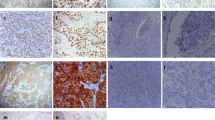
Abstract
Invasive breast carcinoma is the most common cancer among women worldwide. Increase in early detection of breast carcinoma by different diagnostic modalities led to decrease in cancer-related mortality and morbidity. Multiple factors and genes are implicated in breast cancer pathogenesis. Cyclin D1 is an important cell cycle regulatory protein involved in carcinogenesis of various human cancers including breast cancer. Aims of the present study were to evaluate the prognostic importance of cyclin D1 expression in invasive breast carcinoma and its correlation with other prognostic and predictive factors. Patients undergoing mastectomy for breast carcinoma were selected from January 2016 to June 2017 in a tertiary care hospital. Clinical history including demographic parameters was collected in the study pro forma. Immunohistochemical staining for ER, PgR, HER2 and cyclin D1 was performed on all cases. The clinicopathological parameters like age, tumour size, histologic grade, histological type, lymphovascular invasion, axillary lymph node metastasis, ER, PgR and HER2 status were compared and correlated with cyclin D1 expression. Cyclin D1 expression found in 60% cases of breast carcinoma. Expression of cyclin D1 showed a highly significant correlation with histological grade (p = 0.000). Cyclin D1 expression showed significant correlation (p = 0.000) with molecular subtypes. There was also significant correlation between cyclin D1 expression and ER (p = 0.000) and PgR (p = 0.010) status. This study revealed significant cyclin D1 expression in low grade, well-differentiated breast cancer. Therefore, we found cyclin D1 as a favourable prognostic marker in breast carcinoma.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ferlay J, Soerjomataram I, Dikshit R, Eser S, Mathers C, Rebelo M et al (2014) Cancer incidence and mortality worldwide: sources, methods and major patterns in GLOBOCAN 2012. Int J Cancer 136(5):E359–E386
Malvia S, Bagadi SA, Dubey US, Saxena S (2017) Epidemiology of breast cancer in Indian women. Asia Pac J Clin Oncol 13(4):289–295
Hoda SA (2014) Invasive ductal carcinoma: assessment of prognosis with morphologic and biologic markers. In: Rosen PP (ed) Rosen’s breast pathology, 4th edn. Lippincott Williams & Wilkins, Philadelphia, USA, p 413
Esteva FJ, Hortobagyi GN (2004) Prognostic molecular markers in early breast cancer. Breast Cancer Res 6(3):109–118
Sutherland RL, Musgrove EA (2002) Cyclin D1 and mammary carcinoma: new insights from transgenic mouse models. Breast Cancer Res 4(1):14–17
Abraham RT, Vanarsdale T, Shields DV, Lee NV, Koehler M, Arndt K (2014) Braking the cycle: inhibition of the cyclin D-Cdk4/6 pathway in breast cancer. Cancer Res 74(19 Supplement):SY34–SY03
Dickson MA (2014) Molecular pathways: CDK4 inhibitors for cancer therapy. Clin Cancer Res 20(13):3379–3383
Eeckhoute J (2006) A cell-type-specific transcriptional network required for estrogen regulation of cyclin D1 and cell cycle progression in breast cancer. Genes Dev 20(18):2513–2526
Arnold A, Papanikolaou A (2005) Cyclin D1 in breast cancer pathogenesis. J Clin Oncol 23(18):4215–4224
Peurala E, Koivunen P, Haapasaari K-M, Bloigu R, Jukkola-Vuorinen A (2013) The prognostic significance and value of cyclin D1, CDK4 and p16 in human breast cancer. Breast Cancer Res 15(1):R5
Goldhirsch A, Winer EP, Coates AS, Gelber RD, Piccart-Gebhart M, Thürlimann B et al (2013) Personalizing the treatment of women with early breast cancer: highlights of the St Gallen International Expert Consensus on the Primary Therapy of Early Breast Cancer 2013. Ann Oncol 24(9):2206–2223
Hammond M, Hayes D, Dowsett M, Allred D, Hagerty K, Badve S et al (2010) American Society of Clinical Oncology/College of American Pathologists guideline recommendations for immunohistochemical testing of estrogen and progesterone receptors in breast cancer (unabridged version). Arch Pathol Lab Med 134(7):48–72
