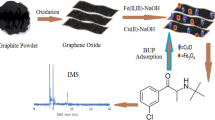
Abstract
A simple, fast and reliable graphene oxide nanosheets based dispersive solid-phase microextraction methodology was described for the quantification of trace amount of ethambutol. The determination of ethambutol quantified with the aim of ion mobility spectroscopy as a sensitive, rapid, inexpensive and environmentally friendly instrument. Effects of relevant experimental parameters on the method efficiency such as pH, type of buffer and its volume, amount of absorbent, desorption solvent and extract time were investigated to reach the maximum efficiency of the proposed method. Under the optimum conditions, the calibration curve was linear in the range of 1 to 120 μg L−1 with the R-squared (R2) of 0.9990. The limit of detection for proposed method (n = 8) was 0.4 μg L−1 and the relative standard deviations were obtained (n = 8) 3.3% and 1.6% for 10 and 100 μg L−1, respectively. The proposed method was successfully applied for the preconcentration and determination of ethambutol in the different biological samples such as plasma, saliva, breast milk and artificial tear.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Marks V (1979) Clinical monitoring of therapeutic drugs. Ann Clin Biochem 16(1-6):370–379. https://doi.org/10.1177/000456327901600195
Pribor HC, Morrell G, Scherr GH (1980) Drug monitoring and pharmacokinetic data. Pathotox Publishers, Illinois
Arthur CL, Pawliszyn J (1990) Solid phase microextraction with thermal desorption using fused silica optical fibers. Anal Chem 62(19):2145–2148. https://doi.org/10.1021/ac00218a019
Ocaña-González JA, Fernández-Torres R, Bello-López MÁ, Ramos-Payán M (2016) New developments in microextraction techniques in bioanalysis. A review. Anal Chim Acta 905:8–23. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aca.2015.10.041
Ouyang G, Pawliszyn J (2006) SPME in environmental analysis. Anal Bioanal Chem 386(4):1059–1073. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00216-006-0460-z
Hernández-Hernández AA, Álvarez-Romero GA, Contreras-López E, Aguilar-Arteaga K, Castañeda-Ovando A (2017) Food nalysis by microextraction methods based on the use of magnetic nanoparticles as supports: recent advances. Food Anal Methods 10(9):2974–2993
Kataoka H (2010) Recent developments and applications of microextraction techniques in drug analysis. Anal Bioanal Chem 396(1):339–364. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00216-009-3076-2
Huang S, Zhu F, Jiang R, Zhou S, Zhu D, Liu H, Ouyang G (2015) Determination of eight pharmaceuticals in an aqueous sample using automated derivatization solid-phase microextraction combined with gas chromatography–mass spectrometry. Talanta 136:198–203. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.talanta.2014.11.071
Ansari S, Karimi M (2017) Recent progress, challenges and trends in trace determination of drug analysis using molecularly imprinted solid-phase microextraction technology. Talanta 164:612–625. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.talanta.2016.11.007
Eisert R, Pawliszyn J (1997) Automated in-tube solid-phase microextraction coupled to high-performance liquid chromatography. Anal Chem 69(16):3140–3147. https://doi.org/10.1021/ac970319a
Tsai WH, Huang TC, Huang JJ, Hsue YH, Chuang HY (2009) Dispersive solid-phase microextraction method for sample extraction in the analysis of four tetracyclines in water and milk samples by high-performance liquid chromatography with diode-array detection. J Chromatogr A 1216(12):2263–2269. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chroma.2009.01.034
Bruheim I, Liu X, Pawliszyn J (2003) Thin-film microextraction. Anal Chem 75(4):1002–1010. https://doi.org/10.1021/ac026162q
Wu Q, Wang C, Liu Z, Wu C, Zeng X, Wen J, Wang Z (2009) Dispersive solid-phase extraction followed by dispersive liquid-liquid microextraction for the determination of some sulfonylurea herbicides in soil by high-performance liquid chromatography. J Chromatogr A 1216(29):5504–5510. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chroma.2009.05.062
Cha C, Shin SR, Annabi N, Dokmeci MR, Khademhosseini A (2013) Carbon-based nanomaterials: multifunctional materials for biomedical engineering. ACS Nano 7(4):2891–2897
Sitko R, Zawisza B, Malicka E (2013) Graphene as a new sorbent in analytical chemistry. TrAC - Trends Anal Chem 51:33–43. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.trac.2013.05.011
