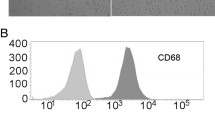
Abstract
Purpose
The presence of M2 macrophages within primary tumors has been correlated with a poor prognosis for many types of cancer. However, little is known about the role of M2 macrophages in gallbladder cancer (GBC).
Methods
The number of M2 macrophages in 78 GBC and 16 normal gallbladder tissue samples was assessed by immunohistochemistry. The THP-1 monocyte cell line was differentiated into M2 macrophages and co-cultured with GBC-derived cell lines. The effect of M2 macrophages on promoting GBC cell migration and invasion was analyzed using migration, invasion and scratch wound healing assays. Western blotting and real-time PCR were used to assess the expression of epithelial-mesenchymal transition (EMT) markers and the activation status of the PI3K/Akt signaling pathway in GBC cells co-cultured with THP-1-derived macrophages.
Results
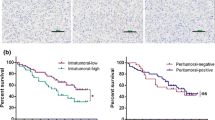
The average number of M2 macrophages was found to be significantly higher in GBC tissues than in normal gallbladder tissues. We also found that GBC patients with higher M2 macrophage counts exhibited poorer overall survival rates. Co-culture with M2 macrophages significantly promoted the migration, invasion and EMT of GBC cells. Moreover, we found that CCL18 secreted from M2 macrophages had the same effect on GBC cells as M2 macrophages. Blocking the function of CCL18 with a neutralizing antibody reversed this effect. Finally, we found that M2 macrophages could activate PI3K/Akt signaling in GBC cells, thereby leading to migration, invasion and EMT of these cells.
Conclusions
Our findings contribute to our understanding of the role of chronic inflammation in GBC development and progression, and may offer potential therapeutic targets for GBC.





Similar content being viewed by others
Change history
01 September 2022
A Correction to this paper has been published: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13402-022-00679-4
References
A.X. Zhu, T.S. Hong, A.F. Hezel, D.A. Kooby, Current management of gallbladder carcinoma. Oncologist 15, 168–181 (2010)
W. Jung, J.Y. Jang, M.J. Kang, Y.R. Chang, Y.C. Shin, J. Chang, S.W. Kim, Effects of surgical methods and tumor location on survival and recurrence patterns after curative resection in patients with T2 gallbladder cancer. Gut Liver 10, 140–146 (2016)
R. Hundal, E.A. Shaffer, Gallbladder cancer: Epidemiology and outcome. Clin Epidemiol 6, 99–109 (2014)
Y. Li, J. Zhang, H. Ma, Chronic inflammation and gallbladder cancer. Cancer Lett 345, 242–248 (2014)
X.S. Wu, L.B. Shi, M.L. Li, Q. Ding, H. Weng, W.G. Wu, Y. Cao, R.F. Bao, Y.J. Shu, Q.C. Ding, J.S. Mu, J. Gu, P. Dong, Y.B. Liu, Evaluation of two inflammation-based prognostic scores in patients with resectable gallbladder carcinoma. Ann Surg Oncol 21, 449–457 (2014)
S.M. Crusz, F.R. Balkwill, Inflammation and cancer: Advances and new agents. Nat Rev Clin Oncol 12, 584–596 (2015)
A. Kuraishy, M. Karin, S.I. Grivennikov, Tumor promotion via injury- and death-induced inflammation. Immunity 35, 467–477 (2011)
P. Nilendu, S.C. Sarode, D. Jahagirdar, I. Tandon, S. Patil, G.S. Sarode, J.K. Pal, N.K. Sharma, Mutual concessions and compromises between stromal cells and cancer cells: Driving tumor development and drug resistance. Cell Oncol 41, 353–367 (2018)
I.A. Voutsadakis, Expression and function of immune ligand-receptor pairs in NK cells and cancer stem cells: Therapeutic implications. Cell Oncol 41, 107–121 (2018)
S. Oguro, Y. Ino, K. Shimada, Y. Hatanaka, Y. Matsuno, M. Esaki, S. Nara, Y. Kishi, T. Kosuge, N. Hiraoka, Clinical significance of tumor-infiltrating immune cells focusing on BTLA and Cbl-b in patients with gallbladder cancer. Cancer Sci 106, 1750–1760 (2015)
S. Su, Q. Liu, J. Chen, J. Chen, F. Chen, C. He, D. Huang, W. Wu, L. Lin, W. Huang, Z. J, X. Cui, F. Zheng, H. Li, H. Yao, F. Su, E. Song, A positive feedback loop between mesenchymal-like cancer cells and macrophages is essential to breast cancer metastasis. Cancer Cell 25, 605–620 (2014)
X. Ye, R.A. Weinberg, Epithelial-mesenchymal plasticity: A central regulator of cancer progression. Trends Cell Biol 25, 675–686 (2015)
O.W. Yeung, C.M. Lo, C.C. Ling, X. Qi, W. Geng, C.X. Li, K.T. Ng, S.J. Forbes, X.Y. Guan, R.T. Poon, S.T. Fan, K. Man, Alternatively activated (M2) macrophages promote tumour growth and invasiveness in hepatocellular carcinoma. J Hepatol 62, 607–616 (2015)
