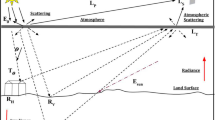
In earth observation, the atmospheric particles contaminate severely, through absorption and scattering, the reflected electromagnetic signal from the earth surface. It will be greatly beneficial for land surface characterization if we can remove these atmospheric effects from imagery and retrieve surface reflectance that characterizes the surface properties with the purpose of atmospheric correction. Giving the geometric parameters of the studied image and assessing the parameters describing the state of the atmosphere, it is possible to evaluate the atmospheric reflectance, and upward and downward transmittances which take part in the garbling data obtained from the image. To that end, an atmospheric correction algorithm for high spectral resolution data over land surfaces has been developed. It is designed to obtain the main atmospheric parameters needed in the image correction and the interpretation of optical observations. It also estimates the optical characteristics of the Earth-observation imagery (LANDSAT and SPOT). The physics underlying the problem of solar radiation propagations that takes into account multiple scattering and sphericity of the atmosphere has been treated using Monte Carlo techniques.






















Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ahern F J, Goodenough D G, Jain S C, Rao V R and Rochon G 1977 Use of clear lakes as standard reflectors for atmospheric measurements; In: Eleventh International Symposium on Remote Sensing of Environment, Ann Arbor, MI: Environmental Research Institute of Michigan, pp. 583–594.
Badescu V (ed.) 2008 Modeling solar radiation at the Earth’s surface: Recent advances (Berlin, Heidelberg: Springer-Verlag), 537p.
Bird R E and Riordan C 1986 Simple solar spectral model for direct and diffuse irradiance on horizontal and tilted planes at the earth’s surface for cloudless atmospheres; J. Climate Appl. Meteorol. 25 87–97.
Bonn F J, Collet C, Caloz R and et Rochon G 2001 Précis de télédétection: Traitements numériques d’images de télédétection; Association des universités partiellement ou entièrement de langue française, UREF, Agence universitaire de la francophonie, PUQ, 160p.
Capderou M 2005 Satellites: Orbits and Missions (France: Springer-Verlag), 544p.
Carr S B 2005 The aerosol models in MODTRAN: Incorporating selected measurements from northern Australia, Intelligence, Surveillance and Reconnaissance Division, Defence Science and Technology Organisation, DSTO-TR-1803, 67p.
Centre d’Etudes Spatiales de la BIOsphère (CESBIO) 2007 Principes Physique de DART, référence DART Handbook, Associated Industrial Company: Magellium, 70p.
Chami M, Santer R and Dilligeard E 2001 Radiative transfer model for the computation of radiance and polarization in an ocean–atmosphere system: Polarization properties of suspended matter for remote sensing; Appl. Opt. 40(15) 2398–2416.
Chander G 2009 Questionnaire for information regarding the CEOS WGCV IVOS subgroup Cal/Val test sites for land imager radiometric gain, Version 1.1, CEOS, 25p.
Chander G, Markham B L and Helder D L 2009 Summary of current radiometric calibration coefficients for Landsat MSS, TM, ETM+, and EO-1 ALI sensors; Remote Sens. Environ. 113 893–903.
Chavez P S Jr 1989 Radiometric calibration of Landsat Thematic Mapper multispectral images; Photogram. Eng. Rem. Sens. 55(9) 1285–1294.
Fraser R S, Ferrare R A, Kaufman Y J, Markham B L and Mattoo S 1992 Algorithm for atmospheric corrections of aircraft and satellite imagery; Int. J. Remote Sens. 13(3) 541–557.
Gascon F 2001 Modélisation Physique d’Images de Télédétection Optique; Thèse de doctorat, université de Toulouse III, discipline: signaux, images et acoustique, 174p.
Gueymard C 1995 SMARTS2, Simple Model of the Atmospheric Radiative Transfer of Sunshine: Algorithms and Performance Assessment; Rep. FSEC-PF-270–95, Florida Solar Energy Center, Cocoa, FL, 84p.
Gueymard C A and Kambezidis H D 1997 Solar radiation and daylight models; In: Solar Spectral Radiation, Elsevier Butterworth-Heinemann, Linacre House, Jordan Hill, Oxford OX2 8DP, pp. 221–301.
