Abstract
Background
River water has been implicated as a source of non-typhoidal Salmonella (NTS) serovars in Mexico.
Objective
To dissect the molecular pathogenesis and defense strategies of seven NTS strains isolated from river water in Mexico.
Methods
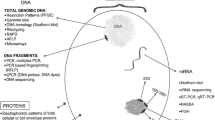
The genome of Salmonella serovars Give, Pomona, Kedougou, Stanley, Oranienburg, Sandiego, and Muenchen were sequenced using the whole-genome shotgun methodology in the Illumina Miseq platform. The genoma annotation and evolutionary analyses were conducted in the RAST and FigTree servers, respectively. The MLST was performed using the SRST2 tool and the comparisons between strains were clustered and visualized using the Gview server. Experimental virulence assay was included to evaluate the pathogenic potential of strains.
Results
We report seven high-quality draft genomes, ranging from ~ 4.61 to ~ 5.12 Mb, with a median G + C value, coding DNA sequence, and protein values of 52.1%, 4697 bp, and 4,589 bp, respectively. The NTS serovars presented with an open pan-genome, offering novel genetic content. Each NTS serovar had an indistinguishable virulotype with a core genome (352 virulence genes) closely associated with Salmonella pathogenicity; 13 genes were characterized as serotype specific, which could explain differences in pathogenicity. All strains maintained highly conserved genetic content regarding the Salmonella pathogenicity islands (1–5) (86.9–100%), fimbriae (84.6%), and hypermutation (100%) genes. Adherence and invasion capacity were confirmed among NTS strains in Caco-2 cells.
Conclusion
Our results demonstrated the arsenal of virulence and defense molecular factors harbored on NTS serovars and highlight that environmental NTS strains are waterborne pathogens worthy of attention.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Achtman M, Wain J, Weill F, Nair S, Zhou Z, Sangal V, Krauland M, Hale J, Harbottle H, Uesbeck A, Dougan G, Harrison L, Brisse S (2012) Multilocus sequence typing as a replacement for serotyping in Salmonella enterica. PLoS Pathog 8:e1002776
Aziz R, Bartels D, Best A, DeJongh M, Disz T, Edwards R, Formsma K, Gerdes S, Glass E, Kubal M, Meyer F, Olsen G, Olson R, Osterman A, Overbeek R, McNeil L, Paarmann D, Paczian T, Parrello B, Pusch G, Reich C, Stevens R, Vassieva O, Vonstein V, Wilke A, Zagnitko O (2008) The RAST server: rapid annotations using subsystems technology. BMC Genom 9:75
Bolger A, Lohse M, Usadel B (2014) Trimmomatic: A flexible trimmer for illumina sequence data. Bioinformatics 30:2114–2120
Castañeda RGM, Jiménez EM (2018) Evaluación de ríos del valle de Culiacán, México, como reservorios de serotipos de Salmonella resistentes a antibióticos. Rev Int Contam Ambie 34:191–201
Casteñeda-Ruelas G, Carreón-Gaxiola C, Castelán-Sánchez H, Acatzi-Silva A, Romero-Martínez S, García-Molina A, Jiménez-Edeza M (2017) Draft genome sequences of 18 Salmonella enterica subsp. enterica serovar oranienburg strains isolated from rivers in Northwestern Mexico. Genome Announc 5:e01585–e01516
CDC (2017) Outbreaks Involving Salmonella|CDC. https://www.cdc.gov/Salmonella/outbreaks.html. Accessed 15 Dec 2017
Chakroun I, Cordero H, Mahdhi A, Morcillo P, Fedhila K, Cuesta A, Bakhrouf A, Mahdouani K, Esteban M (2017) Adhesion, invasion, cytotoxic effect and cytokine production in response to atypical Salmonella typhimurium infection. Microb Pathog 106:40–49
Darling A, Mau B, Perna N (2010) Progressive mauve: multiple genome alignment with gene gain, loss and rearrangement. PLoS One 5:e11147
de Moraes M, Desai P, Porwollik S, Canals R, Perez D, Chu W, McClelland M, Teplitski M (2017) Salmonella persistence in tomatoes requires a distinct set of metabolic functions identified by transposon insertion sequencing. J Appl Environ Microbiol 83:e03028–e03016
Dhanani A, Block G, Dewar K, Forgetta V, Topp E, Beiko R, Diarra M (2015) Genomic comparison of non-typhoidal Salmonella enterica Serovars Typhimurium, Enteritidis, Heidelberg, Hadar and Kentucky isolates from broiler chickens. PLoS One 10:e0128773
Dirección General de Epidemilogia (DGE) (2017) Anuario 1984–2016. http://www.epidemiologia.salud.gob.mx/anuario/html/anuarios.html. Accessed 10 Dec 2017
Dostal A, Gagnon M, Chassard C, Zimmermann M, O’Mahony L, Lacroix C (2014) Salmonella adhesion, invasion and cellular immune responses are differentially affected by iron concentrations in a combined in vitro gut fermentation-cell model. PLoS One 9(3):e93549
