Abstract
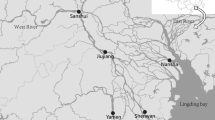
River estuaries are dynamic regions that are influenced by the interactions between freshwater and seawater as well as seasonal variations in river runoffs. Studies focusing on the distribution of Indo-Pacific humpback dolphins (Sousa chinensis) have indicated their general tendency toward estuarine habitats. The seasonal activities of humpback dolphins are likely to synchronize with environmental fluctuations. This study investigated the effects of seasonal changes in river runoffs on the distribution gradient of humpback dolphins by deploying acoustic data loggers along the Xin Huwei River estuary, Western Taiwan, between July 2009 and September 2012. Seasonal shifts were observed in the areas with high detected duration of humpback dolphins, which mainly stayed near the river mouth during the dry seasons but moved seaward during rainy seasons and following heavy rainfall. In addition, the gradient of ambient ultrasonic pulses, dominated by snapping shrimp sounds, exhibited regional differences following heavy rainfall. The outward movements of the humpback dolphins and the snapping shrimp sounds in the estuary indicated a temporary trophic-system shift in response to local environmental changes resulting from high volumes of river runoffs. In the future, the seasonal variation in the distribution of humpback dolphins must be considered during the conservation management of this critically endangered population.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Akamatsu, T., A. Matsuda, S. Suzuki, D. Wang, K. Wang, M. Suzuki, H. Muramoto, N. Sugiyama, and K. Oota. 2005. New stereo acoustic data logger for free-ranging dolphins and porpoises. Marine Technology Society Journal 39: 3–9.
Akamatsu, T., K. Nakamura, R. Kawabe, S. Furukawa, H. Murata, A. Kawakubo, and M. Komaba. 2010. Seasonal and diurnal presence of finless porpoises at a corridor to the ocean from their habitat. Marine Biology 157: 1879–1887.
Au, W.W.L. 1993. The sonar of dolphins. New York: Springer.
Au, W.W.L., and K. Banks. 1998. The acoustics of the snapping shrimp Synalpheus parneomeris in Kaneohe Bay. The Journal of the Acoustical Society of America 103: 41–47.
Barros, N.B., T.A. Jefferson, and E.C.M. Parsons. 2004. Feeding habits of Indo-Pacific humpback dolphins (Sousa chinensis) stranded in Hong Kong. Aquatic Mammals 30: 179–188.
Boyer, J.N., J.W. Fourqurean, and R.D. Jones. 1999. Seasonal and long-term trends in the water quality of Florida Bay (1989–1997). Estuaries 22: 417–430.
Browder, J.A., Z. Zein-Eldin, M.M. Criales, M.B. Robblee, S. Wong, T.L. Jackson, and D. Johnson. 2002. Dynamics of pink shrimp (Farfantepenaeus duorarum) recruitment potential in relation to salinity and temperature in Florida Bay. Estuaries 25: 1355–1371.
Cato, D.H. 1992. The biological contribution to the ambient noise in waters near Australia. Acoustics Australia 20: 76–80.
Cato, D.H., and M.J. Bell. 1992. Ultrasonic ambient noise in Australian shallow waters at frequencies up to 200 kHz. DTIC Document. http://oai.dtic.mil/oai/oai?verb=getRecord&metadataPrefix=html&identifier=ADA251679. Accessed Feb 2013.
Chen, B., D. Zheng, F. Zhai, X. Xu, P. Sun, Q. Wang, and G. Yang. 2008. Abundance, distribution and conservation of Chinese white dolphins (Sousa chinensis) in Xiamen, China. Mammalian Biology 73: 156–164.
Chen, T., S.K. Hung, Y. Qiu, X. Jia, and T.A. Jefferson. 2010. Distribution, abundance, and individual movements of Indo-Pacific humpback dolphins (Sousa chinensis) in the Pearl River Estuary, China. Mammalia 74: 117–125.
