Abstract
Background
Diabetes mellitus (DM) and its complications, including diabetic nephropathy, are rapidly increasing public health concerns. Korean Red Ginseng (KRG) is a popular herbal medicine that has many biological effects. The current literature demonstrates that KRG induced changes to the transcriptome in diabetic nephropathy mouse model are limited. Thus, we designed experiments to confirm whether changes of genes and miRNAs expression patterns in the renal cells of mice with DM, and then whether these changes are reversed by KRG.
Objective
This study aims to whether miRNAs and mRNAs expression and their relationships were contributed in the renal tissues of mice with streptozotocin (STZ)-induced diabetes.
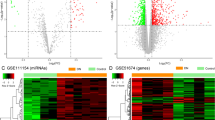
Results
We determined that the expression levels of 46 miRNAs and 827 mRNAs expression were changed in KRG-treated DM renal cells compared to DM renal cells. In addition, we found that mRNAs expression shows anti-correlation with miRNAs expression and further validated their biological processes and signaling pathways by Gene Ontology (GO).
Conclusion
Our data suggest that KRG may regulate miRNA and gene expression in a way that relieves diabetic nephropathy in mice.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Adijanto J, Philp NJ (2012) The SLC16A family of monocarboxylate transporters (MCTs)–physiology and function in cellular metabolism, pH homeostasis, and fluid transport. Curr Top Membr 70:275–311
An YR, Hwang SY (2014) Toxicology study with microRNA. Mol Cell Toxicol 10(2):127–134
Assmann TS et al (2017) MicroRNA expression profiles and type 1 diabetes mellitus: systematic review and bioinformatic analysis. Endocr Connect 6(8):773–790
Byon CH, Kim SW (2020) Regulatory effects of O-GlcNAcylation in vascular smooth muscle cells on diabetic vasculopathy. J Lipid Atheroscler 9(2):243–254
Cooper ME (1998) Pathogenesis, prevention, and treatment of diabetic nephropathy. Lancet 352(9123):213–219
De Vriese AS et al (2000) Endothelial dysfunction in diabetes. Br J Pharmacol 130(5):963–974
Dronavalli S et al (2008) The pathogenesis of diabetic nephropathy. Nat Clin Pract Endocrinol Metab 4(8):444–452
Fekete V et al (2010) Effect of type 2 diabetes on the gene expression pattern of rat hearts: a DNA microarray study. Cardiovasc Res 87:S116–S116
Giacco F, Brownlee M (2010) Oxidative stress and diabetic complications. Circ Res 107(9):1058–1070
Girach A et al (2006) Diabetic microvascular complications: can patients at risk be identified? A review. Int J Clin Pract 60(11):1471–1483
Goligorsky MS et al (2001) Workshop: endothelial cell dysfunction leading to diabetic nephropathy: focus on nitric oxide. Hypertension 37(2 Pt 2):744–748
Guay C et al (2011) Diabetes mellitus, a microRNA-related disease? Transl Res 157(4):253–264
Gui Y, Ryu GH (2013) The effect of extrusion conditions on the acidic polysaccharide, ginsenoside contents and antioxidant properties of extruded Korean red ginseng. J Ginseng Res 37(2):219–226
Hwa-Kyoung Chung W-CC, Park HY, Choi SH, Kwon D, Shin W-S, Song JS, Park B-G (2019) Chronic exposure to ethylenethiourea induces kidney injury and polycystic kidney in mice. Mol Cell Tox 15(1):57–63
James K et al (2005) Evidence for stanniocalcin binding activity in mammalian blood and glomerular filtrate. Kidney Int 67(2):477–482
Jeon BH et al (2000) Effect of Korean red ginseng on blood pressure and nitric oxide production. Acta Pharmacol Sin 21(12):1095–1100
Jovanovski E et al (2014) Modulation of endothelial function by Korean red ginseng (Panax ginseng CA Meyer) and its components in healthy individuals: a randomized controlled trial. Cardiovasc Ther 32(4):163–169
Kanwar YS et al (2008) Diabetic nephropathy: Mechanisms of renal disease progression. Exp Biol Med 233(1):4–11