Eng S, Pusparajah P, Ab Mutalib N, Ser H, Chan K, Lee L (2015) Salmonella: a review on pathogenesis, epidemiology and antibiotic resistance. Front Life Sci 8:284–293
Estrada-Acosta M, Medrano-Felix A, Jimenez M, Gomez-Gil B, Leon-Felix J, Amarillas L, Chaidez C (2013) Draft genome sequence of Salmonella enterica subsp. enterica serotype saintpaul strain S-70, isolated from an aquatic environment. Genome Announc 1:e01016–e01013
Estrada-Acosta M, Jiménez M, Chaidez C, León-Félix J, Castro-del Campo N (2014) Irrigation water quality and the benefits of implementing good agricultural practices during tomato (Lycopersicum esculentum) production. Environ Monit Assess 186:4323–4330
Estrada-Acosta M, Ramirez K, Medrano-Félix J, Castro-Del Campo N, López-Moreno H, Jimenez Edeza M, Martínez-Urtaza J, Chaidez C (2017) Effect of river water exposition on adhesion and invasion abilities of Salmonella oranienburg and Saintpaul. Int J Environ Health Res 28:43–54
Fabrega A, Vila J (2013) Salmonella enterica serovar typhimurium skills to succeed in the host: virulence and regulation. Clin Microbiol Rev 26:308–341
Fricke W, Mammel M, McDermott P, Tartera C, White D, LeClerc J, Ravel J, Cebula T (2011) Comparative genomics of 28 Salmonella enterica Isolates: evidence for CRISPR-mediated adaptive sublineage evolution. J Bacteriol 193:3556–3568
Gerlach R, Hensel M (2007) Salmonella pathogenicity islands in host specificity, host pathogen-interactions and antibiotics resistance of Salmonella enterica. Berl Munch Tierarztl Wochenschr 120:317–327
Gutiérrez-Cogco L, Montiel-Vázquez E, Aguilera-Pérez P, González-Andrade M (2000) Serotipos de Salmonella identificados en los servicios de salud de México. Salud Públ Méx 42:490–495
Halder B, Malakar A, Chakraborty S (2017) Nucleotide composition determines the role of translational efficiency in human genes. Bioinformation 13:46–53
Hayward M, Petrovska L, Jansen V, Woodward M (2016) Population structure and associated phenotypes of Salmonella enterica serovars derby and mbandaka overlap with host range. BMC Microbiol 16:15
Hossain S, De Silva C, Wimalasena S, Heo G, Senarath Pathirana H (2017) Aminoglycoside susceptibility and genetic characterization of Salmonella enterica Subsp. enterica Isolated from Pet Turtles. Korean J Vet Serv 40:27–33
Inouye M, Dashnow H, Raven L, Schultz M, Pope B, Tomita T, Zobel J, Holt K (2014) SRST2: rapid genomic surveillance for public Health and hospital microbiology labs. Genome Med 6:90
Jacobsen A, Hendriksen R, Aaresturp F, Ussery D, Friis C (2011) The Salmonella enterica Pan-genome. Microb Ecol 62:487–504
Jiménez M, Martinez-Urtaza J, Rodriguez-Alvarez M, Leon-Felix J, Chaidez C (2014) Prevalence and genetic diversity of Salmonella spp. in a river in a tropical environment in Mexico. J Water Health 12:874
Karkey A, Jombart T, Walker A, Thompson C, Torres A, Dongol S, Thieu NTV, Thanh DP, Thi NT, Voong V, Singer A, Parkhill J, Thwaites G, Basnyat B, Ferguson N, Baker S (2016) The ecological dynamics of fecal contamination and Salmonella Typhi and Salmonella Paratyphi A in municipal Kathmandu drinking water. PLoS Negl Trop Dis 10(1):e0004346
Khan C (2014) The dynamic interactions between Salmonella and the microbiota, within the challenging Niche of the gastrointestinal tract. Int Sch Res Notices 2014:1–23
Leekitcharoenphon P, Lukjancenko O, Friis C, Aarestrup F, Ussery D (2012) Genomic variation in Salmonella enterica core genes for epidemiological typing. BMC Genom 13:88
Li Y, Weng J, Hsiao C, Chou M, Tseng C, Hung J (2015) PEAT: an intelligent and efficient paired-end sequencing adapter trimming algorithm. BMC Bioinf 16:S2
Lin G, Chai J, Yuan S, Mai C, Cai L, Murphy R, Zhou W, Luo J (2016) VennPainter: a tool for the comparison and identification of candidate genes based on venn diagrams. PLoS One 11:e0154315
López-Cuevas O, León J, Jiménez M, Chaidez C (2009) Detección y resistencia a antibióticos de Escherichia coli y Salmonella en agua y suelo agrícola. Rev Fitotec Mex 32:119–126
Majowicz S, Musto J, Scallan E, Angulo F, Kirk M, O’Brien S, Jones T, Fazil A, Hoekstra R (2010) The global burden of non-typhoidal Salmonella gastroenteritis. Clin Infect Dis 50:882–889
