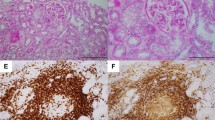
Abstract
Combination therapy, consisting of immune checkpoint inhibitors and traditional chemotherapeutic agents, has significantly improved the clinical outcomes of non-small cell lung cancer. Therefore, it will be a promising first-line therapy, whereas, there is a prospect that associated kidney injury may increase during treatment. We presented four patients, diagnosed with advanced non-small cell lung cancer, who received combination therapy, consisting of pembrolizumab, cisplatin, and pemetrexed as first-line treatment. All of them had been referred to nephrologists and had undergone renal biopsy. We observed that three of four patients presented a very rapid time course for acute kidney injury development. Notably, the three patients received only one or two cycles of the combined chemotherapy. In a renal biopsy, one patient showed severe acute tubular injury rather than interstitial nephritis. Another patient presented focal segmental glomerular sclerosis concomitant with tubulointerstitial nephritis. However, it was challenging to distinguish which agent was primarily responsible for kidney injury. Regarding the treatment, all the patients discontinued pembrolizumab and received corticosteroid treatment. We adjusted the dose and duration of corticosteroid according to the pathological results and patient conditions. The current cases provide a further understanding of clinical features and appropriate management in patients treated with combination therapy including pembrolizumab.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Gettinger S, Herbst RS. B7–H1/PD-1 blockade therapy in non-small cell lung cancer: current status and future direction. Cancer J. 2014;20:281–9.
Reck M, Rodriguez-Abreu D, Robinson AG, Hui R, Csoszi T, Fulop A, Gottfried M, Peled N, Tafreshi A, Cuffe S, O’Brien M, Rao S, Hotta K, Leiby MA, Lubiniecki GM, Shentu Y, Rangwala R, Brahmer JR. Pembrolizumab versus Chemotherapy for PD-L1-Positive Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer. N Engl J Med. 2016;375:1823–33.
Gandhi L, Rodriguez-Abreu D, Gadgeel S, Esteban E, Felip E, De Angelis F, Domine M, Clingan P, Hochmair MJ, Powell SF, Cheng SY, Bischoff HG, Peled N, Grossi F, Jennens RR, Reck M, Hui R, Garon EB, Boyer M, Rubio-Viqueira B, Novello S, Kurata T, Gray JE, Vida J, Wei Z, Yang J, Raftopoulos H, Pietanza MC, Garassino MC. Pembrolizumab plus chemotherapy in metastatic non-small-cell lung cancer. N Engl J Med. 2018;378:2078–92.
Arbour KC, Riely GJ. Systemic therapy for locally advanced and metastatic non-small cell lung cancer: a review. JAMA. 2019;322:764–74.
Rosner MH, Perazella MA. Acute kidney injury in patients with cancer. N Engl J Med. 2017;376:1770–81.
Aratani S, Aburakawa S, Ryotokuji T, Marumo A, Sakai Y, Inokuchi K, Tsuruoka S (2019) Primary tumor infiltration and severe acute kidney injury in patients with acute myeloblastic leukemia. J Nippon Med Sch 2020;87:43–8.
Sassier M, Dugue AE, Clarisse B, Lesueur P, Avrillon V, Bizieux-Thaminy A, Auliac JB, Kaluzinski L, Tillon J, Robinet G, Le Caer H, Monnet I, Madroszyk A, Boza G, Falchero L, Fournel P, Egenod T, Toffart AC, Leiber N, Do P, Gervais R. Renal insufficiency is the leading cause of double maintenance (bevacizumab and pemetrexed) discontinuation for toxicity to advanced non-small cell lung cancer in real world setting. Lung Cancer. 2015;89:161–6.
Postow MA, Sidlow R, Hellmann MD. Immune-related adverse events associated with immune checkpoint blockade. N Engl J Med. 2018;378:158–68.
Perazella MA, Shirali AC. Immune checkpoint inhibitor nephrotoxicity: what do we know and what should we do? Kidney Int. 2020;97:62–74.
Francisco LM, Sage PT, Sharpe AH. The PD-1 pathway in tolerance and autoimmunity. Immunol Rev. 2010;236:219–42.
Spanou Z, Keller M, Britschgi M, Yawalkar N, Fehr T, Neuweiler J, Gugger M, Mohaupt M, Pichler WJ. Involvement of drug-specific T cells in acute drug-induced interstitial nephritis. J Am Soc Nephrol. 2006;17:2919–27.
Dumoulin DW, Visser S, Cornelissen R, van Gelder T, Vansteenkiste J, von der Thusen J, Aerts J. Renal toxicity from pemetrexed and pembrolizumab in the era of combination therapy in patients with metastatic nonsquamous cell NSCLC. J Thorac Oncol. 2020;15:1472–83.
Holditch SJ, Brown CN, Lombardi AM, Nguyen KN, Edelstein CL (2019) Recent Advances in Models, Mechanisms, Biomarkers, and Interventions in Cisplatin-Induced Acute Kidney Injury. Int J Mol Sci 87:43–8.
Gibbs D, Jackman A (2005) Pemetrexed disodium. Nat Rev Drug Discov S16–S17.
King J, de la Cruz J, Lutzky J. Ipilimumab-induced thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura (TTP). J Immunother Cancer. 2017;5:19.
Shirali AC, Perazella MA, Gettinger S. Association of acute interstitial nephritis with programmed cell death 1 inhibitor therapy in lung cancer patients. Am J Kidney Dis. 2016;68:287–91.
Cortazar FB, Kibbelaar ZA, Glezerman IG, Abudayyeh A, Mamlouk O, Motwani SS, Murakami N, Herrmann SM, Manohar S, Shirali AC, Kitchlu A, Shirazian S, Assal A, Vijayan A, Renaghan AD, Ortiz-Melo DI, Rangarajan S, Malik AB, Hogan JJ, Dinh AR, Shin DS, Marrone KA, Mithani Z, Johnson DB, Hosseini A, Uprety D, Sharma S, Gupta S, Reynolds KL, Sise ME, Leaf DE. Clinical features and outcomes of immune checkpoint inhibitor-associated AKI: a multicenter study. J Am Soc Nephrol. 2020;31:435–46.
Izzedine H, Mathian A, Champiat S, Picard C, Mateus C, Routier E, Varga A, Malka D, Leary A, Michels J, Michot JM, Marabelle A, Lambotte O, Amoura Z, Soria JC, Kaaki S, Quellard N, Goujon JM, Brocheriou I. Renal toxicities associated with pembrolizumab. Clin Kidney J. 2019;12:81–8.
Common terminology criteria for adverse events (2021) CTCAE. Cancer Therapy Evaluation Program (CTEP). National Cancer Institute. https://ctep.cancer.gov/protocolDevelopment/electronic_applications/ctc.htm. Accessed 18 Mar 2021.
KDIGO Guidelines (2021). https://kdigo.org/guidelines/. Accessed 18 Mar 2021.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
MS has received honoraria and research funding from MSD K.K, Taiho Pharmaceutical and Eli Lilly Japan K.K, outside the submitted work.
Ethical approval
This case study complied with the Helsinki Declaration standards and was approved by the Ethical Committee of Nippon Medical School Hospital. Written informed consent was obtained from all patients.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
About this article
Cite this article
Aratani, S., Sugano, T., Shimizu, A. et al. Clinicopathological characteristics of kidney injury in non-small cell lung cancer patients under combination therapy including pembrolizumab. CEN Case Rep 11, 97–104 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13730-021-00636-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13730-021-00636-4