Kato M et al (2007) MicroRNA-192 in diabetic kidney glomeruli and its function in TGF-beta-induced collagen expression via inhibition of E-box repressors. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 104(9):3432–3437
Kim CS et al (2002) Effect of Korea red ginseng on cerebral blood flow and superoxide production. Acta Pharmacol Sin 23(12):1152–1156
Koo BK et al (2021) Hypertriglyceridemia is an independent risk factor for cardiovascular diseases in Korean adults aged 30–49 years: a nationwide population-based study. J Lipid Atheroscler 10(1):88–98
Krupa A et al (2010) Loss of MicroRNA-192 promotes fibrogenesis in diabetic nephropathy. J Am Soc Nephrol 21(3):438–447
Kwok HH et al (2010) The ginsenoside protopanaxatriol protects endothelial cells from hydrogen peroxide-induced cell injury and cell death by modulating intracellular redox status. Free Radic Biol Med 48(3):437–445
Lee HB et al (2003) Reactive oxygen species-regulated signaling pathways in diabetic nephropathy. J Am Soc Nephrol 14:S241–S245
Lee J et al (2014) Anti-inflammation effect of exercise and Korean red ginseng in aging model rats with diet-induced atherosclerosis. Nurs Res Pract 8(3):284–291
Lee SE et al (2020) Curcumin attenuates acrolein-induced COX-2 expression and prostaglandin production in human umbilical vein endothelial cells. J Lipid Atheroscler 9(1):184–194
Lee SE, Park YS (2014) Korean Red Ginseng water extract inhibits COX-2 expression by suppressing p38 in acrolein-treated human endothelial cells. J Ginseng Res 38(1):34–39
Lee YB et al (2021) Combination of statin and ezetimibe versus statin monotherapy on cardiovascular disease and type 2 diabetes incidence among adults with impaired fasting glucose: a propensity-matched nationwide cohort study. J Lipid Atheroscler 10(3):303–312
Lim WC, Chow VT (2006) Gene expression profiles of U937 human macrophages exposed to Chlamydophila pneumoniae and/or low density lipoprotein in five study models using differential display and real-time RT-PCR. Biochimie 88(3–4):367–377
Luo CW et al (2004) Paracrine regulation of ovarian granulosa cell differentiation by stanniocalcin (STC) 1: mediation through specific STC1 receptors. Mol Endocrinol 18(8):2085–2096
Menghini R et al (2014) MicroRNAs in vascular aging and atherosclerosis. Ageing Res Rev 17:68–78
Mirnics K, Pevsner J (2004) Progress in the use of microarray technology to study the neurobiology of disease. Nat Neurosci 7(5):434–439
Molitch ME (1994) Ace-inhibitors and diabetic nephropathy. Diabetes Care 17(7):756–760
Morris ME, Felmlee MA (2008) Overview of the proton-coupled MCT (SLC16A) family of transporters: characterization, function and role in the transport of the drug of abuse gamma-hydroxybutyric acid. AAPS J 10(2):311–321
Ness SA (2006) Basic microarray analysis: strategies for successful experiments. Methods Mol Biol 316:13–33
Ness SA (2007a) Microarray analysis: basic strategies for successful experiments. Mol Biotechnol 36(3):205–219
Pan JS et al (2015) Stanniocalcin-1 inhibits renal ischemia/reperfusion injury via an AMP-activated protein kinase-dependent pathway. J Am Soc Nephrol 26(2):364–378
Park SJ, Park DH (2020) REvisiting Lipids in REtinal Diseases: a focused review on age-related macular degeneration and diabetic retinopathy. J Lipid Atheroscler 9(3):406–418
Qin S, Zhang C (2011) MicroRNAs in vascular disease. J Cardiovasc Pharmacol 57(1):8–12
Rahimi R et al (2005) A review on the role of antioxidants in the management of diabetes and its complications. Biomed Pharmacother 59(7):365–373
Rim KT, Kim SJ (2020) A toxicogenomics study of two chemicals in coffee roasting process. Mol Cell Tox 16:25–38
Schalkwijk CG, Stehouwer CDA (2005) Vascular complications in diabetes mellitus: the role of endothelial dysfunction. Clin Sci 109(2):143–159
Schena FP, Gesualdo L (2005) Pathogenetic mechanisms of diabetic nephropathy. J Am Soc Nephrol 16:S30–S33
