Abstract
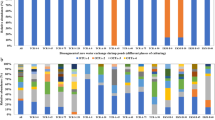
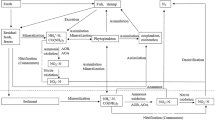
An annual investigation into the abundance of ammonia-oxidizing archaea (AOA) and ammonia-oxidizing bacteria (AOB) in fresh water aquaculture ponds was performed by quantitative PCR of the amoA gene. The results showed that AOB were the main ammonia-oxidizing microorganisms in water, and significantly higher copy numbers of the AOB amoA gene were observed in the summer (Aug 2012), while no significant differences were detected among the other three seasons. AOA showed low abundances throughout the year. The predominance of AOB in aquaculture water was suggested to be related to photoinhibition. Both the AOB and AOA amoA genes in aquaculture pond sediments showed typical seasonal patterns. The maximum density of AOB was observed in the autumn (Nov 2012) and winter (Jan 2013), while the maximum density of AOA was observed in winter. The minimum densities of both AOA and AOB occurred in the summer. The concentration of the AOA amoA gene was higher than that of the AOB amoA gene in sediments by almost one order of magnitude, which indicates that AOA are the dominant ammonia-oxidizing microorganisms in the aquaculture pond sediments. Dissolved oxygen is suggested to be the key factor determining the predominance of AOA in pond sediments.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ackefors H, Enell M (1994) The release of nutrients and organic matter from aquaculture systems in Nordic countries. J Appl Ichthyol 10:225–241
Ando Y, Nakagawa T, Takahashi R, Yoshihara K, Tokuyama T (2009) Seasonal changes in abundance of ammonia-oxidizing archaea and ammonia-oxidizing bacteria and their nitrification in sand of an eelgrass zone. Microbes Environ 24:21–27
Auguet J-C, Nomokonova N, Camarero L, Casamayor EO (2011) Seasonal changes of freshwater ammonia-oxidizing archaeal assemblages and nitrogen species in oligotrophic alpine lakes. Appl Environ Microbiol 77:1937–1945
Bernhard AE, Tucker J, Giblin AE, Stahl DA (2007) Functionally distinct communities of ammonia-oxidizing bacteria along an estuarine salinity gradient. Environ Microbiol 9:1439–1447
Bouskill NJ, Eveillard D, Chien D, Jayakumar A, Ward BB (2012) Environmental factors determining ammonia-oxidizing organism distribution and diversity in marine environments. Environ Microbiol 14:714–729
Caffrey JM, Bano N, Kalanetra K, Hollibaugh JT (2007) Ammonia oxidation and ammonia-oxidizing bacteria and archaea from estuaries with differing histories of hypoxia. ISME J 1:660–662
Chang WYB, Ouyang H (1988) Dynamics of dissolved oxygen and vertical circulation in fish ponds. Aquaculture 74:263–276
Church MJ, Wai B, Karl DM, DeLong EF (2010) Abundances of crenarchaeal amoA genes and transcripts in the Pacific Ocean. Environ Microbiol 12:679–688
Coolen MJL, Abbas B, Bleijswijk JV, Hopmans EC, Kuypers MMM, Wakeham SG, Damsté JSS (2007) Putative ammonia-oxidizing Crenarchaeota in suboxic waters of the Black Sea: a basin-wide ecological study using 16S ribosomal and functional genes and membrane lipids. Environ Microbiol 9:1001–1016
Editorial Board of Monitoring and Analytical Method of Water and Wastewater, State Environmental Protection Administration of China (2002) Monitoring and analytical method of water and wastewater, 4th edn (in Chinese). China Environmental Science Press, Beijing
FAO (2012) The state of world fisheries and aquaculture 2012. Food and Agricultural Organization of the United Nations, Rome, pp 3–4
French E, Kozlowski JA, Mukherjee M, Bullerjahn G, Bollmann A (2012) Ecophysiological characterization of ammonia-oxidizing archaea and bacteria from freshwater. Appl Environ Microbiol 78:5773–5780
Handy RD, Poxton MG (1993) Nitrogen pollution in mariculture: toxicity and excretion of nitrogenous compounds by marine fish. Rev Fish Biol Fish 3:205–241
Hatzenpichler R, Lebedeva EV, Spieck E, Stoecker K, Richter A, Daims H, Wagner M (2008) A moderately thermophilic ammonia-oxidizing crenarchaeote from a hot spring. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 105:2134–2139
He J-Z, Shen J-P, Zhang L-M, Zhu Y-G, Zheng Y-M, Xu M-G, Di HJ (2007) Quantitative analyses of the abundance and composition of ammonia-oxidizing bacteria and ammonia-oxidizing archaea of a Chinese upland red soil under long-term fertilization practices. Environ Microbiol 9:2364–2374
Horak REA, Qin W, Schauer AJ, Armbrust EV, Ingalls AE, Moffett JW, Devol AH (2013) Ammonia oxidation kinetics and temperature sensitivity of a natural marine community dominated by Archaea. ISME J 7:2023–2033