C.Y. Liu, J.Y. Xu, X.Y. Shi, W. Huang, T.Y. Ruan, P. Xie, J.L. Ding, M2-polarized tumor-associated macrophages promoted epithelial-mesenchymal transition in pancreatic cancer cells, partially through TLR4/IL-10 signaling pathway. Lab Investig 93, 844–854 (2013)
T. Kitamura, B.Z. Qian, J.W. Pollard, Immune cell promotion of metastasis. Nat Rev Immunol 15, 73–86 (2015)
J. Chen, Y. Yao, C. Gong, F. Yu, S. Su, J. Chen, B. Liu, H. Deng, F. Wang, L. Lin, H. Yao, F. Su, K.S. Anderson, Q. Liu, M.E. Ewen, X. Yao, E. Song, CCL18 from tumor-associated macrophages promotes breast cancer metastasis via PITPNM3. Cancer Cell 19, 541–555 (2011)
S.Y. Lee, E.K. Jeong, M.K. Ju, H.M. Jeon, M.Y. Kim, C.H. Kim, H.G. Park, S.I. Han, H.S. Kang, Induction of metastasis, cancer stem cell phenotype, and oncogenic metabolism in cancer cells by ionizing radiation. Mol Cancer 16, 10 (2017)
L. Larue, A. Bellacosa, Epithelial-mesenchymal transition in development and cancer: Role of phosphatidylinositol 3' kinase/AKT pathways. Oncogene 24, 7443–7454 (2005)
A. Mantovani, F. Marchesi, A. Malesci, L. Laghi, P. Allavena, Tumour-associated macrophages as treatment targets in oncology. Nat Rev Clin Oncol 14, 399–416 (2017)
J.A. Espinoza, C. Bizama, P. García, C. Ferreccio, M. Javle, J.F. Miquel, J. Koshiol, J.C. Roa, The inflammatory inception of gallbladder cancer. Biochim Biophys Acta 1865, 245–254 (2016)
R. Noy, J.W. Pollard, Tumor-associated macrophages: From mechanisms to therapy. Immunity 41, 49–61 (2014)
P. Italiani, D. Boraschi, From monocytes to M1/M2 macrophages: Phenotypical vs. functional differentiation. Front Immuno l5, 514 (2014)
L.M. Nusblat, M.J. Carroll, C.M. Roth, Crosstalk between M2 macrophages and glioma stem cells. Cell Oncol 40, 471–482 (2017)
C. Ngambenjawong, H.H. Gustafson, S.H. Pun, Progress in tumor-associated macrophage (TAM)-targeted therapeutics. Adv Drug Deliv Rev 114, 206–221 (2017)
G.K. Alderton, Metastasis: Epithelial to mesenchymal and back again. Nat Rev Cancer 13, 3 (2013)
M. Suarez-Carmona, J. Lesage, D. Cataldo, C. Gilles, EMT and inflammation: Inseparable actors of cancer progression. Mol Oncol 11, 805–823 (2017)
D. Huang, S.J. Song, Z.Z. Wu, W. Wu, X.Y. Cui, J.N. Chen, M.S. Zeng, S.C. Su, Epstein-Barr virus-induced VEGF and GM-CSF drive nasopharyngeal carcinoma metastasis via recruitment and activation of macrophages. Cancer Res 77, 3591–3604 (2017)
Z. Lin, W. Li, H. Zhang, W. Wu, Y. Peng, Y. Zeng, Y. Wan, J. Wang, N. Ouyang, CCL18/PITPNM3 enhances migration, invasion, and EMT through the NF-kappaB signaling pathway in hepatocellular carcinoma. Tumour Biol 37, 3461–3468 (2016)
R. Yuan, Y. Chen, X. He, X. Wu, J. Ke, Y. Zou, Z. Cai, Y. Zeng, L. Wang, J. Wang, X. Fan, X. Wu, P. Lan, CCL18 as an independent favorable prognostic biomarker in patients with colorectal cancer. J Surg Res 183, 163–169 (2013)
Acknowledgments
This work was partially supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant No. 81672405), the Key Project of the Natural Science Foundation of Guangdong Province, China (Grant No. 4210016041), the Science and Technology Program of Guangzhou, China (Grant No. 4250016043), a grant from the Guangdong Science and Technology Department (2015B050501004), Grant [2013] 163 from the Key Laboratory of Malignant Tumor Molecular Mechanism and Translational Medicine of the Guangzhou Bureau of Science and Information Technology, and Grant KLB09001 from the Key Laboratory of Malignant Tumor Gene Regulation and Target Therapy of the Guangdong Higher Education Institutes. We thank Pro. Dong Yin from Sun Yat-Sen Memorial Hospital and Dr. Hui Shen from Renji Hospital, School of Medicine, Shanghai Jiao Tong University, for their technical support and Dr. Jing Wei and Fang Su from Sun Yat-Sen Memorial Hospital for conducting the flow cytometry experiments.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Ethical approval
All procedures performed in studies involving human participants were conducted in accordance with the ethical standards of the Institutional Research Committee and with the 1964 Helsinki declaration and its later amendments or comparable ethical standards.
Additional information
The original version of this article was revised: In this article Figures 2b, 3c, 3e, 4a-4c, 5c, and 5d were incorrect. The original article has been corrected.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Zhou, Z., Peng, Y., Wu, X. et al. CCL18 secreted from M2 macrophages promotes migration and invasion via the PI3K/Akt pathway in gallbladder cancer. Cell Oncol. 42, 81–92 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13402-018-0410-8
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13402-018-0410-8