Abstract
The vermicomposting process using sugarcane bagasse as substrate with cow dung and elephant dung were evaluated by using earthworm Eudrilus eugeniae. The significant of the current study to create a biological alternative and humification process for open-air decomposed debris of sugarcane crop residue and animal dungs by using earthworm. FT-IR and GC–MS analysis was performed to determine the maturity and stability stage of vermicompost in the initial and 90th day substrates. The zero day raw material had found 25 organic compounds which was increased to 30 compounds after 90th day of vermicomposting. FT-IR spectroscopy demonstrated that distinct biochemical functional groups included in wastes, underwent variable chemical changes and turnover during vermicomposting. GC–MS profile revealed that existence of numerous humic acids in the predominant level of metabolites and disintegrating compounds viz., Hexadecanoic acid methyl ester (14.89%), Benzenepropanoic acid 3,5-bis(1,1-dimethylethyl)-4-hydroxy-methylester (108.53%), Octadecanoic acid (8.98%), Dodecanoic acid methyl ester (1.99%), Methyl tetradecanoate (1.36%) and interestingly absence of toxic compounds, its clearly demonstrating as an indicator of substrate maturity. All the biochemical compounds are considered biologically and pharmacologically important and this was supported by a fall in the humification index, which focuses on the joint action of earthworms and bacteria in the decomposition of organic substrates. The technique FT-IR verified the mineralization process and formation of a significant amount of carboxylic and aliphatic group degradation and GC–MS profile found the turnover of different organic components in chemical footprints and it were proved to be more promising fast, reliable and conventional method. Therefore, the current study can be regarded as a comprehensive eco-biochemical method that will open a new vista on the significance of sugarcane bagasse for solid waste management. Finally, it was found that the amount of solid waste dumped in landfills could be greatly reduced and that industrial waste could be transformed into high-quality vermicompost.
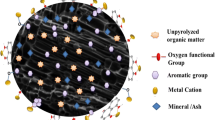
Graphical Abstract







Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availability
Enquiries about data availability should be directed to the authors.
Abbreviations
- GC–MS :
-
Gas chromatography mass spectroscopy
- FT-IR :
-
Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy
- S1 :
-
Sugarcane bagasse + 100% cow dung
- S2 :
-
Sugarcane bagasse + 100% elephant dung
- S3 :
-
Sugarcane bagasse + 50% cow dung + 50% elephant dung
References
Hussain, N., Abbasi, T., Abbasi, S.A.: Transformation of the pernicious and toxic weed parthenium into an organic fertilizer by vermicomposting. Int. J. Environ. Stud. 73, 731–745 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1080/00207233.2016.1185327
Ganguly, R.K., Chakraborty, S.K.: Qualitative assessment of paper mill waste valorization through combinatorial PLFA markers and spectroscopical analysis: an ecotechnology towards biotransformation of waste to resource. Environ. Technol. Innov. 23, 101532 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eti.2021.101532
Mothé, C.G., De Miranda, I.C.: Characterization of sugarcane and coconut fibers by thermal analysis and FTIR. J. Therm. Anal. Calorim. 97, 661–665 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10973-009-0346-3
Bortolotto Teixeira, L., Guzi de Moraes, E., Paolinelli Shinhe, G., Falk, G., Novaes de Oliveira, A.P.: Obtaining biogenic silica from sugarcane bagasse and leaf ash. Waste Biomass Valorization 12, 3205–3221 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12649-020-01230-y
Parker, P.D.: Lake Arthur field: Jefferson Davis Parish, Louisiana. 16–16C (1970)
Jacobs, J., Kreutzer, R., Smith, D.: Rice burning and asthma hospitalizations, Butte County, California, 1983–1992. Environ. Health Perspect. 105, 980–985 (1997). https://doi.org/10.1289/ehp.97105980
