Abstract
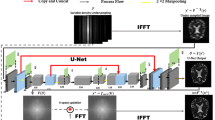
This study assessed the influence of deep learning reconstruction (DLR) on the quality of diffusion-weighted images (DWI) and apparent diffusion coefficient (ADC) using an ice-water phantom. An ice-water phantom with known diffusion properties (true ADC = 1.1 × 10–3 mm2/s at 0 °C) was imaged at various b-values (0, 1000, 2000, and 4000 s/mm2) using a 3 T magnetic resonance imaging scanner with slice thicknesses of 1.5 and 3.0 mm. All DWIs were reconstructed with or without DLR. ADC maps were generated using combinations of b-values 0 and 1000, 0 and 2000, and 0 and 4000 s/mm2. Based on the quantitative imaging biomarker alliance profile, the signal-to-noise ratio (SNRs) in DWIs was calculated, and the accuracy, precision, and within-subject parameter variance (wCV) of the ADCs were evaluated. DLR improved the SNR in DWIs with b-values ranging from 0 to 2000s/mm2; however, its effectiveness was diminished at 4000 s/mm2. There was no noticeable difference in the ADCs of images generated with or without implementing DLR. For a slice thickness of 1.5 mm and combined b-values of 0 and 4000 s/mm2, the ADC values were 0.97 × 10–3and 0.98 × 10–3mm2/s with and without DLR, respectively, both being lower than the true ADC value. Furthermore, DLR enhanced the precision and wCV of the ADC measurements. DLR can enhance the SNR, repeatability, and precision of ADC measurements; however, it does not improve their accuracies.





Similar content being viewed by others
Data statement
The data that has been used is confidential.
References
Weinreb JC, Barentsz JO, Choyke PL, Cornud F, Haider MA, Macura KJ, et al. PI-RADS prostate imaging - reporting and data system: 2015, version 2. Eur Urol. 2016;69:16–40. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eururo.2015.08.052.
Turkbey B, Rosenkrantz AB, Haider MA, Padhani AR, Villeirs G, Macura KJ, Reporting PI, Version DS, et al. Update of prostate imaging reporting and data system version 2. Eur Urol. 2019;2019(76):340–51. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eururo.2019.02.033.
Lee SI, Atri M. 2018 FIGO staging system for uterine cervical cancer: enter cross-sectional imaging. Radiology. 2019;292:15–24. https://doi.org/10.1148/radiol.2019190088.
Le Bihan DBE, Lallemand D, Grenier P, Cabanis E, Laval-Jeantet M. MR imaging of intravoxel incoherent motions: application to diffusion and perfusion in neurologic disorders. Radiology. 1986;161:401–7. https://doi.org/10.1148/radiology.161.2.3763909.
Surov A, Eger KI, Potratz J, Gottschling S, Wienke A, Jechorek D. Apparent diffusion coefficient correlates with different histopathological features in several intrahepatic tumors. Eur Radiol. 2023;33:5955–64. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00330-023-09788-6.
Ueda T, Ohno Y, Yamamoto K, Murayama K, Ikedo M, Yui M, et al. Deep learning reconstruction of diffusion-weighted mri improves image quality for prostatic imaging. Radiology. 2022;303:373–81. https://doi.org/10.1148/radiol.204097.
Kidoh M, Shinoda K, Kitajima M, Isogawa K, Nambu M, Uetani H, et al. Deep learning based noise reduction for brain mr imaging: tests on phantoms and healthy volunteers. Magn Reson Med Sci. 2020;19:195–206. https://doi.org/10.2463/mrms.mp.2019-0018.
Sagawa H, Fushimi Y, Nakajima S, Fujimoto K, Miyake KK, Numamoto H, et al. Deep learning-based noise reduction for fast volume diffusion tensor imaging: assessing the noise reduction effect and reliability of diffusion metrics. Magn Reson Med Sci. 2021;20:450–6. https://doi.org/10.2463/mrms.tn.2020-0061.
Tanabe M, Higashi M, Yonezawa T, Yamaguchi T, Iida E, Furukawa M, et al. Feasibility of high-resolution magnetic resonance imaging of the liver using deep learning reconstruction based on the deep learning denoising technique. Magn Reson Imaging. 2021;80:121–6. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mri.2021.05.001.
Ueda T, Ohno Y, Yamamoto K, Iwase A, Fukuba T, Hanamatsu S, et al. Compressed sensing and deep learning reconstruction for women’s pelvic MRI denoising: utility for improving image quality and examination time in routine clinical practice. Eur J Radiol. 2021;134: 109430. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejrad.2020.109430.