Chou L.S., J.D. Lee, P.F. Lee, C.C. Kao, K.T. Shao, C.T. Chuang, M.H. Chen, C.F. Chen, R.C. Wei, W.C. Yang, and H.C. Tsai. 2011. Population ecology, critical habitat and master planning for marine mammal protected area of Indo-Pacific humpback dolphins, Sousa chinensis. Final Report to Forest Bureau, Council of Agriculture, Republic of China, no. 99-FD-08.1-C-32. http://ethics.forest.gov.tw/public/Attachment/181616351971.pdf. Accessed February 2013
Dong, L., J. Su, L.A. Wong, Z. Cao, and J.C. Chen. 2004. Seasonal variation and dynamics of the Pearl River plume. Continental Shelf Research 24: 1761–1777.
Fury, C.A., and P.L. Harrison. 2011a. Impact of flood events on dolphin occupancy patterns. Marine Mammal Science 27: 185–205.
Fury, C.A., and P.L. Harrison. 2011b. Seasonal variation and tidal influences on estuarine use by bottlenose dolphins (Tursiops aduncus). Estuarine, Coastal and Shelf Science 93: 389–395.
Fury, C.A., and J.S. Reif. 2012. Incidence of poxvirus-like lesions in two estuarine dolphin populations in Australia: Links to flood events. Science of the Total Environment 416: 536–540.
Goold, J.C., and T.A. Jefferson. 2004. A note on clicks recorded from free-ranging Indo-Pacific humpback dolphins, Sousa chinensis. Aquatic Mammals 30: 175–178.
Hastie, G.D., B. Wilson, L.J. Wilson, K.M. Parsons, and P.M. Thompson. 2004. Functional mechanisms underlying cetacean distribution patterns: Hotspots for bottlenose dolphins are linked to foraging. Marine Biology 144: 397–403.
Huang, L., W. Jian, X. Song, X. Huang, S. Liu, P. Qian, K. Yin, and M. Wu. 2004. Species diversity and distribution for phytoplankton of the Pearl River estuary during rainy and dry seasons. Marine Pollution Bulletin 49: 588–596.
Hughes, D.A. 1969. Responses to salinity change as a tidal transport mechanism of pink shrimp, Penaeus Duorarum. The Biological Bulletin 136: 43–53.
Jefferson, T.A. 2000. Population biology of the Indo-Pacific hump-backed dolphin in Hong Kong waters. Wildlife Monographs 144: 1–65.
Jefferson, T.A., and L. Karczmarski. 2001. Sousa chinensis. Mammalian Species 655: 1–9.
Johnson, M.W., F.A. Everest, and R.W. Young. 1947. The role of snapping shrimp (Crangon and Synalpheus) in the production of underwater noise in the sea. Biological Bulletin 93: 122–138.
Kimura, S., T. Akamatsu, S. Li, S. Dong, L. Dong, K. Wang, D. Wang, and N. Arai. 2010. Density estimation of Yangtze finless porpoises using passive acoustic sensors and automated click train detection. The Journal of the Acoustical Society of America 128: 1435–1445.
Kimura, S., T. Akamatsu, S. Li, L. Dong, K. Wang, D. Wang, and N. Arai. 2012. Seasonal changes in the local distribution of Yangtze finless porpoises related to fish presence. Marine Mammal Science 28: 308–324.
Lane, R.R., J.W. Day, B. Marx, E. Reves, and G.P. Kemp. 2002. Seasonal and spatial water quality changes in the outflow plume of the Atchafalaya River, Louisiana, USA. Estuaries 25: 30–42.
Laran, S., and V. Drouot-Dulau. 2007. Seasonal variation of striped dolphins, fin- and sperm whales’ abundance in the Ligurian Sea (Mediterranean Sea). Journal of the Marine Biological Association of the UK 87: 345–352.
Lin, T.-H. 2013. The application of passive acoustic monitoring for studying Indo-Pacific humpback dolphin behavior and habitat use off western Taiwan. Ph.D. dissertation, National Taiwan University (http://handle.ncl.edu.tw/11296/ndltd/17027378804372597052).
Lin, T.-H., T. Akamatsu, and L.-S. Chou. 2013. Tidal influences on the habitat use of Indo-Pacific humpback dolphins in an estuary. Marine Biology 160: 1353–1363.