Balachandar, R., Baskaran, L., Yuvaraj, A., Thangaraj, R., Subbaiya, R., Ravindran, B., Chang, S.W., Karmegam, N.: Enriched pressmud vermicompost production with green manure plants using Eudrilus eugeniae. Bioresour. Technol. 299, 122578 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2019.122578
Pellejero, G., Rodriguez, K., Ashchkar, G., Vela, E., García-Delgado, C., Jiménez-Ballesta, R.: Onion waste recycling by vermicomposting: nutrients recovery and agronomical assessment. Int. J. Environ. Sci. Technol. 17, 3289–3296 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13762-020-02685-1
Ramírez-Estrada, A., Mena-Cervantes, V.Y., Mederos-Nieto, F.S., Pineda-Flores, G., Hernández-Altamirano, R.: Assessment and classification of lignocellulosic biomass recalcitrance by principal components analysis based on thermogravimetry and infrared spectroscopy. Int. J. Environ. Sci. Technol. 19, 2529–2544 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13762-021-03309-y
Deepthi, M.P., Saminathan, K., Rini, J., Kathireswari, P.: Materials today: proceedings chemical foot print of precomposted dung material of Elephus maximus and Bos taurus through GC–MS profile. Mater.Today: Proc. (2020). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matpr.2020.06.458
Rini, J., Deepthi, M.P., Saminathan, K., Narendhirakannan, R.T., Karmegam, N., Kathireswari, P.: Nutrient recovery and vermicompost production from livestock solid wastes with epigeic earthworms. Bioresour. Technol. 313, 123690 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2020.123690
Joseph, R., Saminathan, K., Deepthi, M.P., Kathireswari, P.: Comparative analysis on bioactive compounds presents in dung material of Bos taurus and Bos indicus. Mater. Today Proc. 48, 181–185 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matpr.2020.06.457
Preethee, S., Kathireswari, P., Haripriya, K.S., Sanofar, MF., Deepthi, MP., Saminathan, K., Efficacy of Vermicompost on Growth of Mulberry plant through Air Layering. Journal of Advanced Scientific Research. Oct 31, 12, (03 Suppl 2), 170-9 (2021)
Taylor, P., Gajalakshmi, S., Abbasi, S.A.: Solid waste management by composting: state of the art. Crit. Rev. Environ. Sci. Technol. (2008). https://doi.org/10.1080/10643380701413633
Margenot, A.J., Calderón, F.J., Parikh, S.J.: Limitations and potential of spectral subtractions in fourier-transform infrared spectroscopy of soil samples. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 80, 10–26 (2016). https://doi.org/10.2136/sssaj2015.06.0228
Gupta, R., Garg, V.K.: Vermiremediation and nutrient recovery of non-recyclable paper waste employing Eisenia fetida. J. Hazard. Mater. 162, 430–439 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2008.05.055
Ganguly, R.K., Chakraborty, S.K.: Assessment of qualitative enrichment of organic paper mill wastes through vermicomposting: humification factor and time of maturity. Heliyon 5, e01638 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.heliyon.2019.e01638
Fang, T.Y., Praveena, S.M., deBurbure, C., Aris, A.Z., Ismail, S.N.S., Rasdi, I.: Analytical techniques for steroid estrogens in water samples—a review. Chemosphere 165, 358–368 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2016.09.051
Tagg, A.S., Sapp, M., Harrison, J.P., Ojeda, J.J.: Identification and quantification of microplastics in wastewater using focal plane array-based reflectance micro-FT-IR imaging. Anal. Chem. 87, 6032–6040 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.analchem.5b00495
Fels, E.l., Zamama, L., Hafidi, M.: Advantages and limitations of using FTIR spectroscopy for assessing the maturity of sewage sludge and olive oil waste co-composts. Biodegradation and Bioremediation of Polluted Systems - New Advances and Technologies (2015). https://doi.org/10.5772/60943
Bhat, S.A., Singh, J., Vig, A.P.: Instrumental characterization of organic wastes for evaluation of vermicompost maturity. J. Anal. Sci. Technol. (2017). https://doi.org/10.1186/s40543-017-0112-2
