Abstract
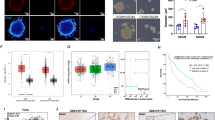
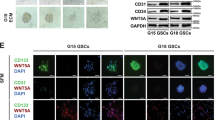
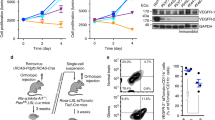
Tumor-remodeled endothelial cells not only facilitate the formation of tumor angiogenesis but also promote tumorigenesis. In this study, we aimed to explore the interaction between glioma-associated endothelial cells (GAEs) and glioma cells. We found that different subtypes of glioma owned distinct GAE abundance. Glioma patients with high GAE abundance exhibited poor prognosis. Both the results of the bioinformatics analysis and the in vitro co-culture system assay revealed that GAE promoted glioma cell invasion. Besides, anti-vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) therapy partially abolished the effects of GAE on gliomas. Moreover, anti-VEGF therapy upregulated IL-2 expression in GAE, and exogenous IL-2 administration inhibits GAE-induced glioma cell invasion. Collectively, our present study provides a novel outstanding of the interaction between GAE and glioma cells.








Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availability
The data used to support the findings of this study are available from the corresponding author upon request.
Abbreviations
- GAEs:
-
Glioma-associated endothelial cells
- VEGF:
-
Vascular endothelial growth factor
- TME:
-
Tumor microenvironment
- DEGs:
-
Differentially expressed genes
- VEGF mAb:
-
Anti-VEGF antibody
- qRT-PCR:
-
Quantitative real-time PCR
- WHO:
-
World Health Organization
- HGGs:
-
Higher-grade gliomas
- LGGs:
-
Lower-grade gliomas
- ECM:
-
Extracellular matrix
- TCA:
-
Tricarboxylic acid cycle
- D2-HG:
-
D2-hydroxyglutarate
References
Andersen B, Faust Akl C, Wheeler M, Chiocca E, Reardon D, Quintana F (2021) Glial and myeloid heterogeneity in the brain tumour microenvironment. Nat Rev Cancer 21(12):786–802. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41568-021-00397-3
Apte R, Chen D, Ferrara N (2019) VEGF in signaling and disease: beyond discovery and development. Cell 176(6):1248–1264. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cell.2019.01.021
Aran D, Hu Z, Butte A (2017) xCell: digitally portraying the tissue cellular heterogeneity landscape. Genome Biol 18(1):220. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13059-017-1349-1
Book A, Fielding K, Kundu N, Wilson M, Fulton A, Laterra J (1998) IL-10 gene transfer to intracranial 9L glioma: tumor inhibition and cooperation with IL-2. J Neuroimmunol 92:50–59. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0165-5728(98)00172-6
Bowman R, Wang Q, Carro A, Verhaak R, Squatrito M (2017) GlioVis data portal for visualization and analysis of brain tumor expression datasets. Neuro Oncol 19(1):139–141. https://doi.org/10.1093/neuonc/now247
Charalambous C, Chen T, Hofman F (2006) Characteristics of tumor-associated endothelial cells derived from glioblastoma multiforme. Neurosurg Focus 20(4):E22. https://doi.org/10.3171/foc.2006.20.4.e22
Dang L, White D, Gross S, Bennett B, Bittinger M, Driggers E, Fantin V, Jang H, Jin S, Keenan M et al (2009) Cancer-associated IDH1 mutations produce 2-hydroxyglutarate. Nature 462(7274):739–744. https://doi.org/10.1038/nature08617
DePalma T, Sivakumar H, Skardal A (2022) Strategies for developing complex multi-component in vitro tumor models: highlights in glioblastoma. Adv Drug Deliv Rev 180:114067. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.addr.2021.114067
Fabian C, Han M, Bjerkvig R, Niclou S (2021) Novel facets of glioma invasion. Int Rev Cell Mol Biol 360:33–64. https://doi.org/10.1016/bs.ircmb.2020.08.001
He X, Qi Y, Zhang X, Liu X, Li X, Li S, Wu Y, Zhang Q (2021) Current landscape of tumor-derived exosomal ncRNAs in glioma progression, detection, and drug resistance. Cell Death Dis 12(12):1145. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41419-021-04430-z
Johansson M, Henriksson R, Bergenheim A, Koskinen L (2000) Interleukin-2 and histamine in combination inhibit tumour growth and angiogenesis in malignant glioma. Br J Cancer 83(6):826–832. https://doi.org/10.1054/bjoc.2000.1354
Li D, Tian Y, Hu Y, Qi Y, Tian N, Li S, Hu P, Wu F, Wei Q, Wei Z et al (2019) Glioma-associated human endothelial cell-derived extracellular vesicles specifically promote the tumourigenicity of glioma stem cells via CD9. Oncogene 38(43):6898–6912. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41388-019-0903-6
