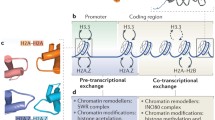
Abstract
It is now evident that transcriptional gene regulation usually requires the re-organization of chromatin architecture. Increasing evidence suggested various kinds of RNAs are involved in this process. Especially the nascent RNAs retained at their site of transcription can serve as a scaffold for organizing transcriptionally either favorable or unfavorable chromatin structures. An emerging concept of phase separation explains how these chromatin structures can be maintained as physically discrete subcompartments within membrane-less nucleoplasm. Evidences that support the crucial role of nascent RNAs in the formation of phase-separated condensates are now rapidly growing.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Almeida M, Pintacuda G, Masui O, Koseki Y, Gdula M, Cerase A, Brown D, Mould A, Innocent C, Nakayama M et al (2017) PCGF3/5-PRC1 initiates polycomb recruitment in X chromosome inactivation. Science 356:1081–1084
Arnold PR, Wells AD, Li XC (2019) Diversity and emerging roles of enhancer RNA in regulation of gene expression and cell fate. Front Cell Dev Biol 7:377
Batki J, Schnabl J, Wang J, Handler D, Andreev VI, Stieger CE, Novatchkova M, Lampersberger L, Kauneckaite K, Xie W et al (2019) The nascent RNA binding complex SFiNX licenses piRNA-guided heterochromatin formation. Nat Struct Mol Biol 26:720–731
Borsani G, Tonlorenzi R, Simmler MC, Dandolo L, Arnaud D, Capra V, Grompe M, Pizzuti A, Muzny D, Lawrence C et al (1991) Characterization of a murine gene expressed from the inactive X chromosome. Nature 351:325–329
Brown CJ, Hendrich BD, Rupert JL, Lafreniere RG, Xing Y, Lawrence J, Willard HF (1992) The human XIST gene: analysis of a 17 kb inactive X-specific RNA that contains conserved repeats and is highly localized within the nucleus. Cell 71:527–542
Cajigas I, Chakraborty A, Swyter KR, Luo H, Bastidas M, Nigro M, Morris ER, Chen S, VanGompel MJW, Leib D et al (2018) The Evf2 ultraconserved enhancer lncRNA functionally and spatially organizes megabase distant genes in the developing forebrain. Mol Cell 71:956-972e959
Chu C, Zhang QC, da Rocha ST, Flynn RA, Bharadwaj M, Calabrese JM, Magnuson T, Heard E, Chang HY (2015) Systematic discovery of Xist RNA binding proteins. Cell 161:404–416
Collis P, Antoniou M, Grosveld F (1990) Definition of the minimal requirements within the human beta-globin gene and the dominant control region for high level expression. EMBO J 9:233–240
Colognori D, Sunwoo H, Kriz AJ, Wang CY, Lee JT (2019) Xist deletional analysis reveals an interdependency between Xist RNA and polycomb complexes for spreading along the inactive X. Mol Cell 74:101-117 e110
De Santa F, Barozzi I, Mietton F, Ghisletti S, Polletti S, Tusi BK, Muller H, Ragoussis J, Wei CL, Natoli G (2010) A large fraction of extragenic RNA pol II transcription sites overlap enhancers. PLoS Biol 8:e1000384
Djebali S, Davis CA, Merkel A, Dobin A, Lassmann T, Mortazavi A, Tanzer A, Lagarde J, Lin W, Schlesinger F et al (2012) Landscape of transcription in human cells. Nature 489:101–108
Dossin F, Pinheiro I, Zylicz JJ, Roensch J, Collombet S, Le Saux A, Chelmicki T, Attia M, Kapoor V, Zhan Y et al (2020) SPEN integrates transcriptional and epigenetic control of X-inactivation. Nature 578:455–460
Ferrari F, Alekseyenko AA, Park PJ, Kuroda MI (2014) Transcriptional control of a whole chromosome: emerging models for dosage compensation. Nat Struct Mol Biol 21:118–125