Pacáková, V., Loukotková, L., Bosáková, Z., Štulík, K.: Analysis for estrogens as environmental pollutants—a review. J. Sep. Sci. 32, 867–882 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1002/jssc.200800673
Svečnjak, L., Baranović, G., Vinceković, M., Prđun, S., Bubalo, D., Gajger, I.T.: N approach for routine analytical detection of beeswax adulteration using ftir-atr spectroscopy. J. Apic. Sci. 59, 37–49 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1515/JAS-2015-0018
Bernabé, G.A., Almeida, S., Ribeiro, C.A., Crespi, M.S.: Evaluation of organic molecules originated during composting process. J. Therm. Anal. Calorim. 106, 773–778 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10973-011-1420-1
Khalil, K.M.S., Khairy, M., Allam, O.A.S., Khalil, M.K.: Formation of improved activated carbons from sugarcanebagasse as environmental materials for adsorption of phenolic pollutants. Int. J. Environ. Sci. Technol. 19, 3103–3116 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13762-021-03382-3
Deepthi, M.P., Kathireswari, P., Rini, J., Saminathan, K., Karmegam, N.: Vermitransformation of monogastric Elephas maximus and ruminant Bos taurus excrements into vermicompost using Eudrilus eugeniae. Bioresour. Technol. 320, 124302 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2020.124302
Preethee, S., Saminathan, K., Chandran, M., Kathireswari, P.: Valorization of phyto-biomass with tertiary combination of animal dung for enriched vermicompost production. Environ. Res. 215, 114365 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envres.2022.114365
Rajiv, P., Rajeshwari, S., Venckatesh, R.: Fourier transform-infrared spectroscopy and gas chromatography-mass spectroscopy: reliable techniques for analysis of Parthenium mediated vermicompost. Spectrochim. Acta—Part A Mol. Biomol. Spectrosc. 116, 642–645 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.saa.2013.08.012
Souza, B.S., Moreira, A.P.D., Teixeira, A.M.R.F.: TG-FTIR coupling to monitor the pyrolysis products from agricultural residues. J. Therm. Anal. Calorim. 97, 637–642 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10973-009-0367-y
Ravindran, B., Sravani, R., Mandal, A.B., Contreras-Ramos, S.M., Sekaran, G.: Instrumental evidence for biodegradation of tannery waste during vermicomposting process using Eudrilus eugeniae. J. Therm. Anal. Calorim. 111, 1675–1684 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10973-011-2081-9
Réveillé, V., Mansuy, L., Jardé, É., Garnier-Sillam, É.: Characterisation of sewage sludge-derived organic matter: lipids and humic acids. Org. Geochem. 34, 615–627 (2003). https://doi.org/10.1016/S0146-6380(02)00216-4
Dumitrescu, L., Sauciuc, A., Manciulea, I., Zaha, C.: Obtaining biofertilizer by composting vegetable waste, sewage sludge and sawdust. Bull. Transilv. Univ. Braşov Ser. I Eng. Sci. 2, 117–122 (2009)
Barriga, S., Méndez, A., Cámara, J., Guerrero, F., Gascó, G.: Agricultural valorisation of de-inking paper sludge as organic amendment in different soils: thermal study. J. Therm. Anal. Calorim. 99, 981–986 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10973-010-0692-1
Senesi, N., D’Orazio, V., Ricca, G.: Humic acids in the first generation of EUROSOILS. Geoderma 116, 325–344 (2003). https://doi.org/10.1016/S0016-7061(03)00107-1
Province, S.: Ournal of. Asian J. Chem. 26, 6097–6100 (2014)
Grube, M., Lin, J.G., Lee, P.H., Kokorevicha, S.: Evaluation of sewage sludge-based compost by FT-IR spectroscopy. Geoderma 130, 324–333 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.geoderma.2005.02.005
Filip, Z., Bielek, P.: Susceptibility of humic acids from soils with various contents of metals to microbial utilization and transformation. Biol. Fertil. Soils 36, 426–433 (2002). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00374-002-0559-0
González, J.A., González-Vila, F.J., Almendros, G., Zancada, M.C., Polvillo, O., Martín, F.: Preferential accumulation of selectively preserved biomacromolecules in the humus fractions from a peat deposit as seen by analytical pyrolysis and spectroscopic techniques. J. Anal. Appl. Pyrolysis. 68–69, 287–298 (2003). https://doi.org/10.1016/S0165-2370(03)00069-X
