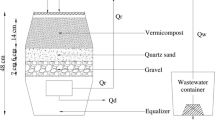
Abstract
This study aims to design a smart closed reactor of vermicomposting to convert sewage sludge and any organic waste to high-quality vermicompost. In this reactor design, all aspects of growth and reproduction of Eisenia Fetida worms, such as aeration, temperature, light, and moisture, were considered. We analyzed the physicochemical, bacterial, and microstructural of produced vermicompost and growth rate of worms in a substrate of 70% sewage sludge, 20% cow manure, and 10% sugarcane bagasse in a container and the smart reactor. The results show that vermicomposting in the smart reactor took 50% less time and 30% more worm growth rate to produce the same quality as in a container. After vermicomposting in the reactor, the parameters of pH, fecal coliform, phosphorus, organic matter, and C/N decreased whereas the parameters of carbon, nitrogen, nitrate, ammonia nitrate, and EC increased, slightly. Although, the EC amount of the reactor production is more than the container one, the amount of moisture, phosphorus, and organic matter of the vermicompost in the container is more than the reactor one. Based on the odor absorption and leachate elimination of this reactor, we recommend that it be utilized for vermicompost production, including out of smelly organic wastes such as sewage sludge, even in any public zone and personal houses.
Graphic Abstract







Similar content being viewed by others
Change history
17 December 2021
A Correction to this paper has been published: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12649-021-01649-x
Abbreviations
- SR:
-
Smart Reactor
- VR:
-
Vermicomposting
- PLC:
-
Programmable Logic Controllers
- SS:
-
Sewage Sludge
- CM:
-
Cow Manure
- SB:
-
Sugarcane Bagasse
References
Haynes, R.J., Naidu, R.: Influence of lime, fertilizer and manure applications on soil organic matter content and soil physical conditions: A review. Nutr. Cycl. Agroecosyst. 51, 123–137 (1998). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1009738307837
Garg, V.K., Yadav, Y.K., Sheoran, A., Chand, S., Kaushik, P.: Livestock excreta management through vermicomposting using an epigeic earthworm Eisenia foetida. Environmentalist 26, 269–276 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10669-006-8641-z
Gupta, R., Garg, V.K.: Stabilization of primary sewage sludge during vermicomposting. J. Hazard. Mater. 153, 1023–1030 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2007.09.055
De Neve, S., Hofman, G.: Influence of soil compaction on carbon and nitrogen mineralization of soil organic matter and crop residues. Biol. Fertil. Soils 30, 544–549 (2000). https://doi.org/10.1007/s003740050034
Trinsoutrot, I., Nicolardot, B., Justes, E., Recous, S.: Decomposition in the field of residues of oilseed rape grown at two levels of nitrogen fertilisation. Effects on the dynamics of soil mineral nitrogen between successive crops. Nutr. Cycl. Agroecosyst. 56, 125–137 (2000). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1009838618133
Hemalatha, B.: Vermicomposting of fruit waste and industrial sludge. International Journal of Advanced Engineering Technology. III, 60–63 (2012)
Huang, K., Li, F., Wei, Y., Chen, X., Technology, X.F.-B., 2013, U.: Changes of bacterial and fungal community compositions during vermicomposting of vegetable wastes by Eisenia foetida. Elsevier. (2013)
Fu, X., Huang, K., Chen, X., Li, F., Cui, G.: Feasibility of vermistabilization for fresh pelletized dewatered sludge with earthworms Bimastus parvus. Biores. Technol. 175, 646–650 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2014.11.007
Huang, K., Xia, H., Cui, G., Li, F.: Effects of earthworms on nitrification and ammonia oxidizers in vermicomposting systems for recycling of fruit and vegetable wastes. Sci. Total Environ. 578, 337–345 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2016.10.172
Lazcano, C., Gómez-Brandón, M., Domínguez, J.: Comparison of the effectiveness of composting and vermicomposting for the biological stabilization of cattle manure. Chemosphere 72, 1013–1019 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2008.04.016
Alidadi, H., Saffari, A.R., Ketabi, D., Peiravi, R., Hosseinzadeh, A.: Comparison of Vermicompost and Cow Manure Efficiency on the Growth and Yield of Tomato Plant. Health Scope (2014). https://doi.org/10.17795/jhealthscope-14661
