Abstract
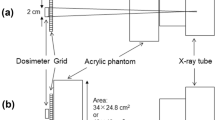
A grid is one of the key components of a digital radiography (DR) system because it removes scattered radiation, which arises when X-rays penetrate an object and improves diagnostic accuracy by enhancing image quality. With the widespread use of DR systems, demand for grids with high precision has simultaneously increased. Because unsuitable grids may decrease image quality and lead to misdiagnosis, using optimised grids for DR systems is critical. In this study, we aimed to analyse the quality of X-ray images acquired using grids with different specifications and proposed standardised criteria for grid use on the basis of our results. We measured modulation transfer function (MTF), normalised noise power spectrum (NNPS) and detective quantum efficiency (DQE) using grids with different ratios (10:1, 12:1 and 15:1) with or without implementing poly methyl methacrylate (PMMA) phantoms (0–20 cm). Pixel pitch of the detector used in this experiment was 143 μm. Based on this, a grid with a line frequency of 85 line pairs/cm was selected to prevent distortion caused by implementing unoptimised grids. As a result, the NNPS was found to increase when using the grid, and the difference in MTF and DQE was only measured when the scattered X-ray was generated by stacking the PMMA phantom. However, grids showed a positive effect MTF and DQE when the PMMA phantom was implemented. Specifically, MTF and DQE improved with increase in grid ratio. Thus, it is desirable to use a high-ratio grid to improve image quality.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bucky G (1913) A grating-diaphragm to cut off secondary rays from the object. Arch Roentgen Ray 18:6–9. https://doi.org/10.1259/arr.1913.0005
Hondius Boldingh W (1964) Grids to reduce scattered X-rays in medical radiography. Technische Hogeschool Eindhoven, Eindhoven. https://doi.org/10.6100/IR62689
Tang C-M, Stier E, Fischer K, Guckel H (1998) Anti-scattering X-ray grid. Microsyst Technol 4:187–192. https://doi.org/10.1007/s005420050128
Hendee William R, Russell Ritenour E (2002) Medical imaging physics. Radiography, 4th edn. Wiley, New York, pp 217–234
Belykh I (2014) Grid artifacts suppression in computed radiographic images. Int J Biomed Biol Eng 8:1402–1405
Papp Jeffrey (2014) Quality management in the imaging sciences, 5th edn. Elsevier, Maryland
Yoon Jai-Woong, Park Young-Guk, Park Chun-Joo, Kim Do-Il, Lee Jin-Ho, Chung Nag-Kun, Choe Bo-Young, Suh Tae-Suk, Lee Hyoung-Koo (2007) Reduction of a grid moiré pattern by integrating a carbon-interspaced high precision X-ray grid with a digital radiographic detector. Med Phys 34:4092–4097. https://doi.org/10.1118/1.2775743
Belykh I, Cornelius CW (2001) Antiscatter stationary-grid artifacts automated detection and removal in projection radiography images. In: Proceedings of the SPIE 4322, Medical imaging 2001: Image processing, pp 1162–1166 https://doi.org/10.1117/12.430992
International Electrotechnical Commission (2013) IEC 60627:2013, Diagnostic X-ray imaging equipment: characteristics of general purpose and mammographic anti-scatter grids, 3rd edn. International Electrotechnical Commission, Geneva
JPI Healthcare (2015) JPI’s grid book, 7th edn. JPI Healthcare, Ansan-si
Khodajou-Chokami H, Sohrabpour M (2015) Design of linear anti-scatter grid geometry with optimum performance for screen-film and digital mammography systems. Phys Med Biol 60:5753–5766. https://doi.org/10.1088/0031-9155/60/15/5753
Ghaffarian P, Sharafi AA, Keshavarz K, Zaidi H (2005) MCNP4C-based Monte Carlo study of grid performance in diagnostic radiology. Biomed Tech 50:1098–1099
Woo-HyunChung Sang-HyunLee (2018) Study of Monte Carlo simulator for estimation of anti-scatter grid physical characteristics on IEC 60627:2013-based. Am J Phys Appl 6:35–42. https://doi.org/10.11648/j.ajpa.20180602.12
Kenneth L, Bontrager MA, Lampignano J (2013) Textbook of radiographic positioning and related anatomy, 8th edn. Elsevier, Maryland
International Electrotechnical Commission (2003) IEC62220-1:2003, Medical electrical equipment – Characteristics of digital X-ray imaging devices – Part 1: determination of the detective quantum efficiency, 1st edn. International Electrotechnical Commission, Geneva
Neitzel Ulrich, Buhr Egbert, Hilgers Gerhard, Granfors Paul R (2004) Determination of the modulation transfer function using the edge method: influence of scattered radiation. Med Phys 31:3485–3491. https://doi.org/10.1118/1.1813872
Samei Ehsan, Flynn Michael J (2003) An experimental comparison of detector performance for direct and indirect digital radiography systems. Med Phys 30:608–622. https://doi.org/10.1118/1.1561285
Samei Ehsan, Flynn Michael J, Reimann David A (1998) A method for measuring the presampled MTF of digital radiographic systems using an edge test device. Med Phys 25:102–113. https://doi.org/10.1118/1.598165
Gupta Arun Kumar, Chowdhury Veena, Khandelwal Niranjan (2013) Diagnostic radiology: recent advances and applied physics in imaging, 2nd edn. Jaypee Brothers Medical Pub, New Delhi
Van Metter Richard L, Beutel Jacob, Kundel Harold L (2000) Handbook of medical imaging volume 1 physics and psychophysics. Applied linear-systems theory. SPIE Press, Bellingham, pp 79–160
Ranger NT, Samei E, Dobbins JT 3rd, Ravin CE (2007) Assessment of detective quantum efficiency: intercomparison of a recently introduced international standard with prior methods. Radiology 243:785–795. https://doi.org/10.1148/radiol.2433060485
Zhou Zhongxing, Gao Feng, Zhao Huijuan, Zhang Lixin (2011) Techniques to improve the accuracy of noise power spectrum measurements in digital X-ray imaging based on background trends removal. Med Phys 38:1600–1610. https://doi.org/10.1118/1.3556566
Williams Mark B, Mangiafico Peter A, Simoni Piero U (1999) Noise power spectra of images from digital mammography detectors. Med Phys 26:1279–1293. https://doi.org/10.1118/1.598623
Dong Sik Kim (2016) Noise power spectrum measurements in digital imaging with gain nonuniformity correction. IEEE 25:3712–3722. https://doi.org/10.1109/TIP.2016.2574985
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors of this manuscript declare relationships with JPI Healthcare, Co., Ltd., and the authors state that this work has not received any funding.
Research involving human participants and/or animals
We did not perform direct experiments on humans or animals. Results of prior human radiological studies were selected.
Informed consent
Informed consent was obtained from all participants in the study.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lee, S., Chung, W. Quantitative analysis of effects of the grid specifications on the quality of digital radiography images. Australas Phys Eng Sci Med 42, 553–561 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13246-019-00756-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13246-019-00756-3