Hugoni M, Etien S, Bourges A, Lepere C, Domaizon I, Mallet C, Bronner G, Debroas D, Mary I (2013) Dynamics of ammonia-oxidizing Archaea and Bacteria in contrasted freshwater ecosystems. Res Microbiol 164:360–370
Koops H-P, Pommerening-Röser A (2001) Distribution and ecophysiology of the nitrifying bacteria emphasizing cultured species. FEMS Microbiol Ecol 37:1–9
Kowalchuk GA, Stephen JR (2001) Ammonia-oxidizing bacteria: a model for molecular microbial ecology. Annu Rev Microbiol 55:485–529
Leininger S, Urich T, Schloter M, Schwark L, Qi J, Nicol GW, Prosser JI, Schuster SC, Schleper C (2006) Archaea predominate among ammonia-oxidizing prokaryotes in soils. Nature 442:806–809
Lu SM, Liao MJ, Zhang M, Qi PZ, Xie CC, He XG (2012) A rapid DNA extraction method for quantitative real-time PCR amplification from fresh water sediment. J Food Agric Environ 10:1252–1255
Merbt SN, Stahl DA, Casamayor EO, Marti E, Nicol GW, Prosser JI (2012) Differential photoinhibition of bacterial and archaeal ammonia oxidation. FEMS Microbiol Lett 327:41–46
Molina V, Belmar L, Ulloa O (2010) High diversity of ammonia-oxidizing archaea in permanent and seasonal oxygen-deficient waters of the eastern South Pacific. Environ Microbiol 12:2450–2465
Pester M, Schleper C, Wagner M (2011) The Thaumarchaeota: an emerging view of their phylogeny and ecophysiology. Curr Opin Microbiol 14:300–306
Radax R, Hoffmann F, Rapp HT, Leininger S, Schleper C (2012) Ammonia-oxidizing archaea as main drivers of nitrification in cold-water sponges. Environ Microbiol 14:909–923
Randall DJ, Tsui TKN (2002) Ammonia toxicity in fish. Mar Pollut Bull 45:17–23
Rotthauwe JH, Witzel KP, Liesack W (1997) The ammonia monooxygenase structural gene amoA as a functional marker: molecular fine-scale analysis of natural ammonia-oxidizing populations. Appl Environ Microbiol 63:4704–4712
Sims A, Gajaraj S, Hu ZQ (2012a) Seasonal population changes of ammonia-oxidizing organisms and their relationship to water quality in a constructed wetland. Ecol Eng 40:100–107
Sims A, Horton J, Gajaraj S, McIntosh S, Miles RJ, Mueller R, Reed R, Hu ZQ (2012b) Temporal and spatial distributions of ammonia-oxidizing archaea and bacteria and their ratio as an indicator of oligotrophic conditions in natural wetlands. Water Res 46:4121–4129
Stahl DA, de la Torre JR (2012) Physiology and diversity of ammonia-oxidizing archaea. Annu Rev Microbiol 66:83–101
Tourna M, Freitag TE, Nicol GW, Prosser JI (2008) Growth, activity and temperature responses of ammonia-oxidizing archaea and bacteria in soil microcosms. Environ Microbiol 10:1357–1364
Wang ZC, Zuo M, Wang YC, Liu YD, Li DH (2011) Dynamics of chlorophyll fluorescence and eco-morphological properties of Microcystis bloom in Meiliang Bay of Lake Taihu, China. Fresenius Environ Bull 20:2295–2305
Wang Y-F, Feng Y-Y, Ma XJ, Gu J-D (2013) Seasonal dynamics of ammonia/ammonium-oxidizing prokaryotes in oxic and anoxic wetland sediments of subtropical coastal mangrove. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 97:7919–7934
Wu YC, Xiang Y, Wang JJ, Zhong JC, He JZ, Wu QL (2010) Heterogeneity of archaeal and bacterial ammonia-oxidizing communities in Lake Taihu, China. Environ Microbiol Rep 2:569–576
Wuchter C, Abbas B, Coolen MJL, Herfort L, van Bleijswijk J, Timmers P, Strous M, Teira E, Herndl GJ, Middelburg JJ, Schouten S, Damste JSS (2006) Archaeal nitrification in the ocean. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 103:12317–12322
Ye WJ, Liu XL, Lin SQ, Tan J, Pan JL, Li DT, Yang H (2009) The vertical distribution of bacterial and archaeal communities in the water and sediment of Lake Taihu. FEMS Microbiol Ecol 70:263–276
Zhou J, Bruns MA, Tiedje JM (1996) DNA recovery from soils of diverse composition. Appl Environ Microbiol 62:316–322
Acknowledgments
This study was supported financially by the Special Fund for National Technology System for Conventional Freshwater Industries (No. nycytx-49-09), Agro-scientific Research in the Public Interest Project (No. 201203083), and National Key Technology R&D Program (2012BAD25B01). We also thank Prof. Liu Zuo-xiong for reading the manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Shimin Lu and Mingjun Liao contributed equally to this work.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lu, S., Liao, M., Xie, C. et al. Seasonal dynamics of ammonia-oxidizing microorganisms in freshwater aquaculture ponds. Ann Microbiol 65, 651–657 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13213-014-0903-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13213-014-0903-2