Galupa R, Heard E (2015) X-chromosome inactivation: new insights into cis and trans regulation. Curr Opin Genet Dev 31:57–66
Harris H (1959) Turnover of nuclear and cytoplasmic ribonucleic acid in two types of animal cell, with some further observations on the nucleolus. Biochem J 73:362–369
Johnson WL, Straight AF (2017) RNA-mediated regulation of heterochromatin. Curr Opin Cell Biol 46:102–109
Johnson WL, Yewdell WT, Bell JC, McNulty SM, Duda Z, O’Neill RJ, Sullivan BA, Straight AF (2017) RNA-dependent stabilization of SUV39H1 at constitutive heterochromatin. Elife 6:e25299
Kim TK, Hemberg M, Gray JM, Costa AM, Bear DM, Wu J, Harmin DA, Laptewicz M, Barbara-Haley K, Kuersten S et al (2010) Widespread transcription at neuronal activity-regulated enhancers. Nature 465:182–187
Lam MT, Li W, Rosenfeld MG, Glass CK (2014) Enhancer RNAs and regulated transcriptional programs. Trends Biochem Sci 39:170–182
Le Thomas A, Rogers AK, Webster A, Marinov GK, Liao SE, Perkins EM, Hur JK, Aravin AA, Toth KF (2013) Piwi induces piRNA-guided transcriptional silencing and establishment of a repressive chromatin state. Genes Dev 27:390–399
Lee JT (2009) Lessons from X-chromosome inactivation: long ncRNA as guides and tethers to the epigenome. Genes Dev 23:1831–1842
Li W, Notani D, Ma Q, Tanasa B, Nunez E, Chen AY, Merkurjev D, Zhang J, Ohgi K, Song X et al (2013) Functional roles of enhancer RNAs for oestrogen-dependent transcriptional activation. Nature 498:516–520
Li W, Notani D, Rosenfeld MG (2016) Enhancers as non-coding RNA transcription units: recent insights and future perspectives. Nat Rev Genet 17:207–223
Li X, Zhou B, Chen L, Gou LT, Li H, Fu XD (2017) GRID-seq reveals the global RNA-chromatin interactome. Nat Biotechnol 35:940–950
Li X, Fu XD (2019) Chromatin-associated RNAs as facilitators of functional genomic interactions. Nat Rev Genet 20:503–519
Ling J, Ainol L, Zhang L, Yu X, Pi W, Tuan D (2004) HS2 enhancer function is blocked by a transcriptional terminator inserted between the enhancer and the promoter. J Biol Chem 279:51704–51713
Loda A, Heard E (2019) Xist RNA in action: Past, present, and future. PLoS Genet 15:e1008333
Maison C, Almouzni G (2004) HP1 and the dynamics of heterochromatin maintenance. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 5:296–304
McHugh CA, Chen CK, Chow A, Surka CF, Tran C, McDonel P, Pandya-Jones A, Blanco M, Burghard C, Moradian A et al (2015) The Xist lncRNA interacts directly with SHARP to silence transcription through HDAC3. Nature 521:232–236
Mikami S, Kanaba T, Takizawa N, Kobayashi A, Maesaki R, Fujiwara T, Ito Y, Mishima M (2014) Structural insights into the recruitment of SMRT by the corepressor SHARP under phosphorylative regulation. Structure 22:35–46
Minajigi A, Froberg J, Wei C, Sunwoo H, Kesner B, Colognori D, Lessing D, Payer B, Boukhali M, Haas W et al (2015) Chromosomes. A comprehensive Xist interactome reveals cohesin repulsion and an RNA-directed chromosome conformation. Science 349:aab2276
Murano K, Iwasaki YW, Ishizu H, Mashiko A, Shibuya A, Kondo S, Adachi S, Suzuki S, Saito K, Natsume T et al (2019) Nuclear RNA export factor variant initiates piRNA-guided co-transcriptional silencing. EMBO J 38:e102870
Nair SJ, Yang L, Meluzzi D, Oh S, Yang F, Friedman MJ, Wang S, Suter T, Alshareedah I, Gamliel A et al (2019) Phase separation of ligand-activated enhancers licenses cooperative chromosomal enhancer assembly. Nat Struct Mol Biol 26:193–203
