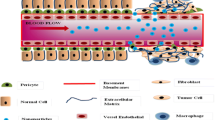
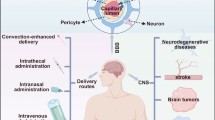
Abstract
Purpose of Review
This review aims at describing the state of the art concerning the design of polymeric nanoparticles for the treatment of neurological diseases. The most important methods of polymeric nanoparticle preparation as well as the required properties for neurological diseases have been summarized.
Recent Findings
Many studies report the design of polymeric nanoparticles to treat diseases such as brain tumors, neurodegenerative and neuroinflammatory diseases. However, none of the engineered nanoparticles have reached clinical trials. The reasons of the lack of translation of laboratory results have been analyzed. Many limiting steps can be attributed to the lack of reproducible studies, some controversial results or the absence of current regulations concerning systems at the nanoscale. However, recent studies indicate that these drawbacks can be overcome.
Summary
It is expected that in the near future, some of the engineered nanoparticles that are under development will become novel drug delivery systems to cross the BBB, giving an efficient treatment to currently untreatable and devastating neurological diseases such as glioblastoma and Alzehimer’s disease.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Andlin-Sobocki P, Jönsson B, Wittchenc H et al (2005) Cost of disorders of the brain in Europe. Eur J Neurol 12(Suppl. 1):1–27. doi:10.1016/j.euroneuro.2011.08.008
Olesen J, Gustavsson A, Svensson M, on behalf of theCDBE2010 study group and the European Brain Council et al (2012) The economic cost of brain disorders in Europe. Eur J Neurol 19:155–162. doi:10.1111/j.1468-1331.2011.03590.x
DiLuca M, Olesen J (2014) The cost of brain diseases: a burden or a challenge? Neuron 82(18):1205–1209. doi:10.1016/j.neuron.2014.05.044
Patel T, Zhou J, Piepmeier JM et al (2012) Polymeric nanoparticles for drug delivery to the central nervous system. Adv Drug Del Rev 64:701–705. doi:10.1016/j.addr.2011.12.006
Goyal K, Koul V, Singh Y et al (2014) Targeted drug delivery to central nervous system (CNS) for the treatment of neurodegenerative disorders: trends and advances. Cent Nerv Syst Agents Med Chem 14:43–59. doi:10.2174/1871524914666141030145948
Wu L, Li X, Janagam DL et al (2014) Overcoming the blood–brain barrier in chemotherapy treatment of pediatric brain tumors. Pharm Res 31:531–540. doi:10.1007/s11095-013-1196-z
• Cheng Y, Morshed RA, Auffinger B et al (2014) Multifunctional nanoparticles for brain tumor imaging and therapy. Adv Drug Deliv Rev 66:42–57. doi:10.1016/j.addr.2013.09.006. Description of the properties that nanoparticles (polymeric and inorganic) must possess to be useful for the treatment of tumors.
Das S, Carnicer-Lombarte A, Fawcett J et al (2016) Bio-inspired nano tools for neuroscience. Prog Neurobiol 142:1–22. doi:10.1016/j.pneurobio.2016.04.008
Kabanov AV, Gendelman HE (2007) Nanomedicine in the diagnosis and therapy of neurodegenerative disorders. Prog Polym Sci 32:1054–1082. doi:10.1016/j.progpolymsci.2007.05.014
Cupaioli FA, Zucca FA, Boraschi D et al (2014) Engineered nanoparticles. How brain friendly is this new guest? Prog Neurobiol 119–120:20–38. doi:10.1016/j.pneurobio.2014.05.002
•• Kreuter J (2014) Drug delivery to the central nervous system by polymeric nanoparticles: what do we know? Adv Drug Deliv Rev 71:2–14. doi:10.1016/j.addr.2013.08.008. Review highlighting the properties that polymeric nanoparticles must possess to cross the BBB and be used as advanced drug delivery systems to treat brain diseases.
