin HZ. Sorption of an anionic dye by uncalcined and calcined layered double hydroxides: a case study. J Hazard Mater. 2005;120(1–3):163–71.
Lv L. Defluoridation of drinking water by calcined MgAl-CO3 layered double hydroxides. Desalination. 2007;208(1–3):125–33.
Vergili I, Barlas H. Removal of 2,4-D, MCPA and Metalaxyl from water using Lewatit VP OC 1163 as sorbent. Desalination. 2009;249(3):1107–14.
Cansado IPP, Mourão PAM, Gomes JAFL, Almodôvar V. Adsorption of MCPA, 2, 4-D and diuron onto activated carbons from wood composites. Ciência & Tecnologia dos Materiais. 2017;29(1):e224-228. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ctmat.2016.07.005.
Kaminski W, Kusmierek K, Swiatkowski A. Sorption equilibrium prediction of competitive adsorption of herbicides 2, 4-D and MCPA from aqueous solution on activated carbon using ANN. Adsorption. 2014;20(7):899–904.
Bazrafshan E, Kord MF, Faridi H, Farzadkia M, Sargazi S, Sohrabi A. Removal of 2, 4-dichlorophenoxyacetic acid (2, 4-D) from aqueous environments using single-walled carbon nanotubes. 2013. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10450-014-9633-9.
Ding L, Lu X, Deng H, Zhang X. Adsorptive removal of 2, 4-dichlorophenoxyacetic acid (2, 4-D) from aqueous solutions using MIEX resin. Ind Eng Chem Res. 2012;51(34):11226–35.
Wang L, Cheng C, Tapas S, Lei J, Matsuoka M, Zhang J, Zhang F. Carbon dots modified mesoporous organosilica as an adsorbent for the removal of 2, 4-dichlorophenol and heavy metal ions. J Mater Chem A. 2015;3(25):13357–64.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
All authors contributed to the study conception and design of this study. Dr. Abdolraouf Samadi-Maybodi, Mr. Hashem Ghezel-Sofla and Dr. Pourya BiParva performed material preparation, data collection and analysis. Mr. Hashem Ghezel-Sofla wrote the first draft of the manuscript and all authors commented on previous versions of the manuscript. All authors read and approved the final manuscript. Dr. Abdolraouf Samadi-Maybodi is the corresponding author.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
The authors have no relevant financial or non-financial interests to disclose.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Samadi-Maybodi, A., Ghezel-Sofla, H. & BiParva, P. Simultaneous removal of phenoxy herbicides, 2-methyl-4-chlorophenoxyacetic acid and 2,4-dichlorophenoxyacetic acid from aqueous media by magnetized MgAl-LDH@Fe3O4 composite: application of partial least squares and Doehlert experimental design. J Environ Health Sci Engineer (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40201-023-00877-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s40201-023-00877-8