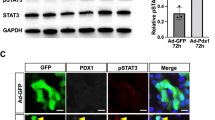
Abstract
Limitation in the number of insulin-producing pancreatic β-cells is a typical feature of diabetes. It has been indicated that activating pancreatic transcription factors can promote the transformation of hepatocytes into insulin-secreting β-like cells, indicating that direct hepatocyte differentiation seems promising as a treatment for diabetes. Nevertheless, the reprogramming efficiency still remains low. Our previous study found that the expression of c-fos-induced growth factor (FIGF) was increased in the pancreatic tissues in partial pancreatectomy mice compared to that in normal mice. Here, we observed that treatment with Ad-FIGF was found to enhance MafA and Ngn3-induced reprogramming of BNL CL.2 cells to β-like cells with the ability of secreting insulin. And FIGF overexpression increased the levels of histone H3/H4 acetylation at MafA and Ngn3 promoter regions in BNL CL.2 cells. Importantly, in vivo study further confirmed that forced expression of FIGF facilitated the insulin expression and decreased the blood glucose levels in STZ mice. These results strengthen the possibility of developing cell-based therapies for diabetes through utilizing β-like cells derived from non-insulin-secreting cells.




Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- Ngn3:
-
Neurogenin-3
- FIGF:
-
C-fos-induced growth factor
- VEGF-D:
-
Vascular endothelial growth factor-D
- DMEM:
-
Dulbecco’s modified Eagle’s medium
- FBS:
-
Fetal bovine serum
- PFA:
-
Paraformaldehyde
- BSA:
-
Bovine serum albumin
- RIPA:
-
Radioimmunoprecipitation assay
- STZ:
-
Streptozotocin
References
Achen MG, Jeltsch M, Kukk E, Mäkinen T, Vitali A, Wilks AF, Alitalo K and Stacker SA 1998 Vascular endothelial growth factor D (VEGF-D) is a ligand for the tyrosine kinases VEGF receptor 2 (Flk1) and VEGF receptor 3 (Flt4). Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 95 548–553
Chang FP, Cho CH, Shen CR, Chien CY, Ting LW, Lee HS and Shen CN 2016 PDGF Facilitates direct lineage reprogramming of hepatocytes to functional ß-like cells induced by Pdx1 and Ngn3. Cell Transplant. 25 1893–1909
Davydova N, Harris N, Roufail S, Paquet-Fifield S, Ishaq M, Streltsov V, Williams S, Karnezis T, et al. 2016 Differential receptor binding and regulatory mechanisms for the lymphangiogenic growth factors vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF)-C and -D. J. Biol. Chem. 291 27265–27278
Docherty HM, Hay CW, Ferguson LA, Barrow J, Durward E and Docherty K 2005 Relative contribution of PDX-1, MafA and E47/beta2 to the regulation of the human insulin promoter. Biochem. J. 389 813–820
Honkanen H, Izzi V, Petäistö T, Holopainen T, Harjunen V, Pihlajaniemi T, Alitalo K and Heljasvaara R 2016 Elevated VEGF-D modulates tumor inflammation and reduces the growth of carcinogen-induced skin tumors. Neoplasia 18 436–446
Jauhiainen S, Häkkinen S, Toivanen P, Heinonen S, Jyrkkänen H, Kansanen E, Leinonen H, Levonen A, et al. 2011 Vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF)-D stimulates VEGF-A, stanniocalcin-1, and neuropilin-2 and has potent angiogenic effects. Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 31 1617–1624
Jung Y, Zhou R, Kato T, Usui JK, Muratani M, Oishi H, Heck MMS and Takahashi S 2018 Isl1beta overexpression with key beta cell transcription factors enhances glucose-responsive hepatic insulin production and secretion. Endocrinology 159 869–882
Kaczorowski DJ, Patterson ES, Jastromb WE and Shamblott MJ 2010 Glucose-responsive insulin-producing cells from stem cells. Diabetes Metab. Res. Rev. 18 442–450
Kholová I, Koota S, Kaskenpää N, Leppänen P, Närväinen J, Kavec M, Rissanen T, Hazes T, et al. 2007 Adenovirus-mediated gene transfer of human vascular endothelial growth factor-d induces transient angiogenic effects in mouse hind limb muscle. Hum. Gene Ther. 18 232–244
