Abstract
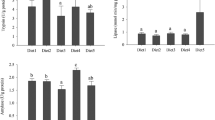
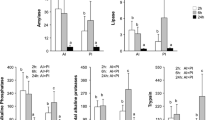
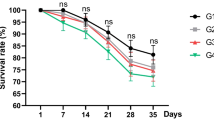
The rabbitfish Siganus canaliculatus is one of the few cultured herbivorous marine teleosts. To better understand the digestive physiology of this fish and provide data for designing formulated feed using macroalgae as an ingredient, the changes of visceral properties and digestive enzyme activities were investigated after the juveniles were fed on different types of food including raw fish (RF), formulated diet (FD) or macroalgae Enteromorpha prolifra (EP) and Gracilaria lemaneiformis (GL) for eight weeks. The results showed that the hepatosomatic and viscerosomatic indices in the RF and FD groups, as well as the relative intestine length (RIL) in the EP and GL groups, were significantly higher than those in other groups. Additionally, differences in the histological structure of the liver and anterior intestine were also observed among different dietary groups. The hepatic nuclei were displaced to the periphery by lipid inclusions in fish fed RF. The highest levels of mucosal folds were found in the anterior intestines of fish fed macroalgae. Digestive enzyme activity profiles showed obvious fluctuations in the first three weeks, and then leveled off in the following weeks. The levels of protease, lipase and α-amylase in the alimentary tract showed changes related to the levels of dietary protein, lipid and carbohydrate, respectively. Although macroalgae significantly inhibited the activity of protease in the stomach, it increased RIL and the number of mucosal folds in the anterior intestine so as to compensate for the influences on protease activities in the stomach. This study suggests that the digestive tract of rabbitfish can well adapt to different diets, and needs about three weeks to physiologically acclimatize to the nutritional status, thus implying that rabbitfish are somewhat omnivorous.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Araújo M, Rema P, Sousa-Pinto I, et al. 2015. Dietary inclusion of IMTA-cultivated Gracilaria vermiculophylla in rainbow trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss) diets: effects on growth, intestinal morphology, tissue pigmentation, and immunological response. J Appl Phycol, 28(1): 679–689, doi: 10.1007/s10811-015-0591-8
Brinker A, Reiter R. 2011. Fish meal replacement by plant protein substitution and guar gum addition in trout feed: Part I. effects on feed utilization and fish quality. Aquaculture, 310(3-4): 350–360
Calder P C. 2013. n?3 fatty acids, inflammation and immunity: new mechanisms to explain old actions Proc Nutr Soc, 72(3): 326–336
Campoy C, Escolano-Margarit M V, Anjos T, et al. 2012. Omega 3 fatty acids on child growth, visual acuity and neurodevelopment. Br J Nutr, 107(S2): S85–S106
Corrêa C F, de Aguiar L H, Lundstedt L M, et al. 2007. Responses of digestive enzymes of tambaqui (Colossoma macropomum) to dietary cornstarch changes and metabolic inferences. Comp Biochem Physiol Part A: Mol Integr Physiol, 147(4): 857–862
De Almeida L C, Lundstedt L M, Moraes G. 2006. Digestive enzyme responses of tambaqui (Colossoma macropomum) fed on different levels of protein and lipid. Aquac Nutr, 12(6): 443–450
de Oliveira M N, Freitas A L P, Carvalho A F U, et al. 2009. Nutritive and non-nutritive attributes of washed-up seaweeds from the coast of Ceará, Brazil. Food Chem, 115(1): 254–259
Deguara S, Jauncey K, Agius C. 2003. Enzyme activities and pH variations in the digestive tract of gilthead sea bream. J Fish Biol, 62(5): 1033–1043
Delgado-Lista J, Perez-Martinez P, Lopez-Miranda J, et al. 2012. Long chain omega-3 fatty acids and cardiovascular disease: a systematic review. Brit J Nutr, 107(S2): S201–S213
Du Y B, Li Y Y, Zhen Y J, et al. 2008. Toxic effects in Siganus oramin by dietary exposure to 4-tert-octylphenol. Bull Environ Contam Toxicol, 80(6): 534–538
FAO. 2014. The State of World Fisheries and Aquaculture 2014. Rome: Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations, 223
German D P. 2011. Digestive efficiency. In: Farrell A P, Cech J J, Richards J G, et al., eds. Encyclopedia of Fish Physiology, From Genome to Environment. San Diego: Elsevier, 1596–1607
Gangadhara B, Nandeesha M C, Varghese T J, et al. 1997. Effect of varying protein and lipid levels on the growth of rohu, Labeo rohita. Asian Fish Sci, 10: 139–147
