Abstract
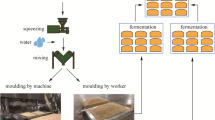
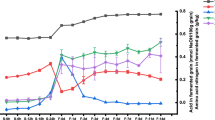
Bacillus is a common bacterial genus in Chinese traditional sun-brewed moromi. Some Bacillus species can metabolize sauce flavour and aroma substances. To address the insufficiency of flavour microbes in soy sauce fermentation, we used 16S rDNA sequence analysis to identify the CS1.03 strain, which was isolated from moromi produced through the traditional and natural sun brewing methods. A Box–Behnken design was used to optimize the addition technology of CS1.03, and ammoniacal nitrogen content and sensory evaluation were adopted as determination indices. GC–MS analysis was also performed to analyse the flavour components. Results identified CS1.03 as Bacillus subtilis. The optimal conditions yielded 10.7 g/L ammoniacal nitrogen in fermented soy sauce with rich aroma and flavour, and a sensory evaluation score of 90.5. GC–MS analysis revealed that the contents of phenol, aldehyde and ketone are all increased. These results demonstrated that CS1.03 could improve the flavour of soy sauce and shows good potential for application in soy sauce fermentation.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bao QA (2011) Science and brewing technology of soy sauce. China Light Industry Press, Beijing
Devanthi PVP, Linforth R, Onyeaka H, Gkatzionis K (2018) Effects of co-inoculation and sequential inoculation of Tetragenococcus halophilus and Zygosaccharomyces rouxii on soy sauce fermentation. Food Chem 240:1–8. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodchem.2017.07.094
Feng XJ, Wu HQ, Huang XL, Li L, Gao YM (2009) Comparison of substances in natural fermented soy sauce and blended soy sauce by GC–MS discriminant analysis. J Instrum Anal 28:66l–665
Feng J, Zhan XB, Wang D, Zhang LM, Lin CC (2012a) Identification and analysis of the metabolic functions of a high-salt-tolerant halophilic aromatic yeast Candida etchellsii for soy sauce production. World J Microbiol Biotechnol 28:1451–1458. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11274-011-0945-6
Feng J, Zhan XB, Zheng ZY, Wang D, Zhang LM, Lin CC (2012b) A two-step inoculation of Candida etchellsii to enhance soy sauce flavour and quality. Int J Food Sci Technol 47:2072–2078. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-2621.2012.03071.x
Feng YZ, Su GW, Zhao HF, Cai Y, Cui C, Sun-Waterhouse DX, Zhao MM (2015) Characterisation of aroma profiles of commercial soy sauce by odour activity value and omission test. Food Chem 167:220–228. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodchem.2014.06.057
Harada R, Yuzuki M, Ito K, Shiga K, Bamba T, Fukusaki E (2017) Influence of yeast and lactic acid bacterium on the constituent profile of soy sauce during fermentation. J Biosci Bioeng 123:203–208. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jbiosc.2016.08.010
Jiang XW, Zhou ST, Ye J, Xu YQ, Chen S, Wu C (2016) Identification of contamination microbes separated from finished deterioration sauce and the analysis of the deterioration reason. Food Mach 32:46–50
Kim HW, Hwang KE, Song DH, Kim YJ, Ham YK, Yeo EJ, Jeong TJ, Choi YS, Kim CJ (2015) Effect of soy sauce type on the quality characteristics of emulsion sausages. Food Sci Biotechnol 24:1309–1315. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10068-015-0168-y
Kim KM, Lim J, Lee JJ, Hurh BS, Lee I (2017) Characterization of Aspergillus sojae isolated from Meju, Korean traditional fermented soybean brick. J Microbiol Biotechnol 27:251–261
Lee SM, Seo BC, Kim YS (2006) Volatile compounds in fermented and acid-hydrolyzed soy sauces. Food Chem Toxicol 71:146–156
Li ZM, Chen L, Bai ZH, Wang DL, Gao LP, Hui BD (2015) Cultivable bacterial diversity and amylase production in two typical light-flavor Daqus of Chinese spirits. Front Life Sci 8:264–270
Liu RQ (2004) Sensory evaluation of soy sauce. China Condiment 29:39–40
Liu JJ, Li DS, Hu Y, Wang C, Gao B, Xu N (2015) Effect of a halophilic aromatic yeast together with Aspergillus oryzae in koji making on the volatile compounds and quality of soy sauce moromi. Int J Food Sci Technol 50:1352–1358. https://doi.org/10.1111/ijfs.12789
Masuda S, Yamaguchi H, Kurokawa T, Shirakami T, Tsuji RF, Nishimura I (2008) Immunomodulatory effect of halophilic lactic acid bacterium Tetragenococcus halophilus Th221 from soy sauce moromi grown in high-salt medium. Int J Food Microbiol 121:245–252. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijfoodmicro.2007.10.011
Meng Q, Hatakeyama M, Sugawara E (2014) Formation by yeast of 2-furanmethanethiol and ethyl 2-mercaptopropionate aroma compounds in Japanese soy sauce. Biosci Biotechnol Biochem 78:109–114
