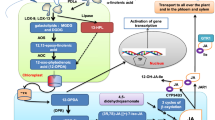
Abstract
Plant hormones regulate growth, development, and defense against biotic and abiotic stresses. Salicylic acid (SA), ethylene (ET), and jasmonate (JA) are major phytohormones that control the defense against pathogens. SA and JA primarily regulate resistance against biotrophic and necrotrophic pathogens, respectively. NPR1 is the key regulator of SA signaling in plants. AtOZF1 function has recently been ascribed to promote both NPR1- dependent and -independent SA signaling. However, the role of AtOZF1 in JA signaling was not known. Here we report AtOZF1 as a positive regulator of JA signaling in Arabidopsis. The atozf1 mutants are more susceptible to the necrotrophic pathogen Botrytis cinerea than wildtype (WT) plants. AtOZF1 positively regulates the expression of JA inducible genes like PDF1.2, VSP2, THI2.1, and ORA59. AtOZF1 takes part in SA-JA cross-talk to an extent similar to that of NPR1. AtOZF1 is essential for the activation of PDF1.2 expression upon exogenous methyl-jasmonate (MeJA) application. Intriguingly, SA can significantly promote MeJA-induced PDF1.2 expression in the absence of AtOZF1. Altogether our results reveal a novel SA-JA interaction pathway in plants.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Caarls L, Van der Does D, Hickman R, Jansen W, Verk MC, Proietti S, Lorenzo O, Solano R, Pieterse CM and Van Wees SC 2017 Assessing the role of ETHYLENE RESPONSE FACTOR transcriptional repressors in salicylic acid-mediated suppression of jasmonic acid-responsive genes. Plant Cell Physiol. 58 266–278
Chini A, Fonseca S, Fernandez G, Adie B, Chico JM, Lorenzo O, Garcia-Casado G, Lopez-Vidriero I, Lozano FM, Ponce MR, Micol JL and Solano R 2007 The JAZ family of repressors is the missing link in jasmonate signalling. Nature 448 666–671
Ding P and Ding Y 2020 Stories of salicylic acid: a plant defense hormone. Trends Plant Sci. 25 549–565
He P, Chintamanani S, Chen Z, Zhu L, Kunkel BN, Alfano JR, Tang X and Zhou JM 2004 Activation of a COI1-dependent pathway in Arabidopsis by Pseudomonas syringae type III effectors and coronatine. Plant J. 37 589–602
Huang P, Chung MS, Ju HW, Na HS, Lee DJ, Cheong HS and Kim CS 2011 Physiological characterization of the Arabidopsis thaliana oxidation-related zinc finger 1 a plasma membrane protein involved in oxidative stress. J. Plant Res. 124 699–705
Huot B, Yao J, Montgomery BL and He SY 2014 Growth-defense tradeoffs in plants: a balancing act to optimize fitness. Mol. Plant 7 1267–1287
Jirage D, Zhou N, Cooper B, Clarke JD, Dong X and Glazebrook J 2001 Constitutive salicylic acid-dependent signaling in cpr1 and cpr6 mutants requires PAD4. Plant J. 26 395–407
Kloek AP, Verbsky ML, Sharma SB, Schoelz JE, Vogel J, Klessig DF and Kunkel BN 2001 Resistance to Pseudomonas syringae conferred by an Arabidopsis thaliana coronatine-insensitive (coi1) mutation occurs through two distinct mechanisms. Plant J. 26 509–522
Lee SJ, Jung HJ, Kang H and Kim SY 2012 Arabidopsis zinc finger proteins AtC3H49/AtTZF3 and AtC3H20/AtTZF2 are involved in ABA and JA responses. Plant Cell Physiol. 53 673–686
Lefevere H, Bauters L and Gheysen G 2020 Salicylic acid biosynthesis in plants. Front. Plant Sci. 11 338
Leon-Reyes A, Spoel SH, De Lange ES, Abe H, Kobayashi M, Tsuda S, Millenaar FF, Welschen RA, Ritsema T and Pieterse CM 2009 Ethylene modulates the role of NONEXPRESSOR OF PATHOGENESIS-RELATED GENES1 in cross talk between salicylate and jasmonate signaling. Plant Physiol. 149 1797–1809
Moffat CS, Ingle RA, Wathugala DL, Saunders NJ, Knight H and Knight MR 2012 ERF5 and ERF6 play redundant roles as positive regulators of JA/Et-mediated defense against Botrytis cinerea in Arabidopsis. PLoS One 7 e35995
Nandi A, Moeder W, Kachroo P, Klessig DF and Shah J 2005 Arabidopsis ssi2-conferred susceptibility to Botrytis cinerea is dependent on EDS5 and PAD4. Mol. Plant Microbe Interact. 18 363–370
Nandi A, Kachroo P, Fukushige H, Hildebrand DF, Klessig DF and Shah J 2003 Ethylene and jasmonic acid signaling affect the NPR1-independent expression of defense genes without impacting resistance to Pseudomonas syringae and Peronospora parasitica in the Arabidopsis ssi1 mutant. Mol. Plant Microbe Interact. 16 588–599
Peng Y, Yang J, Li X and Zhang Y 2021 Salicylic acid: biosynthesis and signaling. Annu. Rev. Plant Biol. 72 761–791