Kocic G, Cukuranovic J, Stoimenov TJ, Cukuranovic R, Djordjevic V, Bogdanovic D and Stefanovic V 2014 Global and specific histone acetylation pattern in patients with Balkan endemic nephropathy, a worldwide disease. Ren. Fail. 36 1078–1082
Lee A, Lee J, Jung Y, Kim D, Kang K, Lee S, Park S, Lee S, et al. 2013 Vascular endothelial growth factor-C and -D are involved in lymphangiogenesis in mouse unilateral ureteral obstruction. Kidney Int. 83 50–62
Matsuoka T, Kaneto H, Kawashima S, Miyatsuka T, Tochino Y, Yoshikawa A, Imagawa A, Miyazaki J. et al. 2015 Preserving Mafa expression in diabetic islet β-cells improves glycemic control in vivo. J. Biol. Chem. 290 7647–7657
Morfoisse F, Tatin F, Hantelys F, Adoue A, Helfer A, Cassant-Sourdy S, Pujol F, Gomez-Brouchet A, et al. 2016 Nucleolin promotes heat shock-associated translation of VEGF-D to promote tumor lymphangiogenesis. Cancer Res. 76 4394–4405
Nishimura W, Takahashi S and Yasuda K 2015 MafA is critical for maintenance of the mature beta cell phenotype in mice. Diabetologia 58 566–574
Orlandini M, Marconcini L, Ferruzzi R and Oliviero S 1996 Identification of a c-fos-induced gene that is related to the platelet-derived growth factor/vascular endothelial growth factor family. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 93 11675–11680
Oropeza D and Horb M 2012 Transient expression of Ngn3 in Xenopus endoderm promotes early and ectopic development of pancreatic beta and delta cells. Genesis 50 271–285
Papiewska-Pająk I, Balcerczyk A, Stec-Martyna E, Koziołkiewicz W and Boncela J 2017 Vascular endothelial growth factor-D modulates oxidant-antioxidant balance of human vascular endothelial cells. J Cell Mol. Med. 21 1139–1149
Roy H, Bhardwaj S, Babu M, Lahteenvuo JE and Yla-Herttuala S 2010 VEGF-DdeltaNdeltaC mediated angiogenesis in skeletal muscles of diabetic WHHL rabbits. Eur. J. Clin. Invest. 40 422–432
Rutanen J, Rissanen T, Markkanen J, Gruchala M, Silvennoinen P, Kivelä A, Hedman A, Hedman M, et al. 2004 Adenoviral catheter-mediated intramyocardial gene transfer using the mature form of vascular endothelial growth factor-D induces transmural angiogenesis in porcine heart. Circulation 109 1029–1035
Sato T, Paquet-Fifield S, Harris N, Roufail S, Turner D, Yuan Y, Zhang Y, Fox S, et al. 2016 VEGF-D promotes pulmonary oedema in hyperoxic acute lung injury. J. Pathol. 239 152–161
Sun L, Duan J, Jiang Y, Wang L, Huang N, Lin L, Liao Y and Liao W 2015 Metastasis-associated in colon cancer-1 upregulates vascular endothelial growth factor-C/D to promote lymphangiogenesis in human gastric cancer. Cancer Lett. 357 242–253
Teng ZG, Wei J and Fan H 2012 The important role of c-fos-induced growth factor in the pancreas regeneration. Chin. J. Diabetes 5 373–376
Xu H, Tsang KS, Chan JC, Yuan P, Fan R, Kaneto H and Xu G 2013 The combined expression of Pdx1 and MafA with either Ngn3 or NeuroD improves the differentiation efficiency of mouse embryonic stem cells into insulin-producing cells. Cell Transplant. 22 147–158
You YH, Ham DS, Park HS, Rhee M, Kim JW and Yoon KH 2011 Adenoviruses expressing PDX-1, BETA2/NeuroD and MafA induces the transdifferentiation of porcine neonatal pancreas cell clusters and adult pig pancreatic cells into beta-cells. Diabetes Metab. J. 35 119–129
Acknowledgements
This study was supported by Project of Ningxia Natural Science Foundation (Grant No.: 2018AAC03264), First-Class Discipline Construction Founded Project of Ningxia Medical University and the School of Clinical Medicine (Grant No.: NXYLXK2017A05) and National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant No.: 81460152).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Additional information
Corresponding editor: Ullas Kolthur-Seetharam
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
He, Y., Xie, X., Li, X. et al. Effect of FIGF overexpression on liver cells transforming to insulin-producing cells. J Biosci 44, 149 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12038-019-9965-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12038-019-9965-4