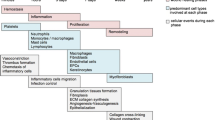
Abstract
One of the most important limitations of hemodialysis (HD) treatment is the vascular access (VA) that is used to connect the patient’s blood vessels to the extracorporeal circulation. The arteriovenous fistula (AVF) obtained with native vessels is the VA of choice for the low incidence of infections and the long-term patency, but it is affected by high incidence of non-maturation or primary failure. Before use for cannulation, AVF must undergo vascular remodeling, with progressive increase in vessel diameter, to accommodate the increase in blood flow. A growing body of evidence indicates that AVF maturation is related to the response of endothelial cells to changes in blood flow and wall shear stress. In the present report we examine the experimental and clinical evidences on the mechanisms that play a role in vascular remodeling during AVF maturation. The physical and biological factors that develop upon arteriovenous surgical connection affect endothelial and smooth muscle cell function, as well as extracellular matrix remodeling. They can explain to a great extent the process of vascular remodeling and put more light on cellular mechanisms of vessel wall adaptation. The understanding of these phenomena, besides indicating the reasons for non-maturation and primary failure, may be fundamental in the future to ameliorate clinical outcomes of AVF creation, with a great impact on the clinical management of HD patients and their quality of life.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ali, F., M. Zakkar, K. Karu, E. A. Lidington, S. S. Hamdulay, J. J. Boyle, et al. Induction of the cytoprotective enzyme heme oxygenase-1 by statins is enhanced in vascular endothelium exposed to laminar shear stress and impaired by disturbed flow. J. Biol. Chem. 284:18882–18892, 2009.
Asif, A., P. Roy-Chaudhury, and G. A. Beathard. Early arteriovenous fistula failure: a logical proposal for when and how to intervene. CJASN 1:332–339, 2006.
Atkins, G. B., and D. I. Simon. Interplay between NF-kappaB and Kruppel-like factors in vascular inflammation and atherosclerosis: location, location, location. J. Am. Heart Assoc. 2:e000290, 2013.
Badero, O. J., M. O. Salifu, H. Wasse, and J. Work. Frequency of swing-segment stenosis in referred dialysis patients with angiographically documented lesions. Am. J. Kidney Dis. Off. J. Natl. Kidney Found. 51:93–98, 2008.
Bergan, J. J., L. Pascarella, and G. W. Schmid-Schonbein. Pathogenesis of primary chronic venous disease: insights from animal models of venous hypertension. J. Vasc. Surg. 47:183–192, 2008.
Bergan, J. J., G. W. Schmid-Schonbein, P. D. C. Smith, A. N. Nicolaides, M. R. Boisseau, and B. Eklof. Chronic venous disease. N. Engl. J. Med. 355:488–498, 2006.
Bharat, A., M. Jaenicke, and S. Shenoy. A novel technique of vascular anastomosis to prevent juxta-anastomotic stenosis following arteriovenous fistula creation. J. Vasc. Surg. 55:274–280, 2012.
Boon, R. A., T. A. Leyen, R. D. Fontijn, J. O. Fledderus, J. M. C. Baggen, O. L. Volger, et al. KLF2-induced actin shear fibers control both alignment to flow and JNK signaling in vascular endothelium. Blood 115:2533–2542, 2010.
Bozzetto, M., B. Ene-Iordache, A. Remuzzi. Transitional flow in the venous side of patient-specific arteriovenous fistulae for hemodialysis. Ann. Biomed. Eng. 2015.
Bozzetto, M., S. Rota, V. Vigo, F. Casucci, C. Lomonte, W. Morale, et al. Clinical use of computational modeling for surgical planning of arteriovenous fistula for hemodialysis. BMC Med. Inform. Decis. Mak. 17:26, 2017.
Brahmbhatt, A., A. Remuzzi, M. Franzoni, and S. Misra. The molecular mechanisms of hemodialysis vascular access failure. Kidney Int. 89:303–316, 2016.
Browne, L. D., P. Griffin, K. Bashar, S. R. Walsh, E. G. Kavanagh, and M. T. Walsh. In vivo validation of the in silico predicted pressure drop across an arteriovenous fistula. Ann. Biomed. Eng. 43:1275–1286, 2015.
Browne, L. D., M. T. Walsh, and P. Griffin. Experimental and numerical analysis of the bulk flow parameters within an arteriovenous fistula. Cardiovasc. Eng. Technol. 6:450–462, 2015.
Caroli, A., S. Manini, L. Antiga, K. Passera, B. Ene-Iordache, S. Rota, et al. Validation of a patient-specific hemodynamic computational model for surgical planning of vascular access in hemodialysis patients. Kidney Int 84:1237–1245, 2013.
