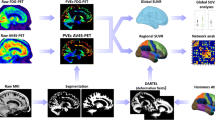
Abstract
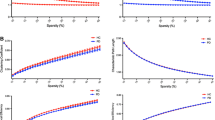
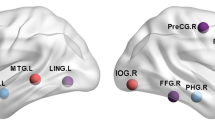
Beta-amyloid (Aβ) in the brain is a key pathological feature of certain neurodegenerative diseases. Recent studies using graph theory have shown that Aβ brain networks are of pathological significance in Alzheimer’s disease (AD). However, the characteristics of Aβ brain networks in Parkinson’s disease (PD) are unknown. In the present study using positron emission tomography (PET) with [11C]-Pittsburgh compound B (PiB), we applied a graph theory–based analysis to assess the topological properties of Aβ brain network in PD patients with and without Aβ burden (PiB-positive and PiB-negative, respectively) and healthy controls with Aβ burden. We found that the PD PiB-positive group demonstrated significantly lower value in global efficiency and modularity compared with PD PiB-negative group. The less robust modular structure indicates the tendency of having increased inter-modular connections than intra-modular connectivity (i.e., reduced segregation). Results of hub organization showed that relative to PD PiB-negative group, different hubs were identified in the PiB-positive group, which were located mainly within the default mode network. Overall, our findings suggest disturbances in Aβ topological organization characterized by abnormal network integration and segregation in PD patients with Aβ burden. The stronger inter-modular connectivity observed in the PD PiB-positive group may suggest the spreading pattern of Aβ between modules in those PD patients with elevated PiB burden, thus providing insight into the beta-amyloidopathy of PD.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Khoo TK, Yarnall AJ, Duncan GW, Coleman S, O’Brien JT, Brooks DJ, Barker RA, Burn DJ (2013) The spectrum of nonmotor symptoms in early Parkinson disease. Neurology 80(3):276–281
Valli M, Mihaescu A, Strafella AP (2017) Imaging behavioural complications of Parkinson’s disease. Brain Imaging Behav. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11682-017-9764-1
Mattila P, Rinne J, Helenius H, Dickson DW, Röyttä M (2000) Alpha-synuclein-immunoreactive cortical Lewy bodies are associated with cognitive impairment in Parkinson’s disease. Acta Neuropathol 100(3):285–290
Petrou M, Bohnen NI, Müller ML, Koeppe RA, Albin RL, Frey KA (2012) Aβ-Amyloid deposition in patients with Parkinson disease at risk for development of dementia. Neurology 79(11):1161–1167
Klunk WE, Engler H, Nordberg A, Wang Y, Blomqvist G, Holt DP, Bergström M, Savitcheva I et al (2004) Imaging brain amyloid in Alzheimer’s disease with Pittsburgh Compound-B. Ann Neurol 55(3):306–319
Mintun M, Larossa G, Sheline Y, Dence C, Lee SY, Mach R, Klunk W, Mathis C et al (2006) [11C] PIB in a nondemented population potential antecedent marker of Alzheimer disease. Neurology 67(3):446–452
Petrou M, Dwamena BA, Foerster BR, MacEachern MP, Bohnen NI, Müller MLTM, Albin RL, Frey KA (2015) Amyloid deposition in Parkinson’s disease and cognitive impairment: a systematic review. Mov Disord 30(7):928–935. https://doi.org/10.1002/mds.26191
Maetzler W, Reimold M, Liepelt I, Solbach C, Leyhe T, Schweitzer K, Eschweiler GW, Mittelbronn M et al (2008) [11C]PIB binding in Parkinson’s disease dementia. Neuroimage 39(3):1027–1033. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuroimage.2007.09.072
Edison P, Rowe CC, Rinne JO, Ng S, Ahmed I, Kemppainen N, Villemagne VL, O’Keefe G et al (2008) Amyloid load in Parkinson’s disease dementia and Lewy body dementia measured with [11C] PIB positron emission tomography. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry 79(12):1331–1338
Gomperts SN, Locascio JJ, Rentz D, Santarlasci A, Marquie M, Johnson KA, Growdon JH (2013) Amyloid is linked to cognitive decline in patients with Parkinson disease without dementia. Neurology 80(1):85–91