Jung S-H, Kwon M-H, Han E-T, Park WS, Hong S-H, Kim Y-M, Ha K-S (2019) Array-based investigation of amino acids responsible for regulation of transamidase and kinase activities of transglutaminase 2. J Biochip 13(3):251–259
Kang SC, Lee SR, Hadiwidjaja M, Negi M, Koo HJ, Jang SA, Kwon JE, Hong H, Lim JD, Namkoong S, Kim K, Sohn E-H (2019) Mitigating effect of fermented Korean red ginseng extract with yeast and probiotics in 1-chloro-2,4-dinitrobenzene-induced skin allergic inflammation. Mol Cell Tox 15(2):111–121
Sheikh-Hamad D (2010) Mammalian stanniocalcin-1 activates mitochondrial antioxidant pathways: new paradigms for regulation of macrophages and endothelium. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol 298(2):F248-254
Song ZM et al (2014) Ginsenoside Rb1 prevents H2O2-induced HUVEC senescence by stimulating sirtuin-1 pathway. PLoS ONE 9(11):e112699
Sung JD et al (2000) Effects of red ginseng upon vascular endothelial function in patients with essential hypertension. Am J Chin Med 28(2):205–216
Tesfamariam B (1994) Free radicals in diabetic endothelial cell dysfunction. Free Radic Biol Med 16(3):383–391
Wang Q et al (2008) MicroRNA-377 is up-regulated and can lead to increased fibronectin production in diabetic nephropathy. FASEB J 22(12):4126–4135
Yang H et al (2016) Effect of Korean Red Ginseng treatment on the gene expression profile of diabetic rat retina. J Ginseng Res 40(1):1–8
Zhang C (2008a) MicroRNAs: role in cardiovascular biology and disease. Clin Sci (lond) 114(12):699–706
Zhang CX (2008b) MicroRNAs: role in cardiovascular biology and disease. Clin Sci 114(11–12):699–706
Zhang Z et al (2009) MicroRNA-21 protects from mesangial cell proliferation induced by diabetic nephropathy in db/db mice. FEBS Lett 583(12):2009–2014
Zhou MS et al (2008) Renoprotection by statins is linked to a decrease in renal oxidative stress, TGF-beta, and fibronectin with concomitant increase in nitric oxide bioavailability. Am J Physiol-Renal Physiol 295(1):F53–F59
Acknowledgements
This research was supported by Basic Science Research Program through the National Research Foundation of Korea (NRF) funded by the Ministry of Education, Science and Technology (NRF-2020R1A2C1011704) and Chung-Ang University Research Scholarship Grants 2020 to C.W. Kang.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Conceptualization, HRP, JK and YSP; Methodology, YY, SM, HY, CWK, SEL; validation, HRP; formal analysis, HRP; investigation, HRP and SEL; resources, HRP; writing-original draft preparation, HRP; writing-review and editing, YSP; visualization, HRP; supervision, YSP; project administration, YSP; funding acquisition, YSP. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
Hye Rim Park declares that he/she has no conflict of interest. Seung Eun Lee declares that he/she has no conflict of interest. Yoojung Yi declares that he/she has no conflict of interest. Sangji Moon declares that he/she has no conflict of interest. Hyunkyung Yoon declares that he/she has no conflict of interest. Chae Won Kang declares that he/she has no conflict of interest. Jaetaek Kim declares that he/she has no conflict of interest. Yong Seek Park declares that he/she has no conflict of interest.
Human and animal rights
Ethical and experimental protocol approvals were obtained from the Institutional Animal Care and Use Committee of Kyung Hee University (Approval number: KHUASP (SE)-17–008).
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Park, H.R., Lee, S.E., Yi, Y. et al. Integrated analysis of miRNA and mRNA expression profiles in diabetic mouse kidney treated to Korean Red Ginseng. Mol. Cell. Toxicol. 18, 637–646 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13273-022-00272-8
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13273-022-00272-8