Sharma, K., Garg, V.K.: Comparative analysis of vermicompost quality produced from rice straw and paper waste employing earthworm Eisenia fetida (Sav.). Biores. Technol. 250, 708–715 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2017.11.101
Castillo-González, E., Giraldi-Díaz, M.R., De Medina-Salas, L., Sánchez-Castillo, M.P.: Pre-composting and vermicomposting of pineapple (Ananas comosus) and vegetable waste. Applied Sciences (Switzerland). (2019). https://doi.org/10.3390/app9173564
Majlessi, M., Eslami, A., Najafi Saleh, H., Mirshafieean, S., Babaii, S.: Vermicomposting of food waste: Assessing the stability and maturity. Iranian Journal of Environmental Health Science and Engineering. (2012). https://doi.org/10.1186/1735-2746-9-25
Ghorbani, M., Sabour, M.R.: Global trends and characteristics of vermicompost research over the past 24 years, https://link.springer.com/article/https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-020-11119-x, (2021)
Ghorbani, M., Dahrazma, B., Fazlolah Saghravani, S., Yousofizinsaz, G.: A comparative study on physicochemical properties of environmentally-friendly lightweight bricks having potato peel powder and sour orange leaf. Constr. Build. Mater. 276, 121937 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2020.121937
Ansari, A.A., Rajpersaud, J.: Physicochemical Changes during Vermicomposting of Water Hyacinth ( Eichhornia crassipes ) and Grass Clippings. ISRN Soil Science. 2012, 1–6 (2012). https://doi.org/10.5402/2012/984783
Fernández-Luqueño, F., Reyes-Varela, V., Martínez-Suárez, C., Salomón-Hernández, G., Yáñez-Meneses, J., Ceballos-Ramírez, J.M., Dendooven, L.: Effect of different nitrogen sources on plant characteristics and yield of common bean (Phaseolus vulgaris L.). Biores. Technol. 101, 396–403 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2009.07.058
Contreras-Ramos, S.M., Escamilla-Silva, E.M., Dendooven, L.: Vermicomposting of biosolids with cow manure and oat straw. Biol. Fertil. Soils 41, 190–198 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00374-004-0821-8
Ndegwa, P.M., Thompson, S.A.: Integrating composting and vermicomposting in the treatment and bioconversion of biosolids. Biores. Technol. 76, 107–112 (2001). https://doi.org/10.1016/S0960-8524(00)00104-8
Aira, M., Monroy, F., Domínguez, J.: Eisenia fetida (Oligochaeta: Lumbricidae) modifies the structure and physiological capabilities of microbial communities improving carbon mineralization during vermicomposting of pig manure. Microb. Ecol. 54, 662–671 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00248-007-9223-4
Vijayan, T., Ya, D.: Automatic water and fertilizer sprinkling system based on PLC for Agriculture application. International Journal of MC Square Scientific Research. 9, 126–134 (2017). https://doi.org/10.20894/ijmsr.117.009.002.015
Futao, Z., Wei, D., Yiheng, X., Zhiren, H.: Programmable logic controller applied in steam generators water levels. In: Conference Record - IAS Annual Meeting (IEEE Industry Applications Society). pp. 1551–1556 (1996)
Bayindir, R., Cetinceviz, Y.: A water pumping control system with a programmable logic controller (PLC) and industrial wireless modules for industrial plants-An experimental setup. ISA Trans. 50, 321–328 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.isatra.2010.10.006
Ding, J.T., Tu, H.Y., Zang, Z.L., Huang, M., Zhou, S.J.: Precise control and prediction of the greenhouse growth environment of Dendrobium candidum. Comput. Electron. Agric. 151, 453–459 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compag.2018.06.037
Liu, X., Zhang, T., Li, B., Tian, F., … Y.T.-2018 37th C., 2018, U.: Wireless measurement and control system of environmental parameters in greenhouse based on ZigBee technology. ieeexplore.ieee.org. (2018)
Erickson, K.T.: Programmable logic controllers. IEEE Potentials 15, 14–17 (1996). https://doi.org/10.1109/45.481370
Edan, Y., Pliskin, N.: Transfer of software engineering tools from information systems to production systems. Comput. Ind. Eng. 39, 19–34 (2001). https://doi.org/10.1016/S0360-8352(00)00062-0
Ioannides, M.G.: Design and implementation of PLC-based monitoring control system for induction motor. IEEE Trans. Energy Convers. 19, 469–476 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1109/TEC.2003.822303