Chemla, E., C. C. Velazquez, F. D’Abate, V. Ramachandran, and G. Maytham. Arteriovenous fistula construction with the VasQ external support device: a pilot study. J. Vasc. Access. 17:243–248, 2016.
Dai, G., M. R. Kaazempur-Mofrad, S. Natarajan, Y. Zhang, S. Vaughn, B. R. Blackman, et al. Distinct endothelial phenotypes evoked by arterial waveforms derived from atherosclerosis-susceptible and -resistant regions of human vasculature. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 101:14871–14876, 2004.
Dammers, R., J. H. M. Tordoir, J. P. Kooman, R. J. T. J. Welten, J. M. M. Hameleers, P. J. E. H. M. Kitslaar, et al. The effect of flow changes on the arterial system proximal to an arteriovenous fistula for hemodialysis. Ultrasound Med. Biol. 31:1327–1333, 2005.
Dember, L. M., P. B. Imrey, G. J. Beck, A. K. Cheung, J. Himmelfarb, T. S. Huber, et al. Objectives and design of the hemodialysis fistula maturation study. Am. J. Kidney Dis. 63:104–112, 2014.
Ene-Iordache, B., L. Cattaneo, G. Dubini, and A. Remuzzi. Effect of anastomosis angle on the localization of disturbed flow in “side-to-end” fistulae for haemodialysis access. Nephrol. Dial. Transplant. 28:997–1005, 2013.
Ene-Iordache, B., L. Mosconi, L. Antiga, S. Bruno, A. Anghileri, G. Remuzzi, et al. Radial artery remodeling in response to shear stress increase within arteriovenous fistula for hemodialysis access. Endothel. J. Endothel. Cell Res. 10:95–102, 2003.
Ene-Iordache, B., and A. Remuzzi. Disturbed flow in radial-cephalic arteriovenous fistulae for haemodialysis: low and oscillating shear stress locates the sites of stenosis. Nephrol. Dial. Transplant. 27:358–368, 2012.
Ene-Iordache, B., C. Semperboni, G. Dubini, and A. Remuzzi. Disturbed flow in a patient-specific arteriovenous fistula for hemodialysis: multidirectional and reciprocating near-wall flow patterns. J. Biomech. 48:2195–2200, 2015. doi:10.1016/j.jbiomech.2015.04.013.
Franzoni, M., I. Cattaneo, L. Longaretti, M. Figliuzzi, B. Ene-Iordache, and A. Remuzzi. Endothelial cell activation by hemodynamic shear stress derived from arteriovenous fistula for hemodialysis access. Am. J. Physiol. Heart Circ. Physiol. 310:H49–H59, 2016.
Franzoni, M., I. Cattaneo, B. Ene-Iordache, A. Oldani, P. Righettini, A. Remuzzi. Design of a cone-and-plate device for controlled realistic shear stress stimulation on endothelial cell monolayers. Cytotechnology 2016.
Gimbrone, M. A. J., and G. Garcia-Cardena. Endothelial Cell Dysfunction and the Pathobiology of Atherosclerosis. Circ Res 118:620–636, 2016.
Hahn, C., and M. A. Schwartz. Mechanotransduction in vascular physiology and atherogenesis. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 10:53–62, 2009.
Hayashi, K., and T. Naiki. Adaptation and remodeling of vascular wall; biomechanical response to hypertension. J. Mech. Behav. Biomed. Mater. 2:3–19, 2009.
Huberts, W., A. S. Bode, W. Kroon, R. N. Planken, J. H. M. Tordoir, F. N. van de Vosse, et al. A pulse wave propagation model to support decision-making in vascular access planning in the clinic. Med. Eng. Phys. 34:233–248, 2012.
Koo, A., C. F. J. Dewey, and G. Garcia-Cardena. Hemodynamic shear stress characteristic of atherosclerosis-resistant regions promotes glycocalyx formation in cultured endothelial cells. Am. J. Physiol. Cell Physiol. 304:C137–C146, 2013.
Lee, T., and S. Misra. New insights into dialysis vascular access: molecular targets in arteriovenous fistula and arteriovenous graft failure and their potential to improve vascular access outcomes. CJASN 11:1504–1512, 2016.
Liyanage, T., T. Ninomiya, V. Jha, B. Neal, H. M. Patrice, I. Okpechi, et al. Worldwide access to treatment for end-stage kidney disease: a systematic review. Lancet Lond. Engl. 385:1975–1982, 2015.
Manini, S., L. Antiga, L. Botti, and A. Remuzzi. pyNS: an open-source framework for 0D haemodynamic modelling. Ann. Biomed. Eng. 43:1461–1473, 2015.
