Abstract
Objectives
To reduce the amount of citrulline produced by arginine-consuming bacteria in the moromi mash during soy sauce production.
Results
Bacillus amyloliquefaciens JY06, a salt-tolerant strain with high arginine consumption ability and low citrulline accumulation capacity, was isolated from moromi mash. The concentration of citrulline was decreased from 26.8 to 5.1 mM and ethyl carbamate in soy sauce, after sterilization, decreased from 97 to 17 μg kg−1 when B. amyloliquefaciens JY06 was added during fermentation. The aroma of the sauce was improved by increasing the ester content.
Conclusions
B. amyloliquefaciens JY06 is a beneficial bacterium that can be used in soy sauce fermentation to eliminate ethyl carbonate and enhance the flavor of the sauce.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bemis JC, Labash C, Avlasevich SL et al (2015) Rat Pig-a mutation assay responds to the genotoxic carcinogen ethyl carbamate but not the non-genotoxic carcinogen methyl carbamate. Mutagenesis 30:343–347
Cui R-Y, Zheng J, Wu C-D et al (2014) Effect of different halophilic microbial fermentation patterns on the volatile compound profiles and sensory properties of soy sauce moromi. Eur Food Res Technol 239:321–331
de Orduña RM, Liu S-Q, Patchett M et al (2000) Ethyl carbamate precursor citrulline formation from arginine degradation by malolactic wine lactic acid bacteria. FEMS Microbiol Lett 183:31–35
Feng J, Zhan X-B, Zheng Z-Y et al (2013) New model for flavour quality evaluation of soy sauce. Czech J Food Sci 31:292–305
Hong Y, Jung H-J, Kim H-Y (2012) Aroma characteristics of fermented Korean soybean paste (Doenjang) produced by Bacillus amyloliquefaciens. Food Sci Biotechnol 21:1163–1172
Jeong SY, Chung SJ, Suh DS et al (2004) Developing a descriptive analysis procedure for evaluating the sensory characteristics of soy sauce. J Food Sci 69:S319–S325
Kim S-H, Lee K-A (2003) Evaluation of taste compounds in water-soluble extract of a doenjang (soybean paste). Food Chem 83:339–342
Liu SQ, Pilone GJ (1998) A review: arginine metabolism in wine lactic acid bacteria and its practical significance. J Appl Microbiol 84:315–327
Matsudo T, Aoki T, Abe K et al (1993) Determination of ethyl carbamate in soy sauce and its possible precursor. J Agric Food Chem 41:352–356
Nam Y-D, Lee S-Y, Lim S-I (2012) Microbial community analysis of Korean soybean pastes by next-generation sequencing. Int J Food Microbiol 155:36–42
Priest F, Goodfellow M, Shute L et al (1987) Bacillus amyloliquefaciens sp. nov., nom. rev. Int J Syst Bacteriol 37:69–71
Rohban R, Amoozegar MA, Ventosa A (2009) Screening and isolation of halophilic bacteria producing extracellular hydrolyses from Howz Soltan Lake, Iran. J Ind Microbiol Biotechnol 36:333–340
Sakanaka A, Kuboniwa M, Takeuchi H et al (2015) Arginine-ornithine antiporter ArcD controls arginine metabolism and interspecies biofilm development of Streptococcus gordonii. J Biol Chem 290:21185–21198
Sürken M, Keller C, Röhker C et al (2008) Anaerobic arginine metabolism of Mycobacterium tuberculosis is mediated by arginine deiminase (arcA), but is not essential for chronic persistence in an aerogenic mouse model of infection. Int J Med Microbial 298:657–661
Vrancken G, Rimaux T, Weckx S et al (2009) Environmental pH determines citrulline and ornithine release through the arginine deiminase pathway in Lactobacillus fermentum IMDO 130101. Int J Food Microbiol 135:216–222
Weber JV, Sharypov VI (2009) Ethyl carbamate in foods and beverages-a review. In:Lichtfouse E (ed) Climate change, intercropping, pest control and beneficial microorganisms, vol 2. Springer, Netherlands, pp 429–452
Xue J, Fu F, Liang M et al (2015) Ethyl carbamate production kinetics during wine storage. S Afr J Enol Vitic 36:277–284
Zaman MZ, Bakar FA, Selamat J, Bakar J (2010) Occurrence of biogenic amines and amines degrading bacteria in fish sauce. Czech J Food Sci 28:440–449
Zhang J, Fang F, Chen J et al (2014) The arginine deiminase pathway of koji bacteria is involved in ethyl carbamate precursor production in soy sauce. FEMS Microbiol Lett 358:91–97
Zhao J, Dai X, Liu X et al (2011) Comparison of aroma compounds in naturally fermented and inoculated Chinese soybean pastes by GC-MS and GC-Olfactometry analysis. Food Control 22:1008–1013
Zhao X, Du G, Zou H et al (2013) Progress in preventing the accumulation of ethyl carbamate in alcoholic beverages. Trends Food Sci Tech 32:97–107
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (31371821) and the Technology Research Program of Guangdong, China (2015B020205002).
Supporting information
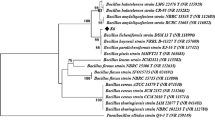
Supplementary Fig. 1—Identification of strain JY06 as Bacillus amyloliquefaciens by phylogenetic analysis based on 16S rDNA and partial arcA sequences.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, J., Du, G., Chen, J. et al. Characterization of a Bacillus amyloliquefaciens strain for reduction of citrulline accumulation during soy sauce fermentation. Biotechnol Lett 38, 1723–1731 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10529-016-2147-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10529-016-2147-7