Alphonsus, E.R., Abdullah, M.O.: A review on the applications of programmable logic controllers (PLCs), https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S1364032116000551, (2016)
Huuck, R.: Semantics and Analysis of Instruction List Programs. In: Electronic Notes in Theoretical Computer Science. pp. 3–18 (2005)
BS EN 61131–1:1994: Programmable controllers. General information. Bsi
Liu, J., Lv, Y. jun: The Application of LOGO! in Control System of a Transmission and Sorting Mechanism. In: Communications in Computer and Information Science. pp. 231–236. Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg (2011)
A5E00324307–01: Drawing number Edition 1 Product information. (2001)
Sita, I.V.: Train comfort, access and security using KNX and LOGO! controllers. In: Electrical Systems for Aircraft, Railway and Ship Propulsion, ESARS (2012)
Tan, W.Y., Then, Y.L., Lew, Y.L., Tay, F.S.: Newly calibrated analytical models for soil moisture content and pH value by low-cost YL-69 hygrometer sensor. Measurement: Journal of the International Measurement Confederation. 134, 166–178 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.measurement.2018.10.071
IAEA: Use of irradiation for chemical and microbial decontamination of water, wastewater and sludge - Final report of a co-ordinated research project 1995–1999- IAEA-TECDOC-1225. (2001)
Borrely, S.I., Cruz, A.C., Del Mastro, N.L., Sampa, M.H.O., Somessari, E.S.: Radiation processing of sewage and sludge. A review. Progress in Nuclear Energy. 33, 3–21 (1998). https://doi.org/10.1016/s0149-1970(97)87287-3
Zhang, L., Xu, C. (Charles), Champagne, P.: Energy recovery from secondary pulp/paper-mill sludge and sewage sludge with supercritical water treatment. Bioresource Technology. 101, 2713–2721 (2010). Doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2009.11.106
Ouatmane, A., Provenzano, M.R., Hafidi, M., Senesi, N.: Compost maturity assessment using calorimetry, spectroscopy and chemical analysis. Compost Science and Utilization. 8, 124–134 (2000). https://doi.org/10.1080/1065657X.2000.10701758
Suthar, S., Singh, S.: Vermicomposting of domestic waste by using two epigeic earthworms (Perionyx excavatus and Perionyx sansibaricus). Int. J. Environ. Sci. Technol. 5, 99–106 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF03326002
Palsania, J., Sharma, R., Srivastava, J.K., Sharma, D.: Effect of moisture content variation over kinetic reaction rate during vermicomposting process. Appl. Ecol. Environ. Res. (2008). https://doi.org/10.15666/aeer/0602_049061
Zularisam, A.W., Zahirah, Z.S., Zakaria, I., Syukri, M.M., Anwar, A., Sakinah, M.: Production of biofertilizer from vermicomposting process of municipal sewage sludge. J. Appl. Sci. 10, 580–584 (2010). https://doi.org/10.3923/jas.2010.580.584
Manyuchi, M.M.M., Phiri Anthony, Chirinida, N., Muredzi, P., Govhaand, J., Sengudzwa, T.: Vermicompostingof Waste Corn Pulp Blended with Cow Dung Manure using Eisenia Fetida. International Journal of Chemical and Molecular Engineering. 6: 753–756 (2012)
Khwairakpam, M., Bhargava, R.: Vermitechnology for sewage sludge recycling. J. Hazard. Mater. 161, 948–954 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2008.04.088
Math, R.K., Dharwadkar, N. V: A wireless sensor network based low cost and energy efficient frame work for precision agriculture. In: 2017 International Conference on Nascent Technologies in Engineering, ICNTE 2017 - Proceedings (2017)
Neidle, M.: Electrical Installation Technology. (1982)
Garg, V.K., Gupta, R.: Effect of temperature variations on vermicomposting of household solid waste and fecundity of eisenia fetida. Bioremediat. J. 15, 165–172 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1080/10889868.2011.598487
Gim-Krumm, M., Donoso, P., Zuñiga, R.N., Estay, H., Troncoso, E.: A comprehensive study of glucose transfer in the human small intestine using an in vitro intestinal digestion system (i-IDS) based on a dialysis membrane process. Elsevier. (2018). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.memsci.2018.07.080
Garcia-Robledo, C., Charlotten-Silva, M., Cruz, C., Kuprewicz, E.K.: Low quality diet and challenging temperatures affect vital rates, but not thermal tolerance in a tropical insect expanding its diet to an exotic plant. J. Therm. Biol 77, 7–13 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jtherbio.2018.07.018
Johnsonelectric.com: Johnson Electric - Johnson Electric, https://www.johnsonelectric.com/en.