He H, Klinowski J, Forster M, Lerf A (1998) A new structural model for graphite oxide. Chem Phys Lett 287(1-2):53–56. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0009-2614(98)00144-4
Yoon YH, Jung KH, Sadun AA, Shin HC, Koh JY (2000) Ethambutol-induced vacuolar changes and neuronal loss in rat retinal cell culture: mediation by endogenous zinc. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol 162(2):107–114. https://doi.org/10.1006/taap.1999.8846
Chellini PR, Mendes TO, Franco PHC et al (2017) Simultaneous determination of rifampicin, isoniazid, pyrazinamide and ethambutol in 4-FDC tablet by Raman spectroscopy associated to chemometric approach. Vib Spectrosc 90:14–20. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.vibspec.2017.03.001
Lima AEB, Luz GE, Batista NC et al (2016) Determination of ethambutol in aqueous medium using an inexpensive gold microelectrode array as amperometric sensor. Electroanalysis 28(5):985–989. https://doi.org/10.1002/elan.201500600
Sepehri Z, Bagheri H, Ranjbari E, Amiri-Aref M, Amidi S, Rouini MR, Ardakani YH (2018) Simultaneous electrochemical determination of isoniazid and ethambutol using poly-melamine/electrodeposited gold nanoparticles modified pre-anodized glassy carbon electrode. Ionics (Kiel) 24(4):1253–1263. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11581-017-2263-y
Thanh Tung B, Thi Luyen L, Manh Hung T et al (2018) Simultaneous determination of pyrazinamide, rifampicin, ethambutol, isoniazid and acetyl isoniazid in human plasma by LC-MS/MS method ARTICLE INFO ABSTRACT. J Appl Pharm Sci 8(9):61–073. https://doi.org/10.7324/JAPS.2018.8910
Hummers WS, Offeman RE (1958) Preparation of graphitic oxide. J Am Chem Soc 80(6):1339. https://doi.org/10.1021/ja01539a017
Marcano DC, Kosynkin DV, Berlin JM, Sinitskii A, Sun Z, Slesarev A, Alemany LB, Lu W, Tour JM (2010) Improved synthesis of graphene oxide. ACS Nano 4(8):4806–4814. https://doi.org/10.1021/nn1006368
Beggs WH, Andrews FA (1974) Chemical characterization of ethambutol binding to Mycobacterium smegmatis. Antimicrob Agents Chemother 5(3):234–239. https://doi.org/10.1128/AAC.5.3.234
Jiang Y, Raliya R, Fortner JD, Biswas P (2016) Graphene oxides in water: correlating morphology and surface chemistry with aggregation behavior. Environ Sci Technol 50(13):6964–6973. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.est.6b00810
Ma CK, Mok CS, Hon PK (1995) Determination of benzhexol hydrochloride and ethambutol hydrochloride tablets by liquid chromatography. Anal Chim Acta 314(1-2):77–85. https://doi.org/10.1016/0003-2670(95)00264-Z
Conte JE, Lin E, Zhao Y, Zurlinden E (2002) A high-pressure liquid chromatographic-tandem mass spectrometric method for the determination of ethambutol in human plasma, bronchoalveolar lavage fluid, and alveolar cells. J Chromatogr Sci 40(2):113–118. https://doi.org/10.1093/chromsci/40.2.113
Yan M, Guo T, Song H, Zhao Q, Sui Y (2007) Determination of ethambutol hydrochloride in the combination tablets by precolumn derivatization. J Chromatogr Sci 45(5):269–272. https://doi.org/10.1093/chromsci/45.5.269
Singh H, Sharma G, Kaur IP (2014) Development and validation of an UPLC method for the quantification of ethambutol in rat plasma. RSC Adv 4(81):42831–42838. https://doi.org/10.1039/C4RA06052K
Prajapati P, Agrawal YK (2016) SFC-MS for the identification and estimation of ethambutol in its dosage form and in human urine samples. Anal Methods 8(24):4895–4902. https://doi.org/10.1039/C6AY01208F
Acknowledgments
The Damghan University Research Council (Damghan, Iran) is thanked for financial support of this project. The authors are grateful to the Verschuren Center for Sustainability in Energy and the Environment, Cape Breton University, Canada for their cooperation in this project. Also, we would like to acknowledge the Iranian Blood Transfusion Organization (Damghan, Iran) for providing the plasma samples.
Funding
This work was funded by the Damghan University Research Council.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Shafiee, A., Aibaghi, B. & Zhang, X. Determination of ethambutol in biological samples using graphene oxide based dispersive solid-phase microextraction followed by ion mobility spectrometry. Int. J. Ion Mobil. Spec. 23, 19–27 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12127-019-00253-z
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12127-019-00253-z