Srivastava, V., Goel, G., Thakur, V.K., Singh, R.P., Ferreira de Araujo, A.S., Singh, P.: Analysis and advanced characterization of municipal solid waste vermicompost maturity for a green environment. J. Environ. Manage. (2020). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jenvman.2019.109914
Paul, S., Kauser, H., Jain, M.S., Khwairakpam, M., Kalamdhad, A.S.: Biogenic stabilization and heavy metal immobilization during vermicomposting of vegetable waste with biochar amendment. J. Hazard. Mater. 390, 121366 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2019.121366
Ravindran, B., Dinesh, S.L., Kennedy, L.J., Sekaran, G.: Vermicomposting of solid waste generated from leather industries using epigeic earthworm Eisenia Foetida. Appl. Biochem. Biotechnol. 151, 480–488 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12010-008-8222-3
Arumugam, K., Renganathan, S., Babalola, O.O., Muthunarayanan, V.: Investigation on paper cup waste degradation by bacterial consortium and Eudrillus eugeinea through vermicomposting. Waste Manag. 74, 185–193 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.wasman.2017.11.009
Ahmed, R., Deka, H.: Vermicomposting of patchouli bagasse—A byproduct of essential oil industries employing Eisenia fetida. Environ. Technol. Innov. 25, 102232 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eti.2021.102232
Chandra, R., Yadav, S., Yadav, S.: Phytoextraction potential of heavy metals by native wetland plants growing on chlorolignin containing sludge of pulp and paper industry. Ecol. Eng. 98, 134–145 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoleng.2016.10.017
Subhash Kumar, M., Rajiv, P., Rajeshwari, S., Venckatesh, R.: Spectroscopic analysis of vermicompost for determination of nutritional quality. Spectrochim. Acta—Part A Mol Biomol. Spectrosc. 135, 252–255 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.saa.2014.07.011
Ahmad, B.: Chemical composition and antifungal, phytotoxic, brine shrimp cytotoxicity, insecticidal and antibacterial activities of the essential oils of Acacia modesta. J. Med. Plants Res. 6, 4653–4659 (2012). https://doi.org/10.5897/jmpr12.016
Sharma, K., Kaur, S., Kumar, N.: Cow urine prominence to humanity. J. Pharmacogn. Phytochem. 9, 459–465 (2020)
Joseph, R., Kathireswari, P.: Efficacy leaf litters as substrate on reproductive potential of epigeic earthworm Eudrilus eugeniae. Indian J. Ecol. 47, 186–189 (2020)
Grover, N., Patni, V.: Phytochemical characterization using various solvent extracts and GC-MS analysis of methanolic extract of Woodfordia fruticosa (L.) Kurz. leaves. Int. J. Pharm. Pharm. Sci. 5, 291–295 (2013)
Jirankalgikar, N., Nariya, P., De, S.: In vitro antioxidant activity evaluation and HPTLC profile of cow dung. Int. J. Green Pharm. 8, 158–162 (2014). https://doi.org/10.4103/0973-8258.140172
Acknowledgements
We thank to University Grants Commission-College of Excellence (UGC-CE), New Delhi funding for Instruments facilities (FT-IR, Shimatzu IR Sprit make and AAS SL168 Elico make) in the Department of Chemistry, Kongunadu Arts and Science College, Coimbatore” and for GCMS analysis the Instrument (Agilent GC 7890A / MS5975C) facilities provided by TUV SUD South Asia Pvt Ltd., Tirupur and the authors wish to thank the management of Kongunadu Arts and Science College, Coimbatore, Tamil Nadu for provide the infrastructure facility to carry out the research work.
Funding
The authors have not disclosed any funding.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors have no conflicts of interest to declare that are relevant to the content of this article.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Saravanan, P., Palanisamy, K. & Kulandaivelu, S. Spectroscopic Assessment of Sugarcane Bagasse Mediated Vermicompost for Qualitative Enrichment of Animal Wastes Elephus maximus and Bos taurus. Waste Biomass Valor 14, 2133–2149 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12649-022-02011-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12649-022-02011-5