Allred DC (2008) Problems and solutions in the evaluation of hormone receptors in breast cancer. J Clin Oncol 26(15):2433–2435
Wolff A, Hammond M, Hicks D, Dowsett M, McShane L, Allison K et al (2014) Recommendations for human epidermal growth factor receptor 2 testing in breast cancer: American Society of Clinical Oncology/College of American Pathologists Clinical Practice Guideline Update. Arch Pathol Lab Med 138(2):241–256
Reis-Filho JS, Savage K, Lambros MBK, James M, Steele D, Jones RL, Dowsett M (2006) Cyclin D1 protein overexpression and CCND1 amplification in breast carcinomas: an immunohistochemical and chromogenic in situ hybridisation analysis. Mod Pathol 19(7):999–1009
Khemka A, Chakrabarti N, Shah S, Patel V (2008) Palpable breast lumps: fine-needle aspiration cytology versus histopathology: a correlation of diagnostic accuracy. Int J Surg 18(1)
Ahmad Z, Khurshid A, Qureshi A, Idress R, Asghar N, Kayani N (2009) Breast carcinoma grading, estimation of tumor size, axillary lymph node status, staging, and Nottingham prognostic index scoring on mastectomy specimens. Indian J Pathol Microbiol 52(4):477–481
Makki J (2015) Diversity of breast carcinoma: histological subtypes and clinical relevance. Clin Med Insights Pathol 8:23–31
Ravikumar G, Ananthamurthy A (2014) Cyclin D1 expression in ductal carcinoma of the breast and its correlation with other prognostic parameters. J Can Res Ther 10(3):671–675
Rakha EA, Martin S, Lee AHS, Morgan D, Pharoah PDP, Hodi Z, Macmillan D, Ellis IO (2011) The prognostic significance of lymphovascular invasion in invasive breast carcinoma. Cancer 118(15):3670–3680
Kim M-J, Ro JY, Ahn S-H, Kim HH, Kim S-B, Gong G (2006) Clinicopathologic significance of the basal-like subtype of breast cancer: a comparison with hormone receptor and Her2/neu-overexpressing phenotypes. Hum Pathol 37(9):1217–1226
Mohammadizadeh F, Hani M, Ranaee M, Bagheri M (2013) J Res Med Sci 18(12):1021–1025
Sutherland RL, Musgrove EA (2004) Cyclins and breast cancer. J Mammary Gland Biol Neoplasia 9(1):95–104
Hwang TS, Han HS, Hong YC, Lee HJ, Paik N-S (2003) Prognostic value of combined analysis of cyclin D1 and estrogen receptor status in breast cancer patients. Pathol Int 53(2):74–80
Chung J, Noh H, Park KH, Choi E, Han A (2014) Longer survival in patients with breast cancer with cyclin D1 over-expression after tumor recurrence: longer, but occupied with disease. J Breast Cancer 17(1):47–53
El-Maqsoud NMRA, Moatasem M (2010) Significance of Cyclin D1 overexpression and amplification in ductal hyperplasia, carcinoma in situ and invasive carcinoma in Egyptian female breast. Int J Cancer Res 6:202–219
Guo L, Liu S, Jakulin A, Yilamu D, Wang B, Yan J (2015) Positive expression of cyclin D1 is an indicator for the evaluation of the prognosis of breast cancer. Int J Clin Exp Med 8(10):18656–18664
Huang W, Nie W, Zhang W, Wang Y, Zhu A, Guan X (2016) The expression status of TRX, AR, and cyclin D1 correlates with clinicopathological characteristics and ER status in breast cancer. Onco Targets Ther 9:4377–4385. https://doi.org/10.2147/OTT.S94703
Lee A, Park WC, Yim HW, Lee MA, Park G, Lee KY (2007) Expression of c-erbB2, cyclin D1 and estrogen receptor and their clinical implications in the invasive ductal carcinoma of the breast. Jpn J Clin Oncol 37:708–714
Umekita Y, Ohi Y, Sagara Y, Yoshida H (2002) Overexpression of cyclinD1 predicts for poor prognosis in estrogen receptor-negative breast cancer patients. Int J Cancer 98(3):415–418
Stendahl M, Kronblad Å, Rydén L, Emdin S, Bengtsson NO, Landberg G (2004) Cyclin D1 overexpression is a negative predictive factor for tamoxifen response in postmenopausal breast cancer patients. Br J Cancer 90(10):1942–1948
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Parvin, T., Das, C., Choudhury, M. et al. Prognostic Utility of Cyclin D1 in Invasive Breast Carcinoma. Indian J Surg Oncol 10, 167–173 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13193-018-0839-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13193-018-0839-2