Yokota Y, Takeda C, Kidoh M, Oda S, Aoki R, Ito K, et al. Effects of deep learning reconstruction technique in high-resolution non-contrast magnetic resonance coronary angiography at a 3-tesla machine. Can Assoc Radiol J. 2021;72:120–7. https://doi.org/10.1177/0846537119900469.
Kashiwagi N, Sakai M, Tsukabe A, Yamashita Y, Fujiwara M, Yamagata K, et al. Ultrafast cervcial spine MRI protocol using deep learning-based reconstruction: diagnostic equivalence to a conventional protocol. Eur J Radiol. 2022;156: 110531. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejrad.2022.110531.
Akai H, Yasaka K, Sugawara H, Tajima T, Kamitani M, Furuta T, et al. Acceleration of knee magnetic resonance imaging using a combination of compressed sensing and commercially available deep learning reconstruction: a preliminary study. BMC Med Imaging. 2023;23:5. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12880-023-00962-2.
Hanamatsu S, Murayama K, Ohno Y, Yamamoto K, Yui M, Toyama H. Deep learning reconstruction for brain diffusion-weighted imaging: efficacy for image quality improvement, apparent diffusion coefficient assessment, and intravoxel incoherent motion evaluation in in vitro and in vivo studies. Diagn Interv Radiol. 2023. https://doi.org/10.4274/dir.2023.232149.
RSNA Quantitative imaging Biomarkers Alliance. QIBA Profile: Magnetic Resonance Diffusion-Weighted Imaging (DWI) of the Apparent Diffusion Coefficient (ADC); 2022. https://qibawiki.rsna.org/images/b/b0/QIBA_DWIProfile_Stage3_15Dec2022_v3.pdf. Accessed 9 Apr 2023.
Chenevert TL, Galban CJ, Ivancevic MK, Rohrer SE, Londy FJ, Kwee TC, et al. Diffusion coefficient measurement using a temperature-controlled fluid for quality control in multicenter studies. J Magn Reson Imaging. 2011;34:983–7. https://doi.org/10.1002/jmri.22363.
Malyarenko D, Galban CJ, Londy FJ, Meyer CR, Johnson TD, Rehemtulla A, et al. Multi-system repeatability and reproducibility of apparent diffusion coefficient measurement using an ice-water phantom. J Magn Reson Imaging. 2013;37:1238–46. https://doi.org/10.1002/jmri.23825.
Doblas S, Almeida GS, Ble FX, Garteiser P, Hoff BA, McIntyre DJ, et al. Apparent diffusion coefficient is highly reproducible on preclinical imaging systems: evidence from a seven-center multivendor study. J Magn Reson Imaging. 2015;42:1759–64. https://doi.org/10.1002/jmri.24955.
Yoshida T, Urikura A, Hosokawa Y, Shirata K, Nakaya Y, Endo M. Apparent diffusion coefficient measurement using thin-slice diffusion-weighted magnetic resonance imaging: assessment of measurement errors and repeatability. Radiol Phys Technol. 2021;14:203–9. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12194-021-00616-4.
Prah DE, Paulson ES, Nencka AS, Schmainda KM. A simple method for rectified noise floor suppression: phase-corrected real data reconstruction with application to diffusion-weighted imaging. Magn Reson Med. 2010;64:418–29. https://doi.org/10.1002/mrm.22407.
Ohno N, Miyati T, Kobayashi S, Gabata T. Modified triexponential analysis of intravoxel incoherent motion for brain perfusion and diffusion. J Magn Reson Imaging. 2016;43:818–23. https://doi.org/10.1002/jmri.25048.
Mournet S, Okubo G, Koubiyr I, Zhang B, Kusahara H, Prevost VH, et al. Higher b-values improve the correlation between diffusion MRI and the cortical microarchitecture. Neuroradiology. 2020;62:1411–9. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00234-020-02462-4.
Michoux NF, Ceranka JW, Vandemeulebroucke J, Peeters F, Lu P, Absil J, et al. Repeatability and reproducibility of ADC measurements: a prospective multicenter whole-body-MRI study. Eur Radiol. 2021;31:4514–27. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00330-020-07522-0.
Acknowledgements
We thank Naoko Mita and Shimpei Yano at Teikyo University Hospital and Seiko Shimizu at Canon Medical Systems Corporation for their technical support. We would like to thank Editage (www.editage.jp) for English language editing.
Funding
This study was partly supported by JSPS KAKENHI (grant number 23K07142).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflicts of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest.
Ethics approval
This study did not involve any experiments using human participants or animals.
Informed consent
Not required.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
About this article
Cite this article
Hayashi, T., Kojima, S., Ito, T. et al. Evaluation of deep learning reconstruction on diffusion-weighted imaging quality and apparent diffusion coefficient using an ice-water phantom. Radiol Phys Technol 17, 186–194 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12194-023-00765-8
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12194-023-00765-8