Abstract
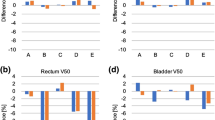
Purpose: To evaluate whether knowledge-based volumetric modulated arc therapy plans for prostate cancer with a multi-institution model (broad model) are clinically useful and effective as a standardization method. Methods: A knowledge-based planning (KBP) model was trained with 561 prostate VMAT plans from five institutions with different contouring and planning policies. Five clinical plans at each institution were reoptimized with the broad and single institution model, and the dosimetric parameters and relationship between Dmean and the overlapping volume (rectum or bladder and target) were compared. Results: The differences between the broad and single institution models in the dosimetric parameters for V50, V80, V90, and Dmean were: rectum; 9.5% ± 10.3%, 3.3% ± 1.5%, 1.7% ± 1.6%, and 3.6% ± 3.6%, (p < 0.001), bladder; 8.7% ± 12.8%, 1.5% ± 2.6%, 0.7% ± 2.4%, and 2.7% ± 4.6% (p < 0.02), respectively. The differences between the broad model and clinical plans were: rectum; 2.4% ± 4.6%, 1.7% ± 1.7%, 0.7% ± 2.4%, and 1.5% ± 2.0%, (p = 0.004, 0.015, 0.112, and 0.009) bladder; 2.9% ± 5.8%, 1.6% ± 1.9%, 0.9% ± 1.7%, and 1.1% ± 4.8%, (p < 0.018), respectively. Positive values indicate that the broad model has a lower value. Strong correlations were observed (p < 0.001) in the relationship between Dmean and the rectal and bladder volume overlapping with the target in the broad model (R = 0.815 and 0.891, respectively). The broad model had the smallest R2 of the three plans. Conclusions: KBP with the broad model is clinically effective and applicable as a standardization method at multiple institutions.




Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availability
The dataset used and/or analyzed during the current study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
References
ICRU (International Commission on Radiation Units (2010) And measurements) prescribing, reporting, and recording photon-beam intensity-modulated radiation therapy (IMRT) ICRU Report 83. Oxford University Press, Oxford, pp 41–53
Batumalai V, Jameson MG, Forstner DF, Vial P, Holloway LC (2013) How important is dosimetrist experience for intensity modulated radiation therapy? A comparative analysis of a head and neck case. Pract Radiat Oncol 3:e99–e106. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.prro.2012.06.009
Bohsung J, Gillis S, Arrans R, Bakai A, De Wagter C, Knöös T, Mijnheer BJ, Paiusco M, Perrin BA, Welleweerd H, Williams P (2005) IMRT treatment planning - A comparative inter-system and inter-centre planning exercise of the QUASIMODO group. Radiother Oncol 76:354–361. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.radonc.2005.08.003
Nelms BE, Robinson G, Markham J, Velasco K, Boyd S, Narayan S, Wheeler J, Sobczak ML (2012) Variation in external beam treatment plan quality: an inter-institutional study of planners and planning systems. Pract Radiat Oncol 2:296–305. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.prro.2011.11.012
Marino C, Villaggi E, Maggi G, Esposito M, Strigari L, Bonanno E, Borzì GR, Carbonini C, Consorti R, Fedele D, Fiandra C, Ielo I, Malatesta T, Malisan MR, Martinotti A, Moretti R, Nardiello B, Oliviero C, Clemente S, Mancosu P (2015) A feasibility dosimetric study on prostate cancer: are we ready for a multicenter clinical trial on SBRT? Strahlenther Onkol 191:573–581. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00066-015-0822-6
Villaggi E, Hernandez V, Fusella M, Moretti E, Russo S, Vaccara EML, Nardiello B, Esposito M, Saez J, Cilla S, Marino C, Stasi M, Mancosu P (2019) Plan quality improvement by DVH sharing and planner’s experience: results of a SBRT multicentric planning study on prostate. Physica Med 62:73–82. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejmp.2019.05.003
Panettieri V, Ball D, Chapman A, Cristofaro N, Gawthrop J, Griffin P, Herath S, Hoyle S, Jukes L, Kron T, Markham C, Marr L, Moloney P, Nelli F, Ramachandran P, Smith A, Hornby CJ (2019) Development of a multicentre automated model to reduce planning variability in radiotherapy of prostate cancer. Phys Imaging Radia Oncol 11:34–40. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.phro.2019.07.005
Good D, Lo J, Lee WR, Wu QJ, Yin FF, Das SK (2013) A knowledge-based approach to improving and homogenizing intensity modulated radiation therapy planning quality among treatment centers: an example application to prostate cancer planning. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 87:176–181. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijrobp.2013.03.015
Alpuche Aviles JE, Cordero Marcos MI, Sasaki D, Sutherland K, Kane B, Kuusela E (2018) Creation of knowledge-based planning models intended for large scale distribution: minimizing the effect of outlier plans. J Appl Clin Med Phys 19:215–226. https://doi.org/10.1002/acm2.12322
Scaggion A, Fusella M, Roggio A, Bacco S, Pivato N, Rossato MA, Peña LMA, Paiusco M (2018) Reducing inter- and intra-planner variability in radiotherapy plan output with a commercial knowledge-based planning solution. Physica Med 53:86–93. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejmp.2018.08.016
