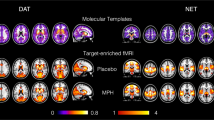
Abstract
The marriage of psychopharmacology with functional neuroimaging enables the investigation of neurochemical modulation of cognitive functions in the human brain. From the point of basic neurocognitive research, pharmacological functional neuroimaging is hence a valuable completion of animal experiments. From the point of clinical neuroscience, pharmacological neuroimaging contributes to the understanding and development of pharmacological treatment approaches for patients with neurological and psychiatric disorders. The present paper provides an overview of the methodological approach and illustrates research findings and recent developments from pharmacological functional magnetic resonance imaging studies by means of selective examples from the dopaminergic and cholinergic neurotransmitter system.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bloom AS, Hoffmann RG, Fuller SA et al (1999) Determination of drug-induced changes in functional MRI signal using a pharmacokinetic model. Hum Brain Mapp 8:235–244
Brozoski TJ, Brown RM, Rosvold HE, Goldman PS (1979) Cognitive deficit caused by regional depletion of dopamine in prefrontal cortex of rhesus monkey. Science 205:929–932
Cools R, D’Esposito M (2011) Inverted-U-shaped dopamine actions on human working memory and cognitive control. Biol Psychiatry 69:e113–e125
Evans S, Gray MA, Dowell NG et al (2013) APOE E4 Carriers show prospective memory enhancement under nicotine, and evidence for specialisation within medial BA10. Neuropsychopharmacology 38:655–663
Dechent P, Frahm J (2004) Funktionelle Magnetresonanz-Tomografie des menschlichen Gehirns. Neuroforum 3:229–236
Furey ML, Pietrini P, Haxby JV (2000) Cholinergic enhancement and increased selectivity of perceptual processing during working memory. Science 290:2315–2319
Giessing C, Fink GR, Rosler F, Thiel CM (2007) fMRI data predict individual differences of behavioral effects of nicotine: a partial least square analysis. J Cogn Neurosci 19:658–670
Giessing C, Thiel CM, Alexander-Bloch AF et al (2013) Human brain functional network changes associated with enhanced and impaired attentional task performance. J Neurosci 33:5903–5914
Greicius M (2008) Resting-state functional connectivity in neuropsychiatric disorders. Curr Opin Neurol 21:424–430
Hasselmo ME (1995) Neuromodulation and cortical function: modeling the physiological basis of behavior. Behav Brain Res 67:1–27
Honey G, Bullmore E (2004) Human pharmacological MRI. Trends Pharmacol Sci 25:366–374
Honey GD, Bullmore ET, Soni W et al (1999) Differences in frontal cortical activation by a working memory task after substitution of risperidone for typical antipsychotic drugs in patients with schizophrenia. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 96:13432–13437
Kukolja J, Thiel CM, Fink GR (2009) Cholinergic stimulation enhances neural activity associated with encoding but reduces neural activity associated with retrieval in humans. J Neurosci 29:8119–8128
Luciana M, Depue RA, Arbisi P, Leon A (1992) Facilitation of working memory in humans by a d2 dopamine receptor agonist. J Cogn Neurosci 4:58–68
Mattay VS, Callicott JH, Bertolino A et al (2000) Effects of dextroamphetamine on cognitive performance and cortical activation. Neuroimage 12:268–275
Rieckmann A, Karlsson S, Fischer H, Backman L (2012) Increased bilateral frontal connectivity during working memory in young adults under the influence of a dopamine D1 receptor antagonist. J Neurosci 32:17067–17072
Rusted J, Ruest T, Gray MA (2011) Acute effects of nicotine administration during prospective memory, an event related fMRI study. Neuropsychologia 49:2362–2368
Rusted JM, Trawley S, Heath J et al (2005) Nicotine improves memory for delayed intentions. Psychopharmacology 182:355–365
Saykin AJ, Wishart HA, Rabin LA et al (2004) Cholinergic enhancement of frontal lobe activity in mild cognitive impairment. Brain 127:1574–1583
Stein EA, Pankiewicz J, Harsch HH et al (1998) Nicotine-induced limbic cortical activation in the human brain: a functional MRI study. Am J Psychiatry 155:1009–1015
Thiel CM, Fink GR (2013) Neuropharmakologische funktionelle Bildgebung. In: Schneider F, Fink GR (eds) Funktionelle Kernspintomographie in Psychiatrie und Neurologie. Springer, pp 191–202
Thiel CM, Zilles K, Fink GR (2005) Nicotine modulates reorienting of visuospatial attention and neural activity in human parietal cortex. Neuropsychopharmacology 30:810–820
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the DFG (TH766-6/1). The manuscript was translated into English by Dr. Carsten Gießing.
Compliance with ethical guidelines
Conflict of interest. C. Thiel states that there are no conflicts of interest. The accompanying manuscript does not include any studies on humans or animals.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Thiel, C. Neuropharmacological functional imaging. e-Neuroforum 4, 92–98 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13295-013-0050-4
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13295-013-0050-4