Pintacuda G, Wei G, Roustan C, Kirmizitas BA, Solcan N, Cerase A, Castello A, Mohammed S, Moindrot B, Nesterova TB et al (2017) hnRNPK recruits PCGF3/5-PRC1 to the Xist RNA B-repeat to establish polycomb-mediated chromosomal silencing. Mol Cell 68:955-969e910
Sabari BR, Dall’Agnese A, Boija A, Klein IA, Coffey EL, Shrinivas K, Abraham BJ, Hannett NM, Zamudio AV, Manteiga JC et al (2018) Coactivator condensation at super-enhancers links phase separation and gene control. Science 361:eaar958
Shin HY (2019) The structural and functional roles of CTCF in the regulation of cell type-specific and human disease-associated super-enhancers. Genes Genomics 41:257–265
Shirai A, Kawaguchi T, Shimojo H, Muramatsu D, Ishida-Yonetani M, Nishimura Y, Kimura H, Nakayama JI, Shinkai Y (2017) Impact of nucleic acid and methylated H3K9 binding activities of Suv39h1 on its heterochromatin assembly. Elife 6:e25317
Sienski G, Donertas D, Brennecke J (2012) Transcriptional silencing of transposons by Piwi and maelstrom and its impact on chromatin state and gene expression. Cell 151:964–980
Sienski G, Batki J, Senti KA, Donertas D, Tirian L, Meixner K, Brennecke J (2015) Silencio/CG9754 connects the Piwi-piRNA complex to the cellular heterochromatin machinery. Genes Dev 29:2258–2271
Tsai PF, Dell’Orso S, Rodriguez J, Vivanco KO, Ko KD, Jiang K, Juan AH, Sarshad AA, Vian L, Tran M et al (2018) A muscle-specific enhancer RNA mediates cohesin recruitment and regulates transcription in trans. Mol Cell 71:129-141e128
Tuan D, Kong S, Hu K (1992) Transcription of the hypersensitive site HS2 enhancer in erythroid cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 89:11219–11223
Velazquez Camacho O, Galan C, Swist-Rosowska K, Ching R, Gamalinda M, Karabiber F, De La Rosa-Velazquez I, Engist B, Koschorz B, Shukeir N et al (2017) Major satellite repeat RNA stabilize heterochromatin retention of Suv39h enzymes by RNA-nucleosome association and RNA:DNA hybrid formation. Elife 6:e25293
Verdel A, Jia S, Gerber S, Sugiyama T, Gygi S, Grewal SI, Moazed D (2004) RNAi-mediated targeting of heterochromatin by the RITS complex. Science 303:672–676
Wutz A, Rasmussen TP, Jaenisch R (2002) Chromosomal silencing and localization are mediated by different domains of Xist RNA. Nat Genet 30:167–174
Yamazaki T, Nakagawa S, Hirose T (2020) Architectural RNAs for membraneless nuclear body formation. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol
Yu Y, Gu J, Jin Y, Luo Y, Preall JB, Ma J, Czech B, Hannon GJ (2015) Panoramix enforces piRNA-dependent cotranscriptional silencing. Science 350:339–342
Zhao J, Sun BK, Erwin JA, Song JJ, Lee JT (2008) Polycomb proteins targeted by a short repeat RNA to the mouse X chromosome. Science 322:750–756
Zylicz JJ, Bousard A, Zumer K, Dossin F, Mohammad E, da Rocha ST, Schwalb B, Syx L, Dingli F, Loew D et al (2019) The implication of early chromatin changes in X chromosome inactivation. Cell 176:182-197e123
Acknowledgements
We apologize to all whose excellent works that was not described here due to space limitation. This work was supported by the General Research Fund of the University of Seoul (#201604271104).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kwon, Y., Chung, Y.D. RNA-mediated regulation of chromatin structures. Genes Genom 42, 609–617 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13258-020-00929-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13258-020-00929-5