Abstract
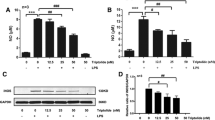
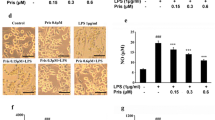
Microglia play an important role in neuronal protection and damage. However, the molecular and cellular relationship between microglia and neurons is unclear. We carried out a prospective study to detect that activation of BV2 microglia induced PC12 cell apoptosis in vitro through the TLR4/adapter protein myeloid differentiation factor 88 (MyD88)/nuclear factor-κB (NF-κB) signaling pathway. BV2 microglia were treated with different concentrations of LPS for 24 h. Western blot was utilized to detect the expression of TLR4 and the downstream signaling pathway. The level of inflammatory mediator was quantified using a specific ELISA kit. The supernatant of 10 μg/ml LPS-treated BV2 cells was used as conditioned medium (CM). PC12 cells were co-culture with CM for 24 h. Cell viability was determined by MTT assay and cell apoptosis was tested by flow cytometry. BV2 microglia were treated with 10, 20, or 30 μg/ml LPS for 24 h. The expression of TLR4, MyD88, and NF-κB significantly increased. When PC12 cells were co-cultured with CM for 24 h, cell viability decreased. CM up-regulated the Bax level and down-regulated the Bcl-2 protein level in PC12 cells. PC12 cells pretreated with interleukin-1 receptor antagonist (IL-1RA) for 30 min, significantly alleviated CM-induced PC12 cell apoptosis. These results suggest that BV2 microglia activated by LPS triggered TLR4/MyD88/NF-κB signaling pathway that induced the release of IL-1β and could participate in the PC12 cells injury.










Similar content being viewed by others
References
Akira S, Uematsu S, Takeuchi O (2006) Pathogen recognition and innate immunity. Cell 124:783–801
Aravalli RN, Peterson PK, Lokensgard JR (2007) Toll-like receptors in defense and damage of the central nervous system. J Neuroimmune Pharm 2:297–312
Arslan F, Keogh B, McGuirk P et al (2010) TLR2 and TLR4 in ischemia reperfusion injury. Mediat Inflamm 2010:704202
Arumugam TV, Okun E, Tang SC et al (2009) Toll-like receptors in ischemia-reperfusion injury. Shock 32:4–16
Baron R (2006) Mechanisms of disease: Neuropathic pain-A clinical perspective. Nat Clin Pract Neurol 2:95–106
Bechade C, Cantaut-Belarif Y, Bessis A (2013) Microglial control of neuronal activity. Front Cell Neurosci 7:32
Bessis A, Bechade C, Bernard D et al (2007) Microglial control of neuronal death and synaptic properties. Glia 55(3):233–238
Block ML, Hong J (2005) Microglia and inflammation-mediated neurodegeneration: Multiple triggers with a common mechanism. Prog Neurobiol 76(2):77–98
Brea D, Blanco M, Sobrino T et al (2010) The levels of expression of toll-like receptors 2 and 4 in neutrophils are associated with the prognosis of ischaemic stroke patients. Rev Neurol 52:12–19
Chao CC, Hu S, Ehrlich L et al (1995) Interleukin-1 and tumor necrosis factor-alpha synergistically mediate neurotoxicity: Involvement of nitric oxide and of N-methyl-D-aspartate receptors. Brain Behav Immun 9:355–365
Coull JA, Beggs S, Boudreau D et al (2005) BDNF from microglia causes the shift in neuronal anion gradient underlying neuropathic pain. Nature 438:1017–1021
De Paola M, Mariani A, Biqini P et al (2012) Neuroprotective effects of toll-like receptor 4 antagonism in spinal cord cultures and in a mouse model of motor neuron degeneration. Mol Med 18:971–981
Ding BJ, Ma WW, He LL et al (2011) Soybean isoflavone alleviates beta-amyloid 1–42 induced inflammatory response to improve learning and memory ability by down regulation of Toll-like receptor 4 expression and nuclear factor-kappaB activity in rats. Int J Dev Neurosci 29:537–542
Esser R, Glienke W, von Briesen H et al (1996) Differential regulation of proinflammatory and hematopoietic cytokines in human macrophages after infection with human immunodeficiency virus. Blood 88:3474–3481
Gao HM, Hong JS (2008) Why neurodegenerative diseases are progressive: uncontrolled inflammation drives disease progression. Trends Immunol 29(8):357–365
Gao HM, Liu B, Zhang W et al (2003) Novel anti-inflammatory therapy for Parkinson’s disease. Trends Pharmacol Sci 24(8):395–401
