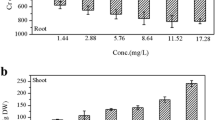
Abstract
Background
Phenylalanine ammonia-lyase (PAL) catalyzes the first step in the biosynthetic phenylpropanoid pathway (PPP) via deamination of phenylalanine to trans-cinnamic acid, a precursor for the lignin and flavonoid biosynthetic pathways. Although its role is well-established in various plants, the functional significance of PAL genes in rice remains poorly understood.
Objective
This study aims to find out the global feature of rice PAL genes associated with phosphate use efficiency.
Methods
To identify the biological functions of individual rice PAL genes, we performed meta-expression profiling analysis based on phylogenomics of rice PAL genes and confirmed the expression patterns using Quantitative real-time PCR (qPCR).
Results
We identified nine genes that were remarkably up-regulated during long-term phosphate (Pi) starvation and recovery processes through RNA-Seq data analysis. Expression patterns of the nine rice PAL genes under Pi starvation were further confirmed by qPCR, indicating that the function of PAL genes is strongly associated with Pi starvation response in rice.
Conclusion
Our study reports the functional significance of rice PAL genes involved in adaptation to low Pi growth conditions and provides useful information to improve Pi use efficiency in crop plant.





Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- 3GT:
-
3-O-glucosyltransferase
- ANS:
-
Anthocyanidin synthase
- CHI:
-
Chalcone isomerase
- CHS:
-
Chalcone synthase
- CRE:
-
Cis-acting regulatory element
- DFR:
-
Dihydroflavonol 4-reductase
- F3H:
-
Flavanone 3-hydroxylase
- FPKM:
-
Fragments per kilobase of transcript per million mapped reads
- PAL:
-
Phenylalanine ammonia-lyase
- PPP:
-
Phenylpropanoid pathway
- Pi:
-
Phosphate
- SA:
-
Salicylic acid
- qPCR:
-
Quantitative real-time PCR
References
Bailey TL, Johnson J, Grant CE, Noble WS (2015) The MEME suite. Nucleic Acids Res 43:39–49
Busk PK, Jensen AB, Pages M (1997) Regulatory elements in vivo in the promoter of the abscisic acid responsive gene rab17 from maize. Plant J 11:1285–1295
Bustos R, Castrillo G, Linhares F, Puga MI, Rubio V, Perez-Perez J, Solano R, Leyva A, Paz-Ares J (2010) A central regulatory system largely controls transcriptional activation and repression responses to phosphate starvation in Arabidopsis. PLoS Genet 6:e1001102
Cao P, Jung KH, Choi D, Hwang D, Ronald PC (2012) The rice oligonucleotide array database: an atlas of rice gene expression. Rice 5:17
Chow CN, Zheng HQ, Wu NY, Chien CH, Huang HD, Lee TY, Chiang-Hsieh YF, Hou PF, Yang TY, Chang WC (2016) PlantPAN 2.0: an update of plant promoter analysis navigator for reconstructing transcriptional regulatory networks in plants. Nucleic Acids Res 44:1154–1160
Cochrane FC, Davin LB, Lewis NG (2004) The Arabidopsis phenylalanine ammonia lyase gene family: kinetic characterization of the four PAL isoforms. Phytochemistry 65:1557–1564
Despres C, DeLong C, Glaze S, Liu E, Fobert PR (2000) The Arabidopsis NPR1/NIM1 protein enhances the DNA binding activity of a subgroup of the TGA family of bZIP transcription factors. Plant Cell 12:279–290
Devaiah BN, Karthikeyan AS, Raghothama KG (2007) WRKY75 transcription factor is a modulator of phosphate acquisition and root development in Arabidopsis. Plant Physiol 143:1789–1801
Dixon RA, Paiva NL (1995) Stress-induced phenylpropanoid metabolism. Plant Cell 7:1085–1097
Dobermann A (2000) Rice: nutrient disorders & nutrient management. International Rice Research Institute, Los Banos, p 191
Dong CJ, Shang QM (2013) Genome-wide characterization of phenylalanine ammonia-lyase gene family in watermelon (Citrullus lanatus). Planta 238:35–49
Gho YS, Jung KH (2019) Comparative expression analyses of rice and arabidopsis phosphate transporter families revealed their conserved roles for the phosphate starvation response. Plant Breed Biotech 7:42–49
Gho YS, An G, Park HM, Jung KH (2018) A systemic view of phosphate starvation-responsive genes in rice roots to enhance phosphate use efficiency in rice. Plant Biotechnol Rep 12:249–264
Higo K, Ugawa Y, Iwamoto M, Higo H (1998) PLACE: a database of plant cis-acting regulatory DNA elements. Nucleic Acids Res 26:358–359
Huang J, Gu M, Lai Z, Fan B, Shi K, Zhou YH, Yu JQ, Chen Z (2010) Functional analysis of the Arabidopsis PAL gene family in plant growth, development, and response to environmental stress. Plant Physiol 153:1526–1538
Jain M, Nijhawan A, Tyagi AK, Khurana JP (2006) Validation of housekeeping genes as internal control for studying gene expression in rice by quantitative real-time PCR. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 345:646–651