Manini, S., K. Passera, W. Huberts, L. Botti, L. Antiga, and A. Remuzzi. Computational model for simulation of vascular adaptation following vascular access surgery in haemodialysis patients. Comput. Methods Biomech. Biomed. Eng. 17:1358–1367, 2014.
National Kideny Foundation K/DOQI clinical practice guidelines for vascular access. Am. J. Kidney Dis. 2006; S176–273.
National Kidney Foundation. K/DOQI Guidelines – Updates 2006, 2014.
Nikam, M., E. S. Chemla, J. Evans, A. Summers, P. Brenchley, A. Tavakoli, et al. Prospective controlled pilot study of arteriovenous fistula placement using the novel Optiflow device. vol. 61, 2015.
Noris, M., M. Morigi, R. Donadelli, S. Aiello, M. Foppolo, M. Todeschini, et al. Nitric oxide synthesis by cultured endothelial cells is modulated by flow conditions. Circ. Res. 76:536–543, 1995.
Novodvorsky, P., and T. J. A. Chico. The role of the transcription factor KLF2 in vascular development and disease. Prog. Mol. Biol. Transl. Sci. 124:155–188, 2014.
Ochsner, A. J., R. J. Colp, and G. E. Burch. Normal blood pressure in the superficial venous system of man at rest in the supine position. Circulation 3:674–680, 1951.
Papaioannou, T. G., and C. Stefanadis. Vascular wall shear stress: basic principles and methods. Hell. J. Cardiol. 46:9–15, 2005.
Passera, K., S. Manini, L. Antiga, and A. Remuzzi. Patient-specific model of arterial circulation for surgical planning of vascular access. J. Vasc. Access. 14:180–192, 2013.
Pries, A. R., and T. W. Secomb. Control of blood vessel structure: insights from theoretical models. Am. J. Physiol. Heart Circ. Physiol. 288:H1010–H1015, 2005.
Remuzzi, A., C. F. J. Dewey, P. F. Davies, and M. A. J. Gimbrone. Orientation of endothelial cells in shear fields in vitro. Biorheology 21:617–630, 1984.
Robbin, M. L., N. E. Chamberlain, M. E. Lockhart, M. H. Gallichio, C. J. Young, M. H. Deierhoi, et al. Hemodialysis arteriovenous fistula maturity: US evaluation. Radiology 225:59–64, 2002.
Roy-Chaudhury, P., L. Arend, J. Zhang, M. Krishnamoorthy, Y. Wang, R. Banerjee, et al. Neointimal hyperplasia in early arteriovenous fistula failure. Am. J. Kidney Dis. Off. J. Natl. Kidney Found. 50:782–790, 2007.
Roy-Chaudhury, P., Y. Wang, M. Krishnamoorthy, J. Zhang, R. Banerjee, R. Munda, et al. Cellular phenotypes in human stenotic lesions from haemodialysis vascular access. Nephrol. Dial. Transplant. 24:2786–2791, 2009.
Singh, P., M. L. Robbin, M. E. Lockhart, and M. Allon. Clinically immature arteriovenous hemodialysis fistulas: effect of US on salvage. Radiology 246:299–305, 2008.
Srivastava, A., V. Mittal, H. Lal, T. Javali, N. Patidar, S. Sureka, et al. Spiral laminar flow, the earliest predictor for maturation of arteriovenous fistula for hemodialysis access. Indian J. Urol. 31:240–244, 2015.
Tsamis, A., N. Stergiopulos, and A. Rachev. A structure-based model of arterial remodeling in response to sustained hypertension. J. Biomech. Eng. 131:101004, 2009.
Van Canneyt, K., T. Pourchez, S. Eloot, C. Guillame, A. Bonnet, P. Segers, et al. Hemodynamic impact of anastomosis size and angle in side-to-end arteriovenous fistulae: a computer analysis. J. Vasc. Access. 11:52–58, 2010.
Yamamoto, K., C. D. Protack, G. Kuwahara, M. Tsuneki, T. Hashimoto, M. R. Hall, et al. Disturbed shear stress reduces Klf2 expression in arterial-venous fistulae in vivo. Physiol. Rep. 2015;3:e12348.
Conflict of Interest
AR and MB declare that that they have no conflict of interests regarding this contribution.
Ethical approval
This article does not contain any studies with human participants or animals performed by any of the authors.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Associate Editors James E. Moore, Jr. and Ajit P. Yoganathan oversaw the review of this article.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Remuzzi, A., Bozzetto, M. Biological and Physical Factors Involved in the Maturation of Arteriovenous Fistula for Hemodialysis. Cardiovasc Eng Tech 8, 273–279 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13239-017-0323-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13239-017-0323-0