Graeber MB (2010) Changing face of microglia. Science 330(6005):783–788
Guo H, Jin YX, Ishikawa M et al (1998) Regulation of betachemokine mRNA expression in adult rat astrocytes by lipopolysaccharide, proinflammatory and immunoregulatory cytokines. Scand J Immunol 48:502–508
Gustafson-Vickers SL, Lu VB, Lai AY et al (2008) Long-term actions of interleukin-1beta on delay and tonic firing neurons in rat superficial dorsal horn and their relevance to central sensitization. Mol Pain 4:63
Hoarau JJ, Krejbich-Trotot P, Jaffar-Bandjee MC et al (2011) Activation and control of CNS innate immune responses in health and diseases: a balancing act finely tuned by neuroimmune regulators (NIReg). CNS Neurol Disord Drug Targets 10(1):25–43
Hughes V (2012) Microglia: the constant gardeners. Nature 485(7400):570–572
Inoue K, Tsuda M (2009) Microglia and neuropathic pain. Glia 57:1469–1479
Johnson GB, Brunn GJ, Platt JL (2003) Activation of mammalian Toll-like receptors by endogenous agonists. Crit Rev Immunol 23:15–44
Kawai T, Akira S (2006) TLR signaling. Cell Death Differ 13(5):816–825
Kawasaki Y, Zhang L, Cheng JK et al (2008) Cytokine mechanisms of central sensitization: Distinct and overlapping role of interleukin-1beta, interleukin-6, and tumor necrosis factor-alpha in regulating synaptic and neuronal activity in the superficial spinal cord. J Neurosci 28(20):5189–5194
Kilic U, Kilic E, Matter CM et al (2008) TLR-4 deficiency protects against focal cerebral ischemia and axotomy-induced neurodegeneration. Neurobiol Dis 31(1):33–40
Lee S, Vravel NH, Konerth ME et al (2010) CX3CR1 deficiency alters microglial activation and reduces β-amyloid deposition in two Alzheimer's disease mouse models. Am J Pathol 177(5):2552–2562
Lehnardt S (2010) Innate immunity and neuroinflammation in the CNS: the role of microglia in Toll-like receptor-mediated neuronal injury. Glia 58:253–263
Lehnardt S, Lachance C, Patrizi S (2002) The toll-like receptor TLR4 is necessary for lipopolysaccharide-induced oligodendrocyte injury in the CNS. J Neurosci 22(7):2478–2486
Lehnardt S, Massillon L, Follett P et al (2003) Activation of innate immunity in the CNS triggers neurodegeneration through a Toll-like receptor 4-dependent pathway. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 100:8514–8519
Lehnardt S, Schott E, Trimbuch T et al (2008) A vicious cycle involving release of heat shock protein60 from injured cells and activation of toll-Like receptor 4 mediates neurodegeneration in the CNS. Neuroscience 28:2320–2331
Liu Y, Walter S (2005) Staqi M, at al: LPS receptor (CD14): a receptor for phagocytosis of Alzheimer's amyloid peptide. Brain 128(8):1778–1789
Liu T, Gao YJ, Ji RR (2012) Emerging role of Toll-like receptors in the control of pain and itch. Neurosci Bull 28(2):131–144
Liu T, Jiang CY, Fujita T et al (2013) Enhancement by interleukin-1beta of AMPA and NMDA receptor-mediated currents in adult rat spinal superficial dorsal horn neurons. Mol Pain 9(1):16
Lu YC, Yeh WC, Ohashi PS (2008) LPS/TLR4 signal transduction pathway. Cytokine 42(2):145–151
Mao SS, Hua R, Zhao XP et al (2012) Exogenous administration of PACAP alleviates traumatic brain injury in rats through a mechanism involving the TLR4/MyD88/NF-κB pathway. J Neurotrauma 29(10):1941–1959
Medzhitov R (2001) Toll-like receptors and innate immunity. Nat Rev Immunol 1:135–145
Medzhitov R (2007) TLR-mediated innate immune recognition. Semin Immunol 19:1–2
Miyake K (2007) Innate immune sensing of pathogens and danger signals by cell surface Toll-like receptor. Semin Immunol 19:3–10
Mogensen TH (2009) Pathogen recognition and inflammatory signaling in innate immune defenses. Clin Microbiol Rev 22:240–273
Nimmerjahn A, Kirchhoff F, Helmchen F (2005) Resting microglial cells are highly dynamic surveillants of brain parenchyma in vivo. Science 308:1314–1318
Panaro MA, Lofrumento DD, Saponaro C et al (2008) Expression of TLR4 and CD14 in the central nervous system (CNS) in a MPTP mouse model of Parkinson's-like disease. Immunopharmacol Immunotoxicol 30:729–740
Qin X, Sun ZQ, Dai XJ et al (2012) Toll-like receptor 4 signaling is involved in PACAP-induced neuroprotection in BV2 microglial cells under OGD/reoxygenation. Neurol Res 34:610–615
