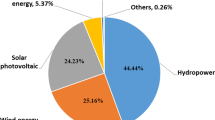
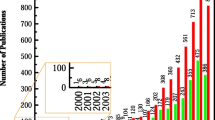
Abstract
Renewable energy generation is a critical component of society’s long-term sustainability, and numerous energy sources, including biogas, solar, biomass, and wind, must be fully utilized to satisfy current demands. Different countries are off the grid. This study includes a real-life case study. Researchers created a mathematical optimization technique utilizing a CPLEX analyzer to produce the required solar capacity simultaneously reducing the cost of energy (COE) to match the requirements of this settlement. Various situations were examined in this research about present energy availability, for instance, at varying periods of each year, economic expenses, the feasibility of sources including such biomass and biogas, and the profitability of wind power generation given the related high prices. Lastly, the study investigated the impact of geothermal power generation on carbon dioxide emission.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Sanchirico, J.N.; Wilen, J.E.: Optimal spatial management of renewable resources: matching policy scope to ecosystem scale. J. Environ. Econ. Manag. 50(1), 23–46 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jeem.2004.11.001
Hilborn, R.; Walters, C.J.; Ludwig, D.: Sustainable exploitation of renewable resources. Annu. Rev. Ecol. Syst. 26(1), 45–67 (1995). https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev.es.26.110195.000401
Clark, C.W.: Mathematical models in the economics of renewable resources. SIAM Rev. 21(1), 81–99 (1979). https://doi.org/10.1137/1021006
Cai, Y.P.; Huang, G.H.; Yang, Z.F.; Lin, Q.G.; Tan, Q.: Community-scale renewable energy systems planning under uncertainty—An interval chance-constrained programming approach. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 13(4), 721–735 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rser.2008.01.008
Veluchamy, K.; Veluchamy, M.: A new energy management technique for microgrid system using muddy soil fish optimization algorithm. Int J Energy Res 45(10), 14824–14844 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1002/er.6758
Wei, X.; Xiangning, X.; Pengwei, C.: Overview of key microgrid technologies. Int. Trans. Electr. Energy Syst. 28(7), e2566 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1002/etep.2566
Bernal-Agustín, J.L.; Dufo-López, R.: Simulation and optimization of stand-alone hybrid renewable energy systems. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 13(8), 2111–2118 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rser.2009.01.010
Alonso, M.; Amaris, H.; Alvarez-Ortega, C.: Integration of renewable energy sources in smart grids by means of evolutionary optimization algorithms. Expert Syst. Appl. 39(5), 5513–5522 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eswa.2011.11.069
Abdelshafy, A.M.; Jurasz, J.; Hassan, H.; Mohamed, A.M.: Optimized energy management strategy for grid connected double storage (pumped storage-battery) system powered by renewable energy resources. Energy 192, 116615 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.energy.2019.116615
Restrepo, M.; Cañizares, C.A.; Simpson-Porco, J.W.; Su, P.; Taruc, J.: Optimization- and rule-based energy management systems at the canadian renewable energy laboratory microgrid facility. Appl. Energy 290, 116760 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apenergy.2021.116760
Takach, M.; Sarajlić, M.; Peters, D.; Kroener, M.; Schuldt, F.; von Maydell, K.: Review of hydrogen production techniques from water using renewable energy sources and its storage in Salt Caverns. Energies 15(4), 1415 (2022). https://doi.org/10.3390/en15041415
Nagadurga, T.; Narasimham, P.; Vakula, V.: Global maximum power point tracking of solar PV strings using the teaching learning based optimisation technique. Int. J. Ambient Energy 43(1), 1883–1894 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1080/01430750.2020.1721327
Femia, N.; Petrone, G.; Spagnuolo, G.; Vitelli, M.: Optimization of perturb and observe maximum power point tracking method. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 20(4), 963–973 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1109/TPEL.2005.850975
Khan, M.J.; Mathew, L.: Comparative study of optimization techniques for renewable energy system. Arch Computat Methods Eng 27(2), 351–360 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11831-018-09306-8
Wu, W.; Chen, J.; Zhang, B.; Sun, H.: A robust wind power optimization method for look-ahead power dispatch. IEEE Trans. Sustain. Energy 5(2), 507–515 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1109/TSTE.2013.2294467
Kanase-Patil, A.; Saini, R.; Sharma, M.: Sizing of integrated renewable energy system based on load profiles and reliability index for the state of Uttarakhand in India. Renewable Energy 36(11), 2809–2821 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.renene.2011.04.022
Maheshwari, Z.; Ramakumar, R.: Smart integrated renewable energy systems (SIRES): a novel approach for sustainable development. Energies 10(8), 1145 (2017). https://doi.org/10.3390/en10081145
Masip, Y.; Gutierrez, A.; Morales, J.; Campo, A.; Valín, M.: Integrated renewable energy system based on IREOM model and spatial-temporal series for isolated rural areas in the region of valparaiso, Chile. Energies 12(6), 1110 (2019). https://doi.org/10.3390/en12061110
Masip Macía, Y.; Rodríguez Machuca, P.; Rodríguez Soto, A.A.; Carmona Campos, R.: Green hydrogen value chain in the sustainability for port operations: case study in the region of valparaiso Chile. Sustainability 13(24), 13681 (2021). https://doi.org/10.3390/su132413681
Gómez Sánchez, M.; Macia, Y.M.; Fernández Gil, A.; Castro, C.; Nuñez González, S.M.; Pedrera Yanes, J.: A mathematical model for the optimization of renewable energy systems. Mathematics 9(1), 39 (2020). https://doi.org/10.3390/math9010039
Gómez Sánchez, M.; Macia, Y.M.; Fernández Gil, A.; Castro, C.; Nuñez González, S.M.; Pedrera Yanes, J.: A mathematical model for the optimization of renewable energy systems. Mathematics 9(1), 39 (2020). https://doi.org/10.3390/math9010039
Tambunan, H.B., et al.: The challenges and opportunities of renewable energy source (RES) penetration in Indonesia: case study of Java-Bali power system. Energies 13(22), 5903 (2020). https://doi.org/10.3390/en13225903
Fan, L.; Liu, G.; Wang, F.; Geissen, V.; Ritsema, C.J.: Factors affecting domestic water consumption in rural households upon access to improved water supply: Insights from the Wei River Basin, China. PLoS ONE 8(8), e71977 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0071977
Kang, D.; Jung, T.Y.: Renewable energy options for a rural village in North Korea. Sustainability 12(6), 2452 (2020)
Albogamy, F.R., et al.: Real-time energy management and load scheduling with renewable energy integration in smart grid. Sustainability 14(3), 1792 (2022). https://doi.org/10.3390/su14031792
Reddy, S.S.: Optimization of renewable energy resources in hybrid energy systems. J. Green Eng. 7(1), 43–60 (2017). https://doi.org/10.13052/jge1904-4720.7123
Acknowledgements
This research is supported by Taif University Researchers Supporting Project number (TURSP-2020/305), Taif University, Taif, Saudi Arabia.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Selim, M.M., Althobaiti, S. A Mathematical Optimization Framework for Managing the Renewable Energy to Attain Maximum Power. Arab J Sci Eng 48, 8021–8034 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13369-022-07396-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13369-022-07396-y