Abstract
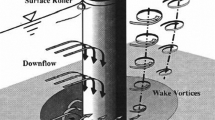
The purpose of this paper was to study the local scour formation due to an inclined circular bridge pier. The experiments for two cases of inclined and vertical piers under clear-water condition with four different flow conditions have been performed. The experiments were conducted in the hydraulic laboratory of Tarbiat Modares University in a rectangular channel. Also, for better interpretation of the observed changes, the longitudinal component values of the velocity in a vertical plain with definite distance located downstream of the vertical and inclined piers were recorded using a velocimeter. The results show that although the scour hole shape and its ridge is changed with the inclination angle of pier, the maximum scour depth in a laterally inclined pier is almost equal to that of a vertical pier and the location of the maximum scour depth in vertical pier has transferred from the 0° area to the approximately 30° area in inclined pier state.
Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- V :
-
Approach flow velocity in the channel
- V c :
-
Critical velocity for sediment motion
- D :
-
Pier diameter
- d 0 :
-
Upstream flow depth
- d 50 :
-
Average diameter of the sediments
- Y :
-
Depth of flow
- u*c :
-
Critical shear velocity of the sediments
- ds:
-
Scour depth in the equilibrium time experiment
References
Melville B.W., Coleman S.E.: Bridge Scour. Water Resources Publications LLC, Colorado (2002)
Bozkus Z., Yaldiz O.: Effects of inclination of bridge piers on scouring depth. J. Hydraul. Eng. ASCE. 130(8), 827–832 (2004)
Lee S., Sturm T.: Effect of sediment size scaling on physical modeling of bridge pier scour. J. Hydraul. Eng. ASCE. 135(10), 793–802 (2009)
Heidarpour M., Afzalimehr H., Izadinia E.: Reduction of local scour around bridge pier groups using collars. Int. J. Sediment. Res. 25(4), 411–422 (2010)
Khosronejad A., Kang S., Sotiropoulos F.: Experimental and computational investigation of local scour around bridge piers. Adv. Water. Resour. 37, 73–85 (2012)
Ghodsian M., Vaghefi M.: Experimental study on scour and flow field in a scour hole around a T-shaped spur dike in a 90 degree bend. Int. J. Sediment. Res. 24(2), 145–158 (2009)
Vaghefi M., Ghodsian M., Salehi Neyshabori S.A.A.: Experimental study on scour around a T-Shaped spur dike in a channel bend. J. Hydraul. Eng. ASCE. 138(5), 471–474 (2012)
Mazumder M.H., Barbhuiya A.K.: Live-bed scour experiments with 45° wing-wall abutments. Sadhana 39(5), 1165–1183 (2014)
Chiew Y.M., Melville B.W.: Local scour around bridge piers. J. Hydraul. Res. 25(1), 15–26 (1987)
Ettema, R.E.: Scour at Bridge Piers. Report No. 236, School of Engineering, University of Auckland, New Zealand (1980)
Melville B.W.: Pier and abutment scour: integrated approach. J. Hydraul. Eng. ASCE. 123(2), 125–136 (1997)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Vaghefi, M., Ghodsian, M. & Salimi, S. Scour Formation Due to Laterally Inclined Circular Pier. Arab J Sci Eng 41, 1311–1318 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13369-015-1920-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13369-015-1920-6