Mallin, M.A., and H.W. Paerl. 1994. Planktonic trophic transfer in an estuary: Seasonal, diel, and community structure effects. Ecology 75: 2168–2184.
Mallin, M.A., H.W. Paerl, and J. Rudek. 1991. Seasonal phytoplankton composition, productivity and biomass in the Neuse River estuary, North Carolina. Estuarine, Coastal and Shelf Science 32: 609–623.
Martin, A.R., and V.M.F. da Silva. 2004. River dolphins and flooded forest: Seasonal habitat use and sexual segregation of botos (Inia geoffrensis) in an extreme cetacean environment. Journal of Zoology 263: 295–305.
Möller Jr., O.O., J.P. Castello, and A.C. Vaz. 2009. The effect of river discharge and winds on the interannual variability of the pink shrimp Farfantepenaeus paulensis production in Patos Lagoon. Estuaries and Coasts 32: 787–796.
Parra, G.J. 2006. Resource partitioning in sympatric delphinids: Space use and habitat preferences of Australian snubfin and Indo-Pacific humpback dolphins. The Journal of Animal Ecology 75: 862–874.
Rayment, W., S. Dawson, and E. Slooten. 2010. Seasonal changes in distribution of Hector’s dolphin at Banks Peninsula, New Zealand: Implications for protected area design. Aquatic Conservation: Marine and Freshwater Ecosystems 20: 106–116.
Soldevilla, M.S., S.M. Wiggins, and J.A. Hildebrand. 2010. Spatial and temporal patterns of Risso’s dolphin echolocation in the Southern California Bight. The Journal of the Acoustical Society of America 127: 124–132.
Stafford, K.M., S.L. Nieukirk, and C.G. Fox. 2001. Geographic and seasonal variation of blue whale calls in the North Pacific. Journal of Cetacean Research and Management 3: 65–76.
Verfuß, U.K., C.G. Honnef, A. Meding, M. Dähne, R. Mundry, and H. Benke. 2007. Geographical and seasonal variation of harbour porpoise (Phocoena phocoena) presence in the German Baltic Sea revealed by passive acoustic monitoring. Journal of the Marine Biological Association of the UK 87: 165–176.
Wenz, G.M. 1962. Acoustic ambient noise in the ocean: Spectra and sources. The Journal of the Acoustical Society of America 34: 1936–1956.
Wilson, B., P.M. Thompson, and P.S. Hammond. 1997. Habitat use by bottlenose dolphins: Seasonal distribution and stratified movement patterns in the Moray Firth, Scotland. Journal of Applied Ecology 34: 1365–1374.
Zimmer, W.M.X., J. Harwood, P.L. Tyack, M.P. Johnson, and P.T. Madsen. 2008. Passive acoustic detection of deep-diving beaked whales. The Journal of the Acoustical Society of America 124: 2823–2832.
Acknowledgments
This study was supported by the Formosa Plastics Group, Forestry Bureau, Council of Agriculture Executive Yuan of Taiwan (100-FD-07.1-C-37), Ministry of Science and Technology of Taiwan (MOST 103-3113-E-002-013-), and Research and Development Program for New Bio-industry Initiatives of Japan. We thank the Tainan Hydraulics Laboratory at National Cheng Kung University and the Industrial Development Bureau of the Ministry of Economic Affairs, Taiwan for allowing us to access the fixed pile at the Xin Huwei River estuary. We appreciate Li-Cing Mei, Long-Jhen Lin, Siou-Syong Wu, and the members of the Cetacean Laboratory, National Taiwan University for their dedicated support in conducting the field surveys of the Indo-Pacific humpback dolphins off the west coast of Taiwan. We also thank Shiang-Lin Huang for improving the quality of this manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Communicated by Iris C. Anderson
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lin, TH., Akamatsu, T. & Chou, LS. Seasonal Distribution of Indo-Pacific Humpback Dolphins at an Estuarine Habitat: Influences of Upstream Rainfall. Estuaries and Coasts 38, 1376–1384 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12237-014-9886-2
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12237-014-9886-2