Sabagh, E.: EL Sabagh et al.: Wheat (Triticum aestivum L) production under drought and heat stress-adverse effects, mechanisms and mitigation: a review-1-APPLIED ECOLOGY AND ENVIRONMENTAL RESEARCH X(y): pp-pp WHEAT (TRITICUM AESTIVUM L) PRODUCTION UNDER DROUGHT AN. Appl Ecol Environ Res. 15, 1625–1651 (2018).
Edwards, C.A., Arancon, N.Q.: the Use of Earthworms in Organic Waste Managements
Arrhenius, O.: Influence of Soil Reaction on Earthworms. Ecology 2, 255–257 (1921). https://doi.org/10.2307/1928978
Salisbury, E.J.: The Influence of Earthworms on Soil Reaction and the Stratification of Undisturbed Soils. J. Linn. Soc. London, Bot. 46, 415–425 (1924). https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1095-8339.1924.tb00496.x
Petrov, B.C.: The active reaction of soil (pH) as a factor in the distribution of earthworms. Zoological Journal. 25, 107–110 (1946)
Electronics, S.: Mean Well Switching Power Supply - 12VDC, 12.5A, https://www.meanwell.com/productSeries.aspx#, (2016)
EPA: Revised Total Coliform Rule And Total Coliform Rule | Drinking Water Requirements for States and Public Water Systems | US EPA. 1–5 (2017)
Institute of Standards and Industrial Research of Iran: Vermicompost- Physical and chemical Specifications. 1st. edition. (2011)
Das, S., Pandey, P., Mohanty, S., Nayak, S.K.: Evaluation of biodegradability of green polyurethane/nanosilica composite synthesized from transesterified castor oil and palm oil based isocyanate. Int. Biodeterior. Biodegradation 117, 278–288 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ibiod.2017.01.015
Soobhany, N., Gunasee, S., Rago, Y.P., Joyram, H., Raghoo, P., Mohee, R., Garg, V.K.: Spectroscopic, thermogravimetric and structural characterization analyses for comparing Municipal Solid Waste composts and vermicomposts stability and maturity. Biores. Technol. 236, 11–19 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2017.03.161
Funding
The authors did not receive support from any organization for the submitted work.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
MG: Conceptualization, Methodology, Validation, Formal analysis, Investigation, Resources, Data Curation, Writing—Original Draft, Visualization, Project administration. MRS Supervision. MB: Software.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors have no conflicts of interest to declare that are relevant to the content of this article.
Ethical Approval
It has not been published elsewhere and that it has not been submitted simultaneously for publication elsewhere.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
The original online version of this article was revised: the affiliations of the authors are updated.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ghorbani, M., Sabour, M.R. & Bidabadi, M. Vermicomposting Smart Closed Reactor Design and Performance Assessment by Using Sewage Sludge. Waste Biomass Valor 12, 6177–6190 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12649-021-01426-w
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12649-021-01426-w