Encyclopedia of Nanoscience and Nanotechnology, edited by Harl Singh Nalwa, 15-volumes set; ISBN: 1-58883-001-2 (vols. 1-10, 2004) plus ISBN: 1-58883-159-0 (vols. 11–25, 2011)
James S (2006) Encyclopedia of pharmaceutical technology. CRC Press, Taylor and Francis Group, Boca Raton. ISBN 9780849393990
Tadros ThF, Izquierdo P, Esquena J et al (2004) Formation and stability of nano-emulsions. Adv Colloid Interface Sci 108–109:303–318. doi:10.1016/j.cis.2003.10.023
Soppimath KS, Aminabhavi TM, Kulkarni AR et al (2001) Biodegradable polymeric nanoparticles as drug delivery devices. J Control Release 70(1–2):1–20. doi:10.1016/S0168-3659(00)00339-4
Pinto Reis C, Neufeld NJ, Keene FR et al (2009) Anionic PAMAM dendrimers as drug delivery vehicles for transition metal-based anticancer drugs. J Inorg Chem 103:373–380. doi:10.1016/j.jinorgbio.2008.11.014
Jain KK (2012) Nanobiotechnology-based strategies for crossing the blood–brain barrier. Nanomedicine 7(8):1225–1233. doi:10.2217/nnm.12.86
Neha B, Ganesh B, Preeti K (2013) Drug delivery to the brain using polymeric nanoparticles: a review. Int J Pharm Life Sci 2(3):107–132. doi:10.3329/ijpls.v2i3.15457
Lee K, Solanki A, Kim JD et al (2016) Nanomedicine: dynamic integration of nanotechnology with biomedical sciences; chapter II and Ellis-Behnke R., a small introduction to the world of nanomedicine; chapter III; and Allhoff R., the coming era of nanomedicine, chapter V. In: Bawa R, Audette GF, Rubinstein I (eds) Handbook of clinical nanomedicine: nanoparticles, imaging, therapy, and clinical applications. Pan Standford Publishing, Singapore
Vauthier C, Dubernet C, Fattal E et al (2003) Poly(alkylcyanoacrylates) as biodegradable materials for biomedical applications. Adv Drug Deliv Rev 55:519–548. doi:10.1016/S0169-409X(03)00041-3
Vauthier C, Bouchemal K (2009) Methods for the preparation and manufacture of polymeric nanoparticles. Pharm Res 26(5):1025–1058. doi:10.1007/s11095-008-9800-3
Danhier F, Ansorena E, Silva JM et al (2012) PLGA-based nanoparticles: AN overview of biomedical applications. J Control Release 161:505–522. doi:10.1016/j.jconrel.2012.01.043
Anton N, Benoit J-P, Saulnier P (2008) Design and production of nanoparticles formulated from nano-emulsions—a review. J Control Release 128(3):185–199. doi:10.1016/j.jconrel.2008.02.007
Solans C, Solè I (2012) Nano-emulsions: formation by low-energy methods. Curr Opin Colloid Interface Sci 17:246–254. doi:10.1016/j.cocis.2012.07.003
• Bazile DV (2014) Nanotechnologies in drug delivery—an industrial perspective. J Drug Deliv Sci Technol 24(1):12–21. doi:10.1016/S1773-2247(14)50002-0. This article gives an industrial point of view of the requirements for polymeric nanoparticles to become novel advanced drug delivery systems.
Lu JM, Wang X, Marin-Muller C et al (2009) Current advances in research and clinical applications of PLGA-based nanotechnology. Expert Rew Mol Diag 9(4):325–341. doi:10.1586/erm.09.15
Ballerini C, Baldi G, Aldinucci A et al (2015) Nanomaterial applications in multiple sclerosis inflamed brain. J Neuroimmune Pharmacol 10:1–13. doi:10.1007/s11481-015-9588-y
•• Dobrovolskaia MA, McNeil S (2013) Handbook of immunological properties of engineered nanomaterials. Frontiers in nanobiomedical research. SAIC-Frederick, Inc., Frederick. This book highlights the properties that engineered nanoparticles must have in order to avoid the detection by the immune system and reach to the target organ, focusing on the interactions with blood components.
