Abstract
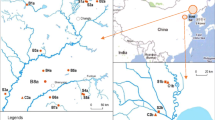
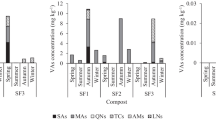
The occurrence and pollution characteristics of common antibiotics in manure, soil, and sewage sludge in Shenyang, the biggest city in northeastern China, were investigated. Commonly used antibiotics tetracyclines (TCs), including tetracycline, chlortetracycline, oxytetracycline, and deoxytetracycline; and sulfonamides (SAs), including sulfadiazine, sulfamerazine, sulfadimidine, and sulfamethoxazole, were measured by high-performance liquid chromatography–tandem mass spectrometry via solid-phase extraction. Multiple antibiotics could be simultaneously measured in a single manure sample. The highest concentration of antibiotics in manure was 143.97 mg kg−1 (chlortetracycline). There were no significant differences in concentrations of antibiotics between large-scale farms and individual household farms. The concentrations of TCs were significantly higher than those of SAs in manure and soils. However, the concentrations and detection frequencies of antibiotics in soils were significantly lower than in manure. The concentrations of antibiotics varied from 2.56 μg kg−1 of sulfadimidine to 1590.16 μg kg−1 of chlortetracycline, and the detection frequencies were 27.14–64.29 % for TCs and 5.71–28.57 % for SAs in soils. The concentrations of antibiotics in the vegetable field fertilized with manure were higher than those in the corn field not fertilized with manure. Various kinds of antibiotics were detected in sewage sludge, although concentrations were not high. Concentrations of antibiotics were higher in winter than in summer, The concentrations of antibiotics observed in this study were similar to those observed in other regions of China, but, in general, higher than those in other countries.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aga DS, O’Connor S, Ensley S, Payero JO, Snow D, Tarkalson D (2005) Determination of the persistence of tetracycline antibiotics and their degradates in manure-amended soil using enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay and liquid chromatography-mass spectrometry. J Agric Food Chem 53:7165–7171
Alcock RE, Sweetman A, Jones KC (1999) Assessment of organic contaminant fate in waste water treatment plants I: selected compounds and physicochemical properties. Chemosphere 38:2247–2262
Aust MO, Godlinski F, Travis GR, Hao X, McAllister TA, Leinweber P, Thiele-Bruhn S (2008) Distribution of sulfamethazine, chlortetracycline and tylosin in manure and soil of Canadian feedlots after subtherapeutic use in cattle. Environ Pollut 156:1243–1251
Avisar D, Primor O, Gozlan I, Mamane H (2010) Sorption of sulfonamides and tetracyclines to montmorillonite clay. Water Air Soil Pollut 209:439–450
Awad YM, Kim SC, Abd El-Azeem SAM, Kim KH, Kim KR, Kim K, Jeon C, Lee SS, Ok YS (2014) Veterinary antibiotics contamination in water, sediment, and soil near a swine manure composting facility. Environ Earth Sci 71:1433–1440
Bound JP, Voulvoulis N (2004) Pharmaceuticals in the aquatic environment—a comparison of risk assessment strategies. Chemosphere 56:1143–1155
Boxall ABA, Blackwell P, Cavallo R, Kay P, Tolls J (2002) The sorption and transport of a sulphonamide antibiotic in soil systems. Toxicol Lett 131:19–28
Brambilla G, Patrizii M, De Filippis SP, Bonazzi G, Mantovi P, Barchi D, Migliore L (2007) Oxytetracycline as environmental contaminant in arable lands. Anal Chim Acta 586:326–329
Chen K, Zhou JL (2014) Occurrence and behavior of antibiotics in water and sediments from the Huangpu River, Shanghai, China. Chemosphere 95:604–612
Chen Y, Zhang H, Luo Y, Song J (2012) Occurrence and assessment of veterinary antibiotics in swine manures: a case study in East China. Chin Sci Bull 57:606–614
Chen YS, Yu G, Cao QM, Zhang HB, Lin QY, Hong YW (2013) Occurrence and environmental implications of pharmaceuticals in Chinese municipal sewage sludge. Chemosphere 93:1765–1772
Cheng MM, Wu LH, Huang YJ, Luo YM, Christie P (2014) Total concentrations of heavy metals and occurrence of antibiotics in sewage sludges from cities throughout China. J Soils Sediments 14:1123–1135
Daughton CG, Ternes TA (1999) Pharmaceuticals and personal care products in the environment: agents of subtle change? Environ Health Perspect 107:907–938
Dong LX, Gao J, Xie XJ, Zhou QX (2012) DNA damage and biochemical toxicity of antibiotics in soil on the earthworm Eisenia fetida. Chemosphere 89:44–51
Gao LH, Shi YL, Li WH, Niu HY, Liu JM, Cai YQ (2012) Occurrence of antibiotics in eight sewage treatment plants in Beijing, China. Chemosphere 86:665–671