Hadjit H 2007 Résolution par la Méthode Monte Carlo des Problèmes de Transfert Radiatif dans une Atmosphère Sphérique, thèse de Magister, université de science et de la technologie d’Oran, 127p.
Hall F G, Strebel D E, Nickeson J E and Goetz S J 1991 Radiometric rectification: Toward a common radiometric response among multidate, multisensor images; Remote Sens. Environ. 35 11–27.
Hinds W C 1998 Aerosol technology: Properties, behavior, and measurement of airborne particles, 2nd edn, A Wiley-Interscience Publication, John Wiley & Sons, INC., 200p.
Iqbal M 1983 An introduction to solar radiation; Academic Press, Toronto.
Kaufman J Y and Sendra C 1988 Algorithm for automatic atmospheric corrections to visible and near-IR satellite imagery; Int. J. Remote Sens. 9(8) 1357–1381.
Kokhanovsky A A 2008 Aerosol optics: Light absorption and scattering by particles in the atmosphere; Springer–Praxis books in Environmental Sciences, 154p.
Kondratyev K Y A 1969 Radiation in the atmosphere, Volume 12, Academic Press, INC, 929p.
Koschmieder H 1924 Theorie der horizontalen Sichtweite; Beitr. Phys. Atmos. 12 33–53.
Koussa M, Malek A and Haddadi M 2006 Validation de quelques modèles de reconstitution des éclairements dus au rayonnement solaire direct, diffus et global par ciel clair; Revue des Energies Renouvelables 9N°4 307–332.
Leckner B 1978 The spectral distribution of solar radiation at the earth’s surface – elements of a model; Solar Energy 20 143–150.
Liang S 2004 Quantitative remote sensing of land surfaces, John Wiley & Sons, Inc., 562p.
Liou K N 2002 An introduction to atmospheric radiation, 2nd edn, Academic Press, An imprint of Elsevier Science, 599p.
Marchuk G I and Mikhailov G A 1980 The Monte Carlo methods in atmospheric optics; Springer series in optical sciences, 210p.
Psiloglou B E, Santamouris M and Asimakopoulos D N 2000 Atmospheric broadband model for computation of solar radiation at the earth’s surface: Application to mediterranean climate, Birkhauser Verlag, Basel; Pure Appl. Geophys. 157 829–860.
Rees W G 2001 Physical principles of remote sensing; 2nd edn, Cambridge University Press, 369p.
Richter R 1996 A spatially adaptive fast atmospheric correction algorithm; Int. J. Remote Sens. 17 1201–1214.
Schowengerdt R A 2007 Remote sensing: Models and methods for image processing, 3rd edn, Academic Press, An imprint of Elsevier Science, 558p.
Shettle E P and Fenn R W 1979 Models for the Aerosols of the lower atmosphere and the effects of humidity on their optical properties, Optical Physics Division, Project 7670, Air Force Geophysics Laboratory, Air Force Systems Command, Usaf, 94p.
Tanre D, Deschamps P Y, Devaux C and Herman M 1988 Estimation of Saharan aerosol optical thickness from blurring effects in Thematic Mapper data; J. Geophys. Res. 93 15,955–15,964.
Teillet P M and Fedosejevs G 1995 On the dark target approach to atmospheric correction of remotely sensed data; Canadian J. Remote Sens. 21(4) 374–387.
Thomas G E and Stamnes K 1999 Radiative Transfer in the Atmosphere and Ocean, Cambridge Atmospheric and Space Science Series, Cambridge University Press, 540p.
Thome K J 2001 Absolute radiometric calibration of Landsat 7 ETM+ using the reflectance-based method; Remote Sens. Environ. 78 27–38.
Van Heuklon T K 1979 Estimating atmospheric ozone for solar radiation models; Solar Energy 22 63–68.
Vermote E, Tanré D, Deuzé J L, Herman M and Morcrette J 1997 Second Simulation of the Satellite Signal in the Solar Spectrum (6S), 6S User Guide Version 2, Formerly affiliated to Laboratoire d’Optique Atmosphérique, part 2, 83p.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
HADJIT, H., OUKEBDANE, A. & BELBACHIR, A.H. Atmospheric correction of Earth-observation remote sensing images by Monte Carlo method. J Earth Syst Sci 122, 1219–1235 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12040-013-0337-4
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12040-013-0337-4