Gawlicka A, Horn M H. 2006. Trypsin gene expression by quantitative in situ hybridization in carnivorous and herbivorous prickleback fishes (Teleostei: Stichaeidae): ontogenetic, dietary, and phylogenetic effects. Physiol Biochem Zool, 79(1): 120–132
German D P, Nagle B C, Villeda J M, et al. 2010. Evolution of herbivoryinacar nivorous clade of minnows (Teleostei: Cyprinidae): effects on gut size and digestive physiology. Physiol Biochem Zool, 83(1): 1–18
Güroy B, Ergün S, Merrifield D L, et al. 2013. Effect of autoclaved Ulva meal on growth performance, nutrient utilization and fatty acid profile of rainbow trout, Oncorhynchus mykiss. Aquacult Int, 21(3): 605–615
Guzman C, Gaxiola G, Rosa C, et al. 2001. The effect of dietary protein and total energy content on digestive enzyme activities, growth and survival of Litopenaeus setiferus (Linnaeus 1767) postlarvae. Aquacult Nutr, 7(2): 113–122
Hardy R W. 2010. Utilization of plant proteins in fish diets: effects of global demand and supplies of fishmeal. Aquac Res, 41(5): 770–776
Horie Y, Sugase K, Horie K. 1995. Physiological differences of soluble and insoluble dietary fibre fractions of brown algae and mushrooms in pepsin activity in vitro and protein digestibility. Asia Pac J Clin Nutr, 4(2): 251–255
Horn M H, Gawlicka A K, German D P, et al. 2006. Structure and function of the stomachless digestive system in three related species of New World silverside fishes (Atherinopsidae) representing herbivory, omnivory, and carnivory. Mar Biol, 149(5): 1237–1245
Hu Liang, Yun Biao, Xue Min, et al. 2013. Effects of fish meal quality and fish meal substitution by animal protein blend on growth performance, flesh quality and liver histology of Japanese seabass (Lateolabrax japonicus). Aquaculture, 372-375: 52–61
Karasov W H, Martínez del Rio C, Caviedes-Vidal E. 2011. Ecological physiology of diet and digestive systems. Annu Rev Physiol, 73: 69–93
Lev R, Spicer S S. 1964. Specific staining of sulphate groups with alcian blue at low pH. J Histochem Cytochem, 12: 309
Li Yuanyou, Hu Changbo, Zheng Yijun, et al. 2008. The effects of dietary fatty acids on liver fatty acid composition and Δ6-desaturase expression differ with ambient salinities in Siganus canaliculatus. Comp Biochem Physiol Part B: Biochem Mol Biol, 151(2): 183–190
Mohanta K N, Mohanty S N, Jena J K, et al. 2008a. Protein requirement of silver barb, Puntius gonionotus fingerlings. Aquacult Nutr, 14(2): 143–152
Mohanta K N, Mohanty S N, Jena J K, et al. 2008b. Optimal dietary lipid level of silver barb, Puntius gonionotus fingerlings in relation to growth, nutrient retention and digestibility, muscle nucleic acid content and digestive enzyme activity. Aquacult Nutr, 14(4): 350–359
Nakagawa H. 1997. Effect of dietary algae on improvement of lipid metabolism in fish. Biomed Pharmacother, 51(8): 345–348
Nakagawa H, Kasahara S, Sugiyama T. 1987. Effect of Ulva meal supplementation on lipid metabolism of black sea bream, Acanthopagrus schlegeli (Bleeker). Aquaculture, 62(2): 109–121
Pan Luqing, Wang Kexing. 1997. The experimental studies on activities of digestive enzyme in the larvae Penaeus chinensis. Journal of Fisheries of China (in Chinese), 21(1): 26–31
Parés-Sierra G, Durazo E, Ponce M A, et al. 2012. Partial to total replacement of fishmeal by poultry by-product meal in diets for juvenile rainbow trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss) and their effect on fatty acids from muscle tissue and the time required to retrieve the effect. Aquacult Res, 45(9): 1459–1469
Pérez-Jiménez A, Cardenete G, Morales A E, et al. 2009. Digestive enzymatic profile of Dentex dentex and response to different dietary formulations. Comp Biochem Physiol Part A: Mol Integr Physiol, 154(1): 157–164
Ricklefs R E. 1996. Morphometry of the digestive tracts of some Passerine birds. The Condor, 98(2): 279–292
Saito H, Yamashiro R, Alasalvar C, et al. 1999. Influence of diet on fatty acids of three subtropical fish, subfamily caesioninae (Caesio diagramma and C. tile) and family siganidae (Siganus canaliculatus). Lipids, 34(10): 1073–1082
Sarker M S A, Satoh S, Kamata K, et al. 2012. Partial replacement of fish meal with plant protein sources using organic acids to practical diets for juvenile yellowtail, Seriola quinqueradiata. Aquacult Nutr, 18(1): 81–89