Berry SL, Ma R, Boczkowski A, Jackson A, Zhang P, Hunt M (2016) Evaluating inter-campus plan consistency using a knowledge based planning model. Radiother Oncol 120:349–355. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.radonc.2016.06.010
Ueda Y, Fukunaga J, Kamima T, Adachi A, Nakamatsu K, Monzen H (2018) Evaluation of multiple institutions’ models for knowledge-based planning of volumetric modulated arc therapy (VMAT) for prostate cancer. Radiat Oncol. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13014-018-0994-1
Kamima T, Ueda Y, Fukunaga J, Shimizu Y, Tamura M, Ishikawa K, Monzen H (2019) Multi-institutional evaluation of knowledge-based planning performance of volumetric modulated arc therapy (VMAT) for head and neck cancer. Physica Med 64:174–181. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejmp.2019.07.004
Fukunaga J, Tamura M, Ueda Y, Kamima T, Shimizu Y (2022) Multi-institution model (big model) versus single-institution model of knowledge-based volumetric modulated arc therapy (VMAT) planning for prostate cancer. Sci Rep 1–10. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-022-19498-6
Monzen H, Tamura M, Ueda Y, Tatsuya F, Yuta K (2020) Dosimetric evaluation with knowledge-based planning created at different periods in volumetric-modulated arc therapy for prostate cancer: a multi-institution study. Radiol Phys Technol. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12194-020-00585-0
Paddick I, Lippitz B (2006) A simple dose gradient measurement tool to complement the conformity index. J Neurosurg 105:194–201. https://doi.org/10.3171/sup.2006.105.7.194
Varian Medical Systems. Eclipse treatment planning 13.5 new features j RapidPlan (EC13.5-WBK-01-B). Palo Alto, CA: Varian Medical
Nitta Y, Ueda Y, Isono M, Ohira S, Masaoka A, Karino T, Inui S, Miyazaki M, Teshima T (2021) Customization of a model for knowledge-based planning to achieve ideal dose distributions in volume modulated arc therapy for pancreatic cancers. J Med Phys 46:66–72. https://doi.org/10.4103/jmp.JMP_76_20
Chang ATY, Hung AWM, Cheung FWK, Lee MCH, Chan OSH, Philips H, Cheng YT, Ng WT (2016) Comparison of Planning Quality and Efficiency between Conventional and Knowledge-based Algorithms in Nasopharyngeal Cancer Patients using intensity modulated Radiation Therapy. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 95:981–990. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijrobp.2016.02.017
Moore KL, Brame RS, Low DA, Mutic S (2011) Experience-based quality control of clinical intensity-modulated radiotherapy planning. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 81(2):545–551. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijrobp.2010.11.030
Numasaki H, Teshima T, Okuda Y, Ogawa K (2020) Japanese structure survey of radiation oncology in 2013. J Radiat Res 61:799–816. https://doi.org/10.1093/jrr/rraa047
Owen JB, Coia LR, Hanks GE (1997) The structure of radiation oncology in the United States in 1994. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 39:179–185. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0360-3016(97)00289-7
Ji YH, Kim MS, Jung H, Yoo SY, Cho CK (2009) Clinical characteristics of Radiation Oncology in Korea during Past 10 years. J Korean Med Sci 24:1165. https://doi.org/10.3346/jkms.2009.24.6.1165
Leung J, Munro PL, James M (2015) Faculty of Radiation Oncology 2014 workforce census. J Med Imaging Radiat Oncol 59:717–727. https://doi.org/10.1111/1754-9485.12320
Acknowledgements
We thank Dr Mikoto Tamura, Mr. Takahiro Hara, and Mr. Masashi Kimura (Varian Medical Systems) for their valuable support. We thank Ashleigh Cooper, PhD, from Edanz (https://jp.edanz.com/ac) for editing a draft of this manuscript.
Funding
This work was supported partly by Japan Society for the Promotion of Science (JSPS) KAKENHI grant number 20K08093.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Concept and design: Y.U., J.F., T.K., Y.S., K.K., H.M. Acquisition of data: Y.U., J.F., T.K., Y.S., K.K., H.D., H.M. Data analysis: Y.U., J.F., T.K., Y.S., K.K., H.M. Drafting the article: Y.U., J.F., T.K., Y.S., K.K., H.M. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Ethics approval
This study was approved at all Institutional Ethical Review Committees. (Kindai University Review Board No. 31–273, Kyushu University Review Board No. 2020– 286, JFCR Review Board No. 2020–1049, Seirei Hamamatsu General Hospital Review Board No. 3333, Osaka International Cancer Institute Review Board No. 20050).
Consent to participate
The institutional consent form was obtained from the patients.
Consent to publish
The authors affirm that human research participants provided informed consent for publication of the images in Fig. 1.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Ueda, Y., Fukunaga, Ji., Kamima, T. et al. Standardization of knowledge-based volumetric modulated arc therapy planning with a multi-institution model (broad model) to improve prostate cancer treatment quality. Phys Eng Sci Med 46, 1091–1100 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13246-023-01278-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13246-023-01278-9