Pieterse CM, Van der Does D, Zamioudis C, Leon-Reyes A and Van Wees SC 2012 Hormonal modulation of plant immunity. Annu. Rev. Cell. Dev. Biol. 28 489–521
Pre M, Atallah M, Champion A, De Vos M, Pieterse CM and Memelink J 2008 The AP2/ERF domain transcription factor ORA59 integrates jasmonic acid and ethylene signals in plant defense. Plant Physiol. 147 1347–1357
Rahman TA, Oirdi ME, Gonzalez-Lamothe R and Bouarab K 2012 Necrotrophic pathogens use the salicylic acid signaling pathway to promote disease development in tomato. Mol. Plant Microbe Interact. 25 1584–1593
Roy S and Nandi AK 2017 Arabidopsis thaliana methionine sulfoxide reductase B8 influences stress-induced cell death and effector-triggered immunity. Plant Mol. Biol. 93 109–120
Shah J 2009 Plants under attack: systemic signals in defence. Curr. Opin. Plant Biol. 12 459–464
Shah J, Kachroo P and Klessig DF 1999 The Arabidopsis ssi1 mutation restores pathogenesis-related gene expression in npr1 plants and renders defensin gene expression salicylic acid dependent. Plant Cell 11 191–206
Shah J, Kachroo P, Nandi A and Klessig DF 2001 A recessive mutation in the Arabidopsis SSI2 gene confers SA- and NPR1-independent expression of PR genes and resistance against bacterial and oomycete pathogens. Plant J. 25 563–574
Singh N, Swain S, Singh A and Nandi AK 2018 AtOZF1 positively regulates defense against bacterial pathogens and NPR1-independent salicylic acid signaling. Mol. Plant Microbe Interact. 31 323–333
Singh V, Singh D, Gautam JK and Nandi AK 2019 RSI1/FLD is a positive regulator for defense against necrotrophic pathogens. Physiol. Mol. Plant Pathol. 107 40–45
Singh V, Roy S, Giri MK, Chaturvedi R, Chowdhury Z, Shah J and Nandi AK 2013 Arabidopsis thaliana FLOWERING LOCUS D is required for systemic acquired resistance. Mol. Plant Microbe Interact. 26 1079–1088
Spoel SH, Koornneef A, Claessens SM, Korzelius JP, Van Pelt JA, Mueller MJ, Buchala AJ, Metraux JP, Brown R, Kazan K, Van Loon LC, Dong X and Pieterse CM 2003 NPR1 modulates cross-talk between salicylate- and jasmonate-dependent defense pathways through a novel function in the cytosol. Plant Cell 15 760–770
Swain S, Singh N and Nandi AK 2015 Identification of plant defence regulators through transcriptional profiling of Arabidopsis thaliana cdd1 mutant. J. Biosci. 40 137–146
Swain S, Roy S, Shah J, Van Wees S, Pieterse CM and Nandi AK 2011 Arabidopsis thaliana cdd1 mutant uncouples the constitutive activation of salicylic acid signalling from growth defects. Mol. Plant Pathol. 12 855–865
Thines B, Katsir L, Melotto M, Niu Y, Mandaokar A, Liu G, Nomura K, He SY, Howe GA and Browse J 2007 JAZ repressor proteins are targets of the SCF(COI1) complex during jasmonate signalling. Nature 448 661–665
Yang J, Duan G, Li C, Liu L, Han G, Zhang Y and Wang C 2019 The crosstalks between jasmonic acid and other plant hormone signaling highlight the involvement of jasmonic acid as a core component in plant response to biotic and abiotic stresses. Front. Plant Sci. 10 1349
Yang YX, Ahammed GJ, Wu C, Fan SY and Zhou YH 2015 Cross-talk among jasmonate, salicylate and ethylene signaling pathways in plant disease and immune responses. Curr. Protein Pept. Sci. 16 450–461
Zhang W, Corwin JA, Copeland DH, Feusier J, Eshbaugh R, Cook DE, Atwell S and Kliebenstein DJ 2019 Plant-necrotroph co-transcriptome networks illuminate a metabolic battlefield. Elife 8 e44279
Zhang X, Zhu Z, An F, Hao D, Li P, Song J, Yi C and Guo H 2014 Jasmonate-activated MYC2 represses ETHYLENE INSENSITIVE3 activity to antagonize ethylene-promoted apical hook formation in Arabidopsis. Plant Cell 26 1105–1117
Acknowledgements
This work is supported by the CSIR research grant (38(1515)/21/EMR-II) to AKN. NS acknowledges the fellowship UGC. The authors acknowledge infrastructural support from the Advanced Instrumentation Research Facility and Common Instrument Facility, and DST FIST-II grant of JNU
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Communicated by Manchikatla Venkat Rajam.
Corresponding editor: Manchikatla Venkat Rajam
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Singh, N., Nandi, A.K. AtOZF1 positively regulates JA signaling and SA-JA cross-talk in Arabidopsis thaliana. J Biosci 47, 8 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12038-021-00243-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12038-021-00243-6