Sibly R M. 1981. Strategies of digestion and defecation. In: Townsend C R, Calow P, eds. Physiological Ecology: An Evolutionary Approach to Resource Use. Oxford: Blackwell Scientific Publications, 109–139
Silva D M, Valente L M P, Sousa-Pinto I, et al. 2014. Evaluation of IMTA-produced seaweeds (Gracilaria, Porphyra, and Ulva) as dietary ingredients in Nile tilapia, Oreochromis niloticus L., juveniles. Effects on growth performance and gut histology. J Appl Phycol, 27(4): 1671–1680, doi: 10.1007/s10811-014-0453-9
Steedman H F. 1950. Alcian blue 8GS: a new stain for mucin. Q J Microsc Sci, 91(4): 477–479
Stevens C E, Hume I D. 1995. Comparative Physiology of the Vertebrate Digestive System. Cambridge, UK: Cambridge University Press
Tacon A G J, Hasan M R, Metian M. 2011. Demand and supply of feed ingredients for farmed fish and crustaceans. FAO fisheries and aquaculture technical paper no. 564. Rome: FAO
Tur J A, Bibiloni M M, Sureda A, et al. 2012. Dietary sources of omega 3 fatty acids: public health risks and benefits. Brit J Nutr, 107(S2): S23–S52
Valente L M P, Araújo M, Batista S, et al. 2015b. Carotenoid deposition, flesh quality and immunological response of Nile tilapia fed increasing levels of IMTA-cultivated Ulva spp. J Appl Phycol, 28(1): 691–701, doi: 10.1007/s10811-015-0590-9
Valente L M P, Rema P, Ferraro V, et al. 2015a. Iodine enrichment of rainbow trout flesh by dietary supplementation with the red seaweed Gracilaria vermiculophylla. Aquaculture, 446: 132–139
Vizcaíno A J, Mendes S I, Varela J L, et al. 2015. Growth, tissue metabolites and digestive functionality in Sparus aurata juveniles fed different levels of macroalgae, Gracilaria cornea and Ulva rigida. Aquacult Res, 47(10): 3224–3238, doi: 10.1111/are.12774
Wahbeh M I. 1997. Amino acid and fatty acid profiles of four species of macroalgae from Aqaba and their suitability for use in fish diets. Aquaculture, 159(1-2): 101–109
Wassef E A, El-Sayed A F M, Sakr E M. 2013. Pterocladia (Rhodophyta) and ulva (Chlorophyta) as feed supplements for European seabass, Dicentrarchus labrax L., fry. J Appl Phycol, 25(5): 1369–1376
Woodland D J. 1983. Zoogeography of the Siganidae (Pisces): an interpretation of distribution and richness patterns. Bull Mar Sci, 33: 713–717
Xu Shude, Liu Xuebing, Wang Shuqi, et al. 2014. Effects of different diets on growth performance and flesh protein and fatty acid composition in juvenile Siganus canaliculatus. Marine Fisheries (in Chinese), 36(6): 529–535
Xu Shude, Wang Shuqi, Zhang Liang, et al. 2012. Effects of replacement of dietary fish oil with soybean oil on growth performance and tissue fatty acid composition in marine herbivorous teleost Siganus canaliculatus. Aquacult Res, 43(9): 1276–1286
Xu Shude, Zhang Liang, Wu Qingyang, et al. 2011. Evaluation of dried seaweed Gracilaria lemaneiformis as an ingredient in diets for teleost fish Siganus canaliculatus. Aquacult Int, 19(5): 1007–1018
Xuan Xiongzhi, Wen Xiaobo, Li Shengkang, et al. 2013. Potential use of macro-algae Gracilaria lemaneiformis in diets for the black sea bream, Acanthopagrus schlegelii, juvenile. Aquaculture, 412-413: 167–172
Ye W, Han D, Zhu X, et al. 2015. Comparative studies on dietary protein requirements of juvenile and on-growing gibel carp (Carassius auratus gibelio) based on fishmeal-free diets. Aquacult Nutr, 21(3): 286–299
You Cuihong, Zeng Fangui, Wang Shuqi, et al. 2014. Preference of the herbivorous marine teleost Siganus canaliculatus for different macroalgae. J Ocean Univ China, 13(3): 516–522
Zhu Dashi, Wen Xiaobo, Xuan Xiongzhi, et al. 2015. The green alga Ulva lactuca as a potential ingredient in diets for juvenile white spotted snapper Lutjanus stellatus Akazaki. J Appl Phycol, 28(1): 703–711, doi: 10.1007/s10811-015-0545-1
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Foundation item: The Major International Joint Research Project from the National Natural Science Foundation of China (NSFC) under contract No. 31110103913; the NSFC Youth Project under contract No. 31602176; China Agriculture Research System under contract No. CARS-47.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Xie, D., Xu, S., Wu, Q. et al. Changes of visceral properties and digestive enzymes in the herbivorous marine teleost Siganus canaliculatus fed on different diets. Acta Oceanol. Sin. 37, 85–93 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13131-018-1165-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13131-018-1165-9