Meng Q, Imamura M, Katayama H, Obata A, Sugawara E (2017) Key compounds contributing to the fruity aroma characterization in Japanese raw soy sauce. Biosci Biotechnol Biochem 81:1–6
Qi CC, Wang M, Shen AB (2016) The impact of adding salt-tolerant lactic acid bacteria on the flavor of high-salt liquid soy sauce. China Condiment 41:102–105
Seo JS, Chang HG, Ji WD, Lee EJ, Choi MR, Kim HJ, Kim JK (1996) Aroma components of traditional Korean soy sauce and soybean paste fermented with the same meju. J Microbiol Biotechnol 6:278–285
Shu K, Kenji U, Osamu I (2013) Studies on the key aroma compounds in raw (unheated) and heated Japanese soy sauce. J Agric Food Chem 61:3396–3402. https://doi.org/10.1021/jf400353h
Shukla S, Kim M (2016) Determination of biogenic amines and total aflatoxins: quality index of starter culture soy sauce samples. Food Sci Biotechnol 25:1221–1224. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10068-016-0194-4
Song YR, Jeong DY, Baik SH (2015) Effects of indigenous yeasts on physicochemical and microbial properties of Korean soy sauce prepared by low-salt fermentation. Food Microbiol 51:8
Wah TT, Walaisri S, Assavanig A, Niamsiri N, Lertsiri S (2013) Co-culturing of Pichia guilliermondii enhanced volatile flavor compound formation by Zygosaccharomyces rouxii in the model system of Thai soy sauce fermentation. Int J Food Microbiol 160:282–289. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijfoodmicro.2012.10.022
Wu MC (2002) Food analysis and sensory evaluation. China Agricultural Press, Beijing
Xu Y, Wang D, Fan WL, Mu XQ, Chen J (2010) Traditional Chinese biotechnology. Adv Biochem Eng/Biotechnol 122:189–233
Xu N, Liu YQ, Hu Y, Zhou MZ, Wang C, Li DS (2016) Autolysis of Aspergillus oryzae mycelium and effect on volatile flavor compounds of soy sauce. J Food Sci 81:C1883–C1890. https://doi.org/10.1111/1750-3841.13396
Yang F, Wang HY, Yao CP, Lin L, Wang L, Lv YH, Ji KL (2010) The difference & the similarities in metabolites of Bacillus subtilis strains by different techniques. Liquor-Making Sci Technol 31:104–106
Yang F, Lin L, Wang HY, Wang L, Yang DY, Lv YH, Ji KL (2011) Comparative analysis of the metabolites of three Bacillus strains in Maotai Daqu starter. Liquor-Making Sci Technol 8:42–46
Yang Z, Yang HL, Yao H, Zhou XW, Tang SZ, Wu XY (2017) Gene sequencing and traditional microbial culture for the detection of aerogen in swelled packing soy sauce. Food Ferment Ind 11:197–201
Yao CP, Wang HY, Yang F, Lin L, Wang L (2010) Optimization of liquid culture conditions for Bacillus subtilis and analysis of its metabolites. Liquor-Making Sci Technol 194:43–45
Zhang HZ, Jiang YJ, Chen M, Hong WY, Zhang JP (2009) The effect of spraying-extraction fermentation on soy sauce flavor. China Condiment 34:91–94
Zhang JR, Du GC, Chen J, Fang F (2016) Characterization of a Bacillus amyloliquefaciens strain for reduction of citrulline accumulation during soy sauce fermentation. Biotech Lett 38:1723–1731
Zhao GZ, Yao YP, Wang XH, Hou LH, Wang CL, Cao XH (2013) Functional properties of soy sauce and metabolism genes of strains for fermentation. Int J Food Sci Technol 48:903–909
Zhu LX, Cai X (2014) Application of natural drying method in improving the flavor of low-salt solid soy sauce. China Condiment 39:78–81
Zhu ZX, Wu HQ, Huang XL (2007) Identification of volatile compounds in soy sauce. Food Res Dev 28:135–138
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by Hunan Provincial Natural Science Foundation of China, analysis of brewing microorganism and construction of dominant flora in soy sauce with high-salt liquid state technology (No. 2018JJ2421) and the Foundation Project of Changsha Science and Technology Program, research and demonstration of key technology in soy sauce production with multi-strain fermentation (No. kq1601013). There are no copyright disputes. We thank Liwen Bianji, Edanz Group China (www.liwenbianji.cn/ac), for editing the English text of a draft of this manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The author declares that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
The strain of CS1.03 has been collected in China Center for Type Culture Collection (CCTCC, Wuhan University, Wuhan City, China), and its collection number is M 2015791.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Jiang, X., Xu, Y., Ye, J. et al. Isolation, identification and application on soy sauce fermentation flavor bacteria of CS1.03. J Food Sci Technol 56, 2016–2026 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13197-019-03678-w
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13197-019-03678-w