Costantino L, Boraschi D (2012) Is there a clinical future for polymeric nanoparticles as brain-targeting drug delivery agents? Drug Discov Today 17(7/8):367–380. doi:10.1016/j.drudis.2011.10.028
He C, Hu Y, Yin L et al (2010) Effects of particle size and surface charge on cellular uptake and biodistribution of polymeric nanoparticles. Biomaterials 31:3657–3666. doi:10.1016/j.biomaterials.2010.01.065
Fornaguera C, Dols-Perez A, Calderó G, García-Celma MJ, Camarasa J, Solans C (2015) PLGA nanoparticles prepared by nano-emulsion templating using low-energy methods as efficient nanocarriers for drug delivery across the blood–brain barrier. J Control Release 10(211):134–143. doi:10.1016/j.jconrel.2015.06.002
Pardridge WM (2002) Blood–brain barrier drug targeting enables neuroprotection in brain ischemia following delayed intravenous administration of neurotrophins. Adv Exp Med Biol 513:397–430
Bravo-Osua I, Vauthier C, Farabollini A et al (2007) Mucoadhesion mechanism of chitosan and thiolated chitosan-poly(isobutyl cyanoacrylate) core-shell nanoparticles. Biomaterials 28(13):2233–2243. doi:10.1016/j.biomaterials.2007.01.005
Sharma D, Sharma RK, Sharma N et al (2015) Nose-to-brain delivery of PLGA-diazepam nanoparticles. AAPS PharmSciTech 16(5):1108–1121. doi:10.1208/s12249-015-0294-0
Cabral H, Kataoka K (2014) Progress of drug-loaded polymeric micelles into clinical studies. J Control Release 190:465–476. doi:10.1016/j.jconrel.2014.06.042
Guo J, Gao X, Su L et al (2011) Aptamer-functionalized PEG–PLGA nanoparticles for enhanced anti-glioma drug delivery. Biomaterials 32:8010–8020. doi:10.1016/j.biomaterials.2011.07.004
Reddy MK, Labhasetwar V (2009) Nanoparticle-mediated delivery of superoxide dismutase to the brain: an effective strategy to reduce ischemia-reperfusion injury. FASEB J. 23:1384–1395. doi:10.1096/fj.08-116947
Alyautdin R, Khalin I, Nafeeza MI et al (2014) Nanoscale drug delivery systems and the blood–brain barrier. Int J Nanomed 9:795–811. doi:10.2147/IJN.S52236
Hu K, Shi Y, Jiang W et al (2011) Lactoferrin conjugated PEGPLGA nanoparticles for brain delivery: preparation, characterization and efficacy in Parkinson’s disease. Int J Pharm 415:273–283. doi:10.1016/j.ijpharm.2011.05.062
Papa S, Ferrari R, De Paola M et al (2014) Polymeric nanoparticle system to target activated microglia/macrophages in spinal cord injury. J Control Release 174:15–26. doi:10.1016/j.jconrel.2013.11.001
Klyachko NL, Haney MJ, Zhao Y (2013) Macrophages offer a paradigm switch for CNS delivery of therapeutic proteins. Nanomedicine 9(9):1403–1422. doi:10.2217/nnm.13.115
Lemos H, Huang L, Chandler PR et al (2014) Activating of the STING adaptor attenuates experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis. J Immunol 192:5571–5578. doi:10.4049/jimmunol.1303258
Tosi G, Vergoni AV, Ruozi B et al (2010) Sialic acid and glycopeptides conjugated PLGA nanoparticles for central nervous system targeting: in vivo pharmacological evidence and biodistribution. J Control Release 145:49–57. doi:10.1016/j.jconrel.2010.03.008
Getts DR, Terry RL, Getts MT et al (2014) Therapeutic inflammatory monocyte modulation using immune-modifying microparticles. Sci Transl Med 6:219ra7. doi:10.1126/scitranslmed.3007563
Kreuter J (1994) Drug targeting with nanoparticles. Eur J Drug Metab Pharmacokinet 19:253–256. doi:10.1007/BF03188928
Acknowledgments
Financial support from Spanish Ministry of Economy and Competitiveness, MINECO (Grant CTQ 2011-29336-CO3-01 and CTQ2014-52687), Generalitat de Catalunya (Grant 2014SGR-1655) and CIBER-BBN is gratefully acknowledged.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of Interest
C Fornaguera and C. Solans declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Human and Animal Rights and Informed Consent
This article does not contain any studies with human or animal subjects performed by any of the authors.
Additional information
This article is part of the Topical collection on Nanoparticle-based Drug Delivery.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Fornaguera, C., Solans, C. Polymeric Nanoparticles for Drug Delivery in Neurological Diseases. Curr Pathobiol Rep 4, 189–197 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40139-016-0118-2
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s40139-016-0118-2