Haller MY, Müller SR, McArdell CS, Alder AC, Suter MJF (2002) Quantification of veterinary antibiotics (sulfonamides and trimethoprim) in animal manure by liquid chromatography-mass spectrometry. J Chromatogr A 952:111–120
Hamscher G, Sczesny S, Höper H, Nau H (2002) Determination of persistent tetracycline residues in soil fertilized with liquid manure by high-performance liquid chromatography with electrospray ionization tandem mass spectrometry. Anal Chem 74:1509–1518
Hawker DW, Cropp R, Boonsaner M (2013) Uptake of zwitterionic antibiotics by rice (Oryza sativa L.) in contaminated soil. J Hazard Mater 263:458–466
Ho YB, Zakaria MP, Latif PA, Saari N (2012) Simultaneous determination of veterinary antibiotics and hormone in broiler manure, soil and manure compost by liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry. J Chromatogr A 1262:160–168
Hu XG, Luo Y, Zhou QX, Xu L (2008) Determination of thirteen antibiotics residues in manure by solid phase extraction and high performance liquid chromatography. Chin J Anal Chem 36:1162–1166
Hu X, Zhou Q, Luo Y (2010) Occurrence and source analysis of typical veterinary antibiotics in manure, soil, vegetables and groundwater from organic vegetable bases, northern China. Environ Pollut 158:2992–2998
International Conference on Harmonisation (ICH) Steering Committee (1996) Validation of analytical procedures: methodology
Jacobsen AM, Halling-Sorensen B (2006) Multi-component analysis of tetracyclines, sulfonamides and tylosin in swine manure by liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry. Anal Bioanal Chem 384:1164–1174
Jacobsen AM, Halling-Sorensen B, Ingerslev F, Hansen SH (2004) Simultaneous extraction of tetracycline, macrolide and sulfonamide antibiotics from agricultural soils using pressurised liquid extraction, followed by solid-phase extraction and liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry. J Chromatogr A 1038:157–170
Jiang HY, Zhang DD, Xiao SC, Geng CN, Zhang X (2013) Occurrence and sources of antibiotics and their metabolites in river water, WWTPs, and swine wastewater in Jiulongjiang River basin, south China. Environ Sci Pollut Res 20:9075–9083
Karci A, Balcioğlu IA (2009) Investigation of the tetracycline, sulfonamide, and fluoroquinolone antimicrobial compounds in animal manure and agricultural soils in Turkey. Sci Total Environ 407:4652–4664
Kemper N (2008) Veterinary antibiotics in the aquatic and terrestrial environment. Ecol Indic 8:1–13
Kim SC, Carlson K (2007) Quantification of human and veterinary antibiotics in water and sediment using SPE/LC/MS/MS. Anal Bioanal Chem 387:1301–1315
Kim S, Eichhorn P, Jensen JN, Weber AS, Aga DS (2005) Removal of antibiotics in wastewater: effect of hydraulic and solid retention times on the fate of tetracycline in the activated sludge process. Environ Sci Technol 39:5816–5823
Kulshrestha P, Rossman FG, Aga DS (2004) Investigating the molecular interactions of oxytetracycline in clay and organic matter: insights on factors affecting its mobility in soil. Environ Sci Technol 38:4097–4105
Leung HW, Minh TB, Murphy MB, Lam JCW, So MK, Martin M, Lam PKS, Richardson BJ (2012) Distribution, fate and risk assessment of antibiotics in sewage treatment plants in Hong Kong, South China. Environ Int 42:1–9
Li YW, Wu XL, Mo CH, Tai YP, Huang XP, Xiang L (2011) Investigation of sulfonamide, tetracycline, and quinolone antibiotics in vegetable farmland soil in the Pearl River Delta area, southern China. J Agric Food Chem 59:7268–7276
Li WH, Shi YL, Gao LH, Liu JM, Cai YQ (2013a) Occurrence and removal of antibiotics in a municipal wastewater reclamation plant in Beijing, China. Chemosphere 92:435–444
Li WH, Shi YL, Gao LH, Liu JM, Cai YQ (2013b) Occurrence, distribution and potential affecting factors of antibiotics in sewage sludge of wastewater treatment plants in China. Sci Total Environ 445:306–313
Lin DS, Zhou QX, Xu YM, Chen C, Li Y (2012) Physiological and molecular responses of the earthworm (Eisenia fetida) to soil chlortetracycline contamination. Environ Pollut 171:46–51
Lunestad BT, Goksoyr J (1990) Reduction in the antibacterial effect of oxytertracycline in sea-water by complex-formation with magnesium and calcium. Dis Aquat Org 9:67–72
Luo Y, Xu L, Rysz M, Wang YQ, Zhang H, Alvarez PJJ (2011) Occurrence and transport of tetracycline, sulfonamide, quinolone, and macrolide antibiotics in the Haihe River Basin, China. Environ Sci Technol 45:1827–1833