Akhtar RS, Xie SX, Chen YJ, Rick J, Gross RG, Nasrallah IM, Van Deerlin VM, Trojanowski JQ et al (2017) Regional brain amyloid-β accumulation associates with domain-specific cognitive performance in Parkinson disease without dementia. PLoS One 12(5):e0177924. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0177924
Campbell MC, Markham J, Flores H, Hartlein JM, Goate AM, Cairns NJ, Videen TO, Perlmutter JS (2013) Principal component analysis of PiB distribution in Parkinson and Alzheimer diseases. Neurology 81(6):520–527. https://doi.org/10.1212/WNL.0b013e31829e6f94
Bullmore E, Sporns O (2009) Complex brain networks: graph theoretical analysis of structural and functional systems. Nat Rev Neurosci 10(3):186–198
Sporns O (2011) The human connectome: a complex network. Ann N Y Acad Sci 1224:109–125. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1749-6632.2010.05888.x
Sepulcre J, Sabuncu MR, Becker A, Sperling R, Johnson KA (2013) In vivo characterization of the early states of the amyloid-beta network. Brain 136 (Pt 7:2239–2252. https://doi.org/10.1093/brain/awt146
Jiang J, Duan H, Huang Z, Yu Z, Alzheimer’s Disease Neuroimaging I (2015) Study of amyloid-beta peptide functional brain networks in AD, MCI and HC. Biomed Mater Eng 26(Suppl 1):S2197–S2205. https://doi.org/10.3233/BME-151525
Duan H, Jiang J, Xu J, Zhou H, Huang Z, Yu Z, Yan Z, Initiative ADN (2017) Differences in Aβ brain networks in Alzheimer’s disease and healthy controls. Brain Res 1655:77–89
Pereira JB, Strandberg TO, Palmqvist S, Volpe G, van Westen D, Westman E, Hansson O, Initiative ADN (2017) Amyloid network topology characterizes the progression of Alzheimer’s disease during the predementia stages. Cereb Cortex 28(1):340–349
Defer GL, Widner H, Marié RM, Rémy P, Levivier M (1999) Core assessment program for surgical interventional therapies in Parkinson’s disease (CAPSIT-PD). Mov Disord 14(4):572–584
Tomlinson CL, Stowe R, Patel S, Rick C, Gray R, Clarke CE (2010) Systematic review of levodopa dose equivalency reporting in Parkinson’s disease. Mov Disord 25(15):2649–2653
Beck AT, Steer RA, Brown GK (1996) Manual for the Beck depression inventory-II. San Antonio: TX: Psychological Corporation.
Rusjan P, Mamo D, Ginovart N, Hussey D, Vitcu I, Yasuno F, Tetsuya S, Houle S et al (2006) An automated method for the extraction of regional data from PET images. Psychiatry Res Neuroimaging 147(1):79–89
Talairach J, Tournoux P (1988) Co-planar stereotaxic atlas of the human brain: 3-dimensional proportional system: an approach to cerebral imaging.
Logan J, Fowler JS, Volkow ND, Wang G-J, Ding Y-S, Alexoff DL (1996) Distribution volume ratios without blood sampling from graphical analysis of PET data. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab 16(5):834–840
Rowe CC, Ng S, Ackermann U, Gong SJ, Pike K, Savage G, Cowie T, Dickinson K et al (2007) Imaging β-amyloid burden in aging and dementia. Neurology 68(20):1718–1725
Lopresti BJ, Klunk WE, Mathis CA, Hoge JA, Ziolko SK, Lu X, Meltzer CC, Schimmel K et al (2005) Simplified quantification of Pittsburgh Compound B amyloid imaging PET studies: a comparative analysis. J Nucl Med 46(12):1959–1972
Knezevic D, Verhoeff NPL, Hafizi S, Strafella AP, Graff-Guerrero A, Rajji T, Pollock BG, Houle S et al (2018) Imaging microglial activation and amyloid burden in amnestic mild cognitive impairment. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab 38(11):1885–1895. https://doi.org/10.1177/0271678X17741395
Villeneuve S, Rabinovici GD, Cohn-Sheehy BI, Madison C, Ayakta N, Ghosh PM, La Joie R, Arthur-Bentil SK et al (2015) Existing Pittsburgh Compound-B positron emission tomography thresholds are too high: statistical and pathological evaluation. Brain 138(7):2020–2033. https://doi.org/10.1093/brain/awv112
Rubinov M, Sporns O (2010) Complex network measures of brain connectivity: uses and interpretations. Neuroimage 52(3):1059–1069
Hosseini SH, Hoeft F, Kesler SR (2012) GAT: a graph-theoretical analysis toolbox for analyzing between-group differences in large-scale structural and functional brain networks. PLoS One 7(7):e40709