Jiang C, Gao X, Liao L, Harberd NP, Fu X (2007) Phosphate starvation root architecture and anthocyanin accumulation responses are modulated by the gibberellin-DELLA signaling pathway in Arabidopsis. Plant Physiol 145:1460–1470
Jung KH, Cao P, Seo YS, Dardick C, Ronald PC (2010) The rice kinase phylogenomics database: a guide for systematic analysis of the rice kinase super-family. Trends Plant Sci 15:595–599
Juszczuk IM, Wiktorowska A, Malusá E, Rychter AM (2004) Changes in the concentration of phenolic compounds and exudation induced by phosphate deficiency in bean plants (Phaseolus vulgaris L.). Plant Soil 267:41–49
Koukol J, Conn EE (1961) The metabolism of aromatic compounds in higher plants. IV. Purification and properties of the phenylalanine deaminase of Hordeum vulgare. J Biol Chem 236:2692–2698
Kumar S, Stecher G, Tamura K (2016) MEGA7: molecular evolutionary genetics analysis version 7.0 for bigger datasets. Mol Biol Evol 33:1870–1874
Kuo HF, Chiou TJ (2011) The role of microRNAs in phosphorus deficiency signaling. Plant Physiol 156:1016–1024
Liu W, Kohlen W, Lillo A, Op den Camp R, Ivanov S, Hartog M, Limpens E, Jamil M, Smaczniak C, Kaufmann K, Yang WC, Hooiveld GJ, Charnikhova T, Bouwmeester HJ, Bisseling T, Geurts R (2011) Strigolactone biosynthesis in medicago truncatula and rice requires the symbiotic GRAS-type transcription factors NSP1 and NSP2. Plant Cell 23:3853–3865
MacDonald MJ, D’Cunha GB (2007) A modern view of phenylalanine ammonia lyase. Biochem Cell Biol 85:273–282
Morris RT, O’Connor TR, Wyrick JJ (2008) Osiris: an integrated promoter database for Oryza sativa L. Bioinformatics 24:2915–2917
Nilsson L, Muller R, Nielsen TH (2010) Dissecting the plant transcriptome and the regulatory responses to phosphate deprivation. Physiol Plant 139:129–143
Payyavula RS, Navarre DA, Kuhl JC, Pantoja A, Pillai SS (2012) Differential effects of environment on potato phenylpropanoid and carotenoid expression. BMC Plant Biol 12:39
Reichert AI, He XZ, Dixon RA (2009) Phenylalanine ammonia-lyase (PAL) from tobacco (Nicotiana tabacum): characterization of the four tobacco PAL genes and active heterotetrameric enzymes. Biochem J 424:233–242
Rubio V, Linhares F, Solano R, Martin AC, Iglesias J, Leyva A, Paz-Ares J (2001) A conserved MYB transcription factor involved in phosphate starvation signaling both in vascular plants and in unicellular algae. Genes Dev 15:2122–2133
Schmittgen TD, Livak KJ (2008) Analyzing real-time PCR data by the comparative C(T) method. Nat Protoc 3:1101–1108
Schunmann PH, Richardson AE, Vickers CE, Delhaize E (2004) Promoter analysis of the barley Pht1;1 phosphate transporter gene identifies regions controlling root expression and responsiveness to phosphate deprivation. Plant Physiol 136:4205–4214
Secco D, Jabnoune M, Walker H, Shou H, Wu P, Poirier Y, Whelan J (2013) Spatio-temporal transcript profiling of rice roots and shoots in response to phosphate starvation and recovery. Plant Cell 25:4285–4304
Tonnessen BW, Manosalva P, Lang JM, Baraoidan M, Bordeos A, Mauleon R, Oard J, Hulbert S, Leung H, Leach JE (2015) Rice phenylalanine ammonia-lyase gene OsPAL4 is associated with broad spectrum disease resistance. Plant Mol Biol 87:273–286
Tsai CJ, Harding SA, Tschaplinski TJ, Lindroth RL, Yuan Y (2006) Genome-wide analysis of the structural genes regulating defense phenylpropanoid metabolism in Populus. New Phytol 172:47–62
Yamamoto S, Nakano T, Suzuki K, Shinshi H (2004) Elicitor-induced activation of transcription via W box-related cis-acting elements from a basic chitinase gene by WRKY transcription factors in tobacco. Biochim Biophys Acta (BBA) - Gene Struct Exp 1679(3):279–287
Yokota K, Soyano T, Kouchi H, Hayashi M (2010) Function of GRAS proteins in root nodule symbiosis is retained in homologs of a non-legume, rice. Plant Cell Physiol 51:1436–1442
Yoshida S, Forno DA, Cock JH, Gomez KA (1976) Laboratory manual for physiological studies of rice, 3rd edn. Int Rice Res Inst, Manila
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by grants from the Next-Generation BioGreen 21 Program (grant number, PJ01325901 to KHJ) supported by the Rural Development Administration, and the National Research Foundation of Korea (NRF) (NRF-2016R1D1A1A09919568 to KHJ), Republic of Korea.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Gho, YS., Kim, Sj. & Jung, KH. Phenylalanine ammonia-lyase family is closely associated with response to phosphate deficiency in rice. Genes Genom 42, 67–76 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13258-019-00879-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13258-019-00879-7