Martínez-Carballo E, González-Barreiro C, Scharf S, Gans O (2007) Environmental monitoring study of selected veterinary antibiotics in animal manure and soils in Austria. Environ Pollut 148:570–579
McClellan K, Halden RU (2010) Pharmaceuticals and personal care products in archived US biosolids from the 2001 EPA national sewage sludge survey. Water Res 44:658–668
Motoyama M, Nakagawa S, Tanoue R, Sato Y, Nomiyama K, Shinohara R (2011) Residues of pharmaceutical products in recycled organic manure produced from sewage sludge and solid waste from livestock and relationship to their fermentation level. Chemosphere 84:432–438
Okuda T, Yamashita N, Tanaka H, Matsukawa H, Tanabe K (2009) Development of extraction method of pharmaceuticals and their occurrences found in Japanese wastewater treatment plants. Environ Int 35:815–820
Pan X, Qiang ZM, Ben WW, Chen MX (2011) Residual veterinary antibiotics in swine manure from concentrated animal feeding operations in Shandong Province, China. Chemosphere 84:695–700
Pei LZ, Wang YP, Zhang P, Yang WZ (2015) Production status and market prospect of tetracycline antibiotics. Chin J Vet Drug 49:64–68 (in Chinese)
Pena A, Paulo M, Silva LJG, Seifrtová M, Lino CM, Solich P (2010) Tetracycline antibiotics in hospital and municipal wastewaters: a pilot study in Portugal. Anal Bioanal Chem 396:2929–2936
Richardson BJ, Larn PKS, Martin M (2005) Emerging chemicals of concern: pharmaceuticals and personal care products (PPCPs) in Asia, with particular reference to southern China. Mar Pollut Bull 50:913–920
Sarmah AK, Meyer MT, Boxall ABA (2006) A global perspective on the use, sales, exposure pathways, occurrence, fate and effects of veterinary antibiotics (VAs) in the environment. Chemosphere 65:725–759
Spongberg AL, Witter JD (2008) Pharmaceutical compounds in the wastewater process stream in northwest Ohio. Sci Total Environ 397:148–157
Srinivasan P, Sarmah AK (2014) Dissipation of sulfamethoxazole in pasture soils as affected by soil and environmental factors. Sci Total Environ 479:284–291
Vaclavik E, Halling-Sørensen B, Ingerslev F (2004) Evaluation of manometric respiration tests to assess the effects of veterinary antibiotics in soil. Chemosphere 56:667–676
Vieno N, Tuhkanen T, Kronberg L (2007) Elimination of pharmaceuticals in sewage treatment plants in Finland. Water Res 41:1001–1012
Wang QQ, Yates SR (2008) Laboratory study of oxytetracycline degradation kinetics in animal manure and soil. J Agric Food Chem 56:1683–1688
Winckler C, Engels H, Hund-Rinke K, Luckow T, Simon M, Steffens G (2003) Verhalten von Tetracyclinen und anderen Veterinärantibiotika in Wirtschaftsdünger und Boden. UFOPLAN 200 73 248, Berlin
Xu WH, Zhang G, Li XD, Zou SC, Li P, Hu ZH, Li J (2007) Occurrence and elimination of antibiotics at four sewage treatment plants in the Pearl River Delta (PRD), south China. Water Res 41:4526–4534
Yan Q, Gao X, Chen YP, Peng XY, Zhang YX, Gan XM, Zi CF, Guo JS (2014a) Occurrence, fate and ecotoxicological assessment of pharmaceutically active compounds in wastewater and sludge from wastewater treatment plants in Chongqing, the Three Gorges Reservoir Area. Sci Total Environ 470:618–630
Yan Q, Gao X, Huang L, Gan XM, Zhang YX, Chen YP, Peng XY, Guo JS (2014b) Occurrence and fate of pharmaceutically active compounds in the largest municipal wastewater treatment plant in southwest China: mass balance analysis and consumption back-calculated model. Chemosphere 99:160–170
Zhang YL, Lin SS, Dai CM, Shi L, Zhou XF (2014) Sorption–desorption and transport of trimethoprim and sulfonamide antibiotics in agricultural soil: effect of soil type, dissolved organic matter, and pH. Environ Sci Pollut Res 21:5827–5835
Zhao L, Dong YH, Wang H (2010) Residues of veterinary antibiotics in manures from feedlot livestock in eight provinces of China. Sci Total Environ 408:1069–1075
Acknowledgments
This research was jointly supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 21277150, 31370523, and 41001340), a research fund for the public welfare granted by the Ministry of Environmental Protection of PRC (No. 201209030), and a research fund for science and technology Project of Shenyang (No. F13-146-3-00).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
An, J., Chen, H., Wei, S. et al. Antibiotic contamination in animal manure, soil, and sewage sludge in Shenyang, northeast China. Environ Earth Sci 74, 5077–5086 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-015-4528-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-015-4528-y