Markowitz V, Chen I, Palaniappan K, Chu K, Szeto E, Grechkin Y, Ratner A, Jacob B, Huang J, Williams P, Huntemann M, Anderson I, Mavromatis K, Ivanova N, Kyrpides N (2012) IMG: the integrated microbial genomes database and comparative analysis system. Nucleic Acids Res 40:D115–D122
McClelland M, Sanderson K, Spieth J, Clifton S, Latreille P, Courtney L, Porwollik S, Ali J, Dante M, Du F, Hou S, Layman D, Leonard S, Nguyen C, Scott K, Holmes A, Grewal N, Mulvaney E, Ryan E, Sun H, Florea L, Miller W, Stoneking T, Nhan M, Waterston R, Wilson R (2001) Complete genome sequence of Salmonella enterica serovar typhimurium LT2. Nature 413:852–856
Medrano-Félix A, Estrada-Acosta M, Peraza-Garay F, Castro-del Campo N, Martínez-Urtaza J, Chaidez C (2017) Differences in carbon source utilization of Salmonella oranienburg and saintpaul Isolated from river water. Int J Environ Health Res 27:252–263
Moest T, Méresse S (2013) Salmonella T3SSs: successful mission of the secret (ion) agents. Curr Opin Microbiol 16(1):38–44
Mourão J, Novais C, Machado J, Peixe L, Antunes P (2015) Metal tolerance in emerging clinically relevant multidrug-resistant Salmonella enterica Serotype 4,[5],12:i:– clones circulating in Europe. Int J Antimicrob Agents 45:610–616
Nairz M, Schroll A, Haschka D, Dichtl S, Tymoszuk P, Demetz E, Moser P, Haas H, Fang F, Theurl I, Weiss G (2017) Genetic and dietary iron overload differentially affect the course of Salmonella typhimurium infection. Front Cell Infect Microbiol 7:110
Petkau A, Stuart-Edwards M, Stothard P, Van Domselaar G (2010) Interactive microbial genome visualization with GView. Bioinformatics 26:3125–3126
Retamal P, Fresno M, Dougnac C, Gutierrez S, Gornall V, Vidal R, Vernal R, Pujol M, Barreto M, Gonzalez-Acuña D, Abalos P (2015) Genetic and phenotypic evidence of the Salmonella enterica Serotype enteritidis human-animal interface in Chile. Front Microbiol 6:464
Spector M, Kenyon W (2012) Resistance and survival strategies of Salmonella enterica to environmental stresses. Food Res Int 45:455–481
Tatusova T, DiCuccio M, Badretdin A, Chetvernin V, Nawrocki E, Zaslavsky L, Lomsadze A, Pruitt K, Borodovsky M, Ostell J (2016) NCBI prokaryotic genome annotation pipeline. Nucleic Acids Res 44:6614–6624
Tritt A, Eisen J, Facciotti M, Darling A (2012) An Integrated pipeline for de novo assembly of microbial genomes. PLoS One 7:e42304
Vázquez-Garcidueñas M, Romero-Pérez N, Figueroa-Aguilar G, Jaime-Sánchez J, Vázquez-Marrufo G (2014) Investigation of a food-borne Salmonella oranienburg outbreak in a Mexican prison. J Infect Dev Ctries 8:143–153
von Wintersdorff C, Penders J, van Niekerk J, Mills N, Majumder S, van Alphen L, Wolffs P (2016) Dissemination of antimicrobial resistance in microbial ecosystems through horizontal gene transfer. Front Microbiol 7:173
Wang C, Zhu S, Wang X, Feng Y, Li B, Li Y, Johnston R, Liu G, Zhou J, Liu S (2015) Complete genome sequence of Salmonella enterica subspecies arizonae. str. RKS2983. Stand Genomic Sci 10:30
Winfield M, Groisman E (2003) Role of Nonhost environments in the lifestyles of Salmonella and Escherichia coli. Appl Environ Microbiol 69:3687–3694
Zhang S, Yin Y, Jones M, Zhang Z, Deatherage Kaiser B, Dinsmore B, Fitzgerald C, Fields P, Deng X (2015) Salmonella serotype determination utilizing high-throughput genome sequencing data. J Clin Microbiol 53:1685–1692
Acknowledgements
The authors thank the Laboratorio Nacional para la Investigación en Inocuidad Alimentaria (LANIIA) in Mexico for sharing the NTS strains and permitting their use in this study. We also thank Mr. Cesar Carreón Gaxiola for his technical assistance. This work was supported by the National Council of Science and Technology (CONACyT) grant CB-2014/235989. The authors would like to thank Enago (http://www.enago.com) for the English language review.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
None of the authors have conflicts of interest, financial or otherwise, to declare.
Ethical approval
This article does not contain any studies with human subjects or animals.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Burgueño-Roman, A., Castañeda-Ruelas, G.M., Pacheco-Arjona, R. et al. Pathogenic potential of non-typhoidal Salmonella serovars isolated from aquatic environments in Mexico. Genes Genom 41, 767–779 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13258-019-00798-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13258-019-00798-7