Qin X, Sun ZQ, Zhang XW et al (2013) TLR4 signaling is involved in the protective effect of propofol in BV2 microglia against OGD/reoxygenation. J Physiol Biochem 64(4):707–718
Rajagopal N (2008) Inhibition of toll-like receptor signaling in primary murine microglia. J Neuroimmune Pharm 3:5–11
Rev P (2011) Physiology of microglia. Physiol Rev 91:461–553
Schulz J (2007) Woolf CJ: The neuropathic pain triad: Neurons, immune cells and glia. Nat Neurosci 10:1361–1368
Shu HF, Wang BR, Bi H et al (2007) PC12 cells express IL-1 receptor type I and response to IL-1 stimulation. Respir Physiol Neurobiol 157:187–195
Smith HS (2010) Activated microglia in nociception. Pain Physicians 13:295–304
Surace MJ, Block ML (2012) Targeting microglia-mediated neurotoxicity: the potential of NOX2 inhibitors. Cell Mol Life Sci 69:2409–2427
Suter MR, Wen YR, Decosterd I et al (2007) Do glial cells control pain? Neuron Glia Biol 3:255–268
Suzumura A (2013) Neuron-Microglia Interaction in Neuroinflammation. Curr Protein Pept Sci 14(1):16–20
Takeuchi O, Akira S (2010) Pattern recognition receptors and inflammation. Cell 140:805–820
Tanga FY, Nutile-McMenemy N, DeLeo JA (2005) The CNS role of Toll-like receptor 4 in innate neuroimmunity and painful neuropathy. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 102(16):5856–5861
Trang T, Beggs S, Salter MW (2012) ATP receptor gate microglia signaling in neuropathic pain. Exp Neurol 234:354–361
Tsuda M, Shigemoto-Mogami Y, Koizumi S et al (2003) P2X4 receptors induced in spinal microglia gate tactile allodynia after nerve injury. Nature 424:778–783
Tsuda M, Tozaki-Saitoh H, Inoue K (2012) Purinergic system, microglia and neuropathic pain. Curr Opin Pharmacol 12:74–79
Ulmann L, Hatcher JP, Hughes JP et al (2008) Up-regulation of P2X4 receptors in spinal microglia after peripheral nerve injury mediates BDNF release and neuropathic pain. Neuroscience 28:11263–11268
Vollmar P, Kullmann JS, Thilo B, Claussen MC, Rothhammer V, Jacobi H, Sellner J, Waak J, Weber SS, Waldenmaier A et al (2009) Regulation of astrocyte inflammatory responses by the Parkinson's disease-associated gene DJ-1. FASEB J 23:2478–2489
Wang C, Wang MW, Tashiro S et al (2005) IL-1β acts in synergy with endogenous IL-1β in A375-S2 human melanoma cell apoptosis through mitochondrial pathway. J Korean Med Sci 20:555–561
Yao L, Kan EM, Lu J et al (2013) Toll-like receptor 4 mediates microglial activation and production of inflammatory mediators in neonatal rat brain following hypoxia: role of TLR4 in hypoxic microglia. J Neuroinflammation 10:23
Ye L, Huang Y, Zhao L et al (2013) IL-1β and TNF-α induce neurotoxicity through glutamate production: a potential role for neuronal glutaminase. Neurochemistry 125(6):897–908
Zeng KW, Zhang T, Fu H et al (2012) Schisandrin B exerts anti-neuroinflammatory activity by inhibiting the Toll-like receptor 4-dependent MyD88/IKK/NF-κB signaling pathway in lipopolysaccharide-induced microglia. Eur J Pharmacol 692(1–3):29–37
Acknowledgments
This project was supported by grants from the National Natural Science of China (81171041), the Natural Science foundation of Jiangsu Province (BK2011197), Key Subject of Colleges and Universities Natural Science Foundation of Jiangsu Province (13KJA320001), the Natural Science fund for colleges and universities of Jiangsu Province (12KJD320005), the Innovation Project of Nanjing Military Region (ZD13), the University Graduate Student Science and Technology Innovation Project of Jiangsu Province (XYYC-1214), and sponsored by Qing Lan Project.
Competing interests
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Xiao-jing Dai and Na Li contributed equally to this work.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Dai, Xj., Li, N., Yu, L. et al. Activation of BV2 microglia by lipopolysaccharide triggers an inflammatory reaction in PC12 cell apoptosis through a toll-like receptor 4-dependent pathway. Cell Stress and Chaperones 20, 321–331 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12192-014-0552-1
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12192-014-0552-1