He Y, Chen ZJ, Evans AC (2007) Small-world anatomical networks in the human brain revealed by cortical thickness from MRI. Cereb Cortex 17(10):2407–2419. https://doi.org/10.1093/cercor/bhl149
Seo EH, Lee DY, Lee J-M, Park J-S, Sohn BK, Lee DS, Choe YM, Woo JI (2013) Whole-brain functional networks in cognitively normal, mild cognitive impairment, and Alzheimer’s disease. PLoS One 8(1):e53922
Achard S, Bullmore E (2007) Efficiency and cost of economical brain functional networks. PLoS Comput Biol 3(2):e17. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pcbi.0030017
Latora V, Marchiori M (2001) Efficient behavior of small-world networks. Phys Rev Lett 87(19):198701
Watts DJ, Strogatz SH (1998) Collective dynamics of ‘small-world’networks. Nature 393(6684):440–442
Newman ME (2006) Finding community structure in networks using the eigenvectors of matrices. Phys Rev E 74(3):036104
Freeman LC (1978) Centrality in social networks conceptual clarification. Soc Networks 1(3):215–239
Wang T, Wang K, Qu H, Zhou J, Li Q, Deng Z, Du X, Lv F et al (2016) Disorganized cortical thickness covariance network in major depressive disorder implicated by aberrant hubs in large-scale networks. Sci Rep 6:27964
Bassett DS, Bullmore E (2006) Small-world brain networks. Neuroscientist 12:512–523. https://doi.org/10.1177/1073858406293182
Ramsay JO, Dalzell CJ (1991) Some tools for functional data analysis. J R Stat Soc Ser B Methodol 53(3):539–572
Kotagal V, Bohnen NI, Müller ML, Frey KA, Albin RL (2017) Cerebral amyloid burden and Hoehn and Yahr stage 3 scoring in Parkinson disease. J Park Dis 7(1):143–147
Dyrba M, Mohammadi A, Grothe MJ, Kirste T, Teipel SJ (2018) Assessing inter-modal and inter-regional dependencies in prodromal Alzheimer’s disease using multimodal MRI/PET and Gaussian graphical models. arXiv preprint arXiv:180400049
Yang J, Hu C, Guo N, Dutta J, Vaina LM, Johnson KA, Sepulcre J, Fakhri GE et al (2017) Partial volume correction for PET quantification and its impact on brain network in Alzheimer’s disease. Sci Rep 7(1):13035. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-017-13339-7
Thal DR, Rüb U, Orantes M, Braak H (2002) Phases of Aβ-deposition in the human brain and its relevance for the development of AD. Neurology 58(12):1791–1800
Sporns O, Honey CJ, Kötter R (2007) Identification and classification of hubs in brain networks. PLoS One 2(10):e1049
Leyton CE, Cassidy B, Villemagne VL, Jones G, Kwok JB, Rowe CC, Ballard KJ, Piguet O et al (2016) Divergent network patterns of amyloid-β deposition in logopenic and amnestic Alzheimer’s disease presentations. Biol Psychiatry Cogn Neurosci Neuroimaging 1(1):24–31
Culham JC, Cavina-Pratesi C, Singhal A (2006) The role of parietal cortex in visuomotor control: what have we learned from neuroimaging? Neuropsychologia 44(13):2668–2684
Garcia-Diaz AI, Segura B, Baggio HC, Marti MJ, Valldeoriola F, Compta Y, Bargallo N, Uribe C et al (2018) Structural brain correlations of visuospatial and visuoperceptual tests in Parkinson’s disease. J Int Neuropsychol Soc 24(1):33–44
Funding
This work was supported by the Canadian Institutes of Health Research (MOP-136778). Dr. Antonio Strafella is supported by the Canada Research Chair Program.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Study conception and design: JK and APS
Data acquisition: CG and LC
Data analysis: JK and CG
Data interpretation: JK and APS
Manuscript drafting: JK
Manuscript review and critique for important intellectual content: JK, CG, SSC, AM, LC, MV, SH, and APS
Approved version to be published: JK and APS
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kim, J., Ghadery, C., Cho, S.S. et al. Network Patterns of Beta-Amyloid Deposition in Parkinson’s Disease. Mol Neurobiol 56, 7731–7740 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12035-019-1625-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12035-019-1625-z