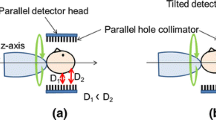
Abstract
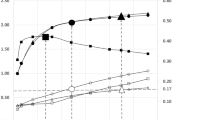
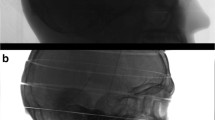
Head holder attenuation affects brain perfusion single-photon emission computed tomography (SPECT) image quality. Here, we proposed a head holder-attenuation correction (AC) method using attenuation coefficient maps calculated by Chang’s method from CT images. Then, we evaluated the effectiveness of the head holder-AC method by numerical phantom and clinical cerebral perfusion SPECT studies. In the numerical phantom, the posterior counts were 10.7% lower than the anterior counts without head holder-AC method. However, by performing head holder-AC, the posterior count recovered by approximately 6.8%, approaching the true value. In the clinical study, the normalized count ratio was significantly increased by performing the head holder-AC method in the posterior-middle cerebral artery, posterior cerebral artery and cerebellum regions. There were no significant increases in other regions. The head holder-AC method can correct the counts attenuated by the head holder.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Drobný M, Svaleková A, Stevík M, Reznák I, Luksová D, Krátky M, Bil’o P. Single-photon emission-computed tomography in the diagnosis of cerebrovascular diseases. Bratisl Lek Listy. 1997;98(12):678–86.
Nare Torosyan and Daniel H. S. Silverman, Neuronuclear Imaging in the Evaluation of Dementia and Mild Decline in Cognition. Semin Nucl Med. 2012; 42(6): 415–422
Van Paesschen W, Dupont P, Sunaert S, Goffin K, Van Laere K. The use of SPECT and PET in routine clinical practice in epilepsy. Curr Opin Neurol. 2007;20(2):194–202.
Kapucu OL, Nobili F, Varrone A, Booij J, Vander Borght T, Någren K, Darcourt J, Tatsch K, Van Laere KJ. EANM procedure guideline for brain perfusion SPECT using 99mTc-labelled radiopharmaceuticals, version 2. Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging. 2009;36(12):2093–102.
Working Group for Investigation and Research on Nuclear Medicine Image Quantification and Standardization, Japanese Society of Nuclear Medicine Technology. Questionnaire report for practical conditions of nuclear medicine examination and standardization of image acquisition, processing, display and output. Jpn J Nucl Med Technol. 2004;24:95–118.
Ishii K, Hanaoka K, Okada M, Kumano S, Komeya Y, Tsuchiya N, Hosono M, Murakami T. Impact of CT attenuation correction by SPECT/CT in brain perfusion images. Ann Nucl Med. 2012;26(3):241–7.
Ohba M, Kokubo Y, Suzuki K, Kanoto M, Sonoda Y. Influence of a headrest on reconstruction and attenuation correction of human brain SPECT images. J Nucl Med Technol. 2021;49(1):54–7.
Iwao Y, Akamatsu G, Tashima H, Takahashi M, Yamaya T. Pre-acquired CT-based attenuation correction with automated headrest removal for a brain-dedicated PET system. Radiol Phys Technol. 2023 Oct 11.
Iida H, Takahashi M, Motomura N, Hachiya T, Nakagawara J. Effects of Compton scatter in quantitative brain SPECT. Kaku Igaku. 1996;33(2):143–51.
Kanda Y. Investigation of the freely available easy-to-use software “EZR” for medical statistics. Bone Marrow Transplant. 2013;48(3):452–8.
Shibutani T, Onoguchi M, Miyamoto N, Yamamoto Y, Kinuya S. Influence of attenuation correction by brain perfusion SPECT/CT using a simulated abnormal bone structure: comparison between chang and CT methods. J Nucl Med Technol. 2017;45(3):208–13.
Camargo EE. Brain SPECT in neurology and psychiatry. J Nucl Med. 2001;42(4):611–23.
Akamatsu M, Yamashita Y, Akamatsu G, Tsutsui Y, Ohya N, Nakamura Y, Sasaki M. Influences of reconstruction and attenuation correction in brain SPECT images obtained by the hybrid SPECT/CT device: evaluation with a 3-dimensional brain phantom. Asia Ocean J Nucl Med Biol. 2014;2(1):24–9.
Nishiyama Y, Kinuya S, Kato T, Kayano D, Sato S, Tashiro M, Tatsumi M, Hashimoto T, Baba S, Hirata K, Yoshimura M, Yoneyama H. Nuclear medicine practice in Japan: a report of the eighth nationwide survey in 2017. Ann Nucl Med. 2019;33(10):725–32.
Brambilla M, Cannillo B, Dominietto M, Leva L, Secco C, Inglese E. Characterization of ordered-subsets expectation maximization with 3D post-reconstruction Gauss filtering and comparison with filtered backprojection in 99mTc SPECT. Ann Nucl Med. 2005;19(2):75–82.
Yokoi T, Shinohara H, Onishi H. Performance evaluation of OSEM reconstruction algorithm incorporating three-dimensional distance-dependent resolution compensation for brain SPECT: a simulation study. Ann Nucl Med. 2002;16(1):11–8.
Onishi H, Motomura N, Fujino K, Natsume T, Haramoto Y. Quantitative performance of advanced resolution recovery strategies on SPECT images: evaluation with use of digital phantom models. Radiol Phys Technol. 2013;6(1):42–53.
Acknowledgements
We would like to thank Editage (www.editage.com) for the English language editing.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
Yuta Yamazaki is an employee of Canon Medical Systems Corporation. Nakashima received software created in the interface definition language from Canon Medical Systems Corporation.
Ethics approval
All the procedures performed in this study, which involved human participants, were in accordance with the ethical standards of the institutional and/or national research committee and the 1964 Helsinki Declaration and its later amendments or comparable ethical standards. This study was approved by the Bioethics Committee of Okayama University Hospital (No. 2104–015).
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
About this article
Cite this article
Nakashima, M., Yamazaki, Y. Evaluation of attenuation correction method for head holder in brain perfusion single-photon emission computed tomography. Radiol Phys Technol 17, 322–328 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12194-024-00778-x
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12194-024-00778-x