Lin P (2020) Aneuploid circulating tumor-derived endothelial cell (CTEC): a novel versatile player in tumor neovascularization and cancer metastasis. Cells 9(6). https://doi.org/10.3390/cells9061539
Lissoni P (2017) Therapy implications of the role of interleukin-2 in cancer. Expert Rev Clin Immunol 13(5):491–498. https://doi.org/10.1080/1744666x.2017.1245146
Liu F, Peng B, Li M, Ma J, Deng G, Zhang S, Sheu W, Zou P, Wu H, Liu J et al (2022) Targeted disruption of tumor vasculature via polyphenol nanoparticles to improve brain cancer treatment. Cell reports. Physical Science 3(1). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.xcrp.2021.100691
Liu T, Ma W, Xu H, Huang M, Zhang D, He Z, Zhang L, Brem S, O’Rourke D, Gong Y et al (2018) PDGF-mediated mesenchymal transformation renders endothelial resistance to anti-VEGF treatment in glioblastoma. Nat Commun 9(1):3439. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-018-05982-z
Louis D, Ohgaki H, Wiestler O, Cavenee W, Burger P, Jouvet A, Scheithauer B, Kleihues P (2007) The 2007 WHO classification of tumours of the central nervous system. Acta Neuropathol 114(2):97–109. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00401-007-0243-4
Louis D, Perry A, Wesseling P, Brat D, Cree I, Figarella-Branger D, Hawkins C, Ng H, Pfister S, Reifenberger G et al (2021) The 2021 WHO classification of tumors of the central nervous system: a summary. Neuro Oncol 23(8):1231–1251. https://doi.org/10.1093/neuonc/noab106
Luan J, Wu M, Wang X, Qiao L, Guo G, Zhang C (2020) The diagnostic value of quantitative analysis of ASL, DSC-MRI and DKI in the grading of cerebral gliomas: a meta-analysis. Radiat Oncol 15(1):204. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13014-020-01643-y
Markwell S, Ross J, Olson C, Brat D (2022) Necrotic reshaping of the glioma microenvironment drives disease progression. Acta Neuropathol 143(3):291–310. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00401-021-02401-4
Moffat B, Chen M, Kariaapper M, Hamstra D, Hall D, Stojanovska J, Johnson T, Blaivas M, Kumar M, Chenevert T et al (2006) Inhibition of vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF)-A causes a paradoxical increase in tumor blood flow and up-regulation of VEGF-D. Clin Cancer Res 12(5):1525–1532. https://doi.org/10.1158/1078-0432.Ccr-05-1408
Norden A, Drappatz J, Wen P (2008) Novel anti-angiogenic therapies for malignant gliomas. Lancet Neurol 7(12):1152–1160. https://doi.org/10.1016/s1474-4422(08)70260-6
Norden A, Drappatz J, Wen P (2009) Antiangiogenic therapies for high-grade glioma. Nat Rev Neurol 5(11):610–620. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrneurol.2009.159
Park S, Piao Y, Jeong K, Dong J, de Groot J (2016) Periostin (POSTN) regulates tumor resistance to antiangiogenic therapy in glioma models. Mol Cancer Ther 15(9):2187–2197. https://doi.org/10.1158/1535-7163.Mct-15-0427
Quail D, Joyce J (2017) The microenvironmental landscape of brain tumors. Cancer Cell 31(3):326–341. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ccell.2017.02.009
Rao J (2003) Molecular mechanisms of glioma invasiveness: the role of proteases. Nat Rev Cancer 3(7):489–501. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrc1121
Sengupta S, Mondal M, Prasasvi K, Mukherjee A, Magod P, Urbach S, Friedmann-Morvinski D, Marin P, Somasundaram K (2022) Differentiated glioma cell-derived Fibromodulin activates Integrin-dependent Notch signaling in endothelial cells to promote tumor angiogenesis and growth. eLife 11. https://doi.org/10.7554/eLife.78972
Seok J, Yoon S, Lee S, Jung J, Lee Y (2019) The oncometabolite d-2-hydroxyglutarate induces angiogenic activity through the vascular endothelial growth factor receptor 2 signaling pathway. Int J Oncol 54(2):753–763. https://doi.org/10.3892/ijo.2018.4649
Shenoy A, Lu J (2016) Cancer cells remodel themselves and vasculature to overcome the endothelial barrier. Cancer Lett 380(2):534–544. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.canlet.2014.10.031
Sun C, Zhao Y, Shi J, Zhang J, Yuan Y, Gu Y, Zhang F, Gao X, Wang C, Wang Y et al (2019) Isocitrate dehydrogenase1 mutation reduces the pericyte coverage of microvessels in astrocytic tumours. J Neurooncol 143(2):187–196. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11060-019-03156-5
Sun D, Wang J, Han Y, Dong X, Ge J, Zheng R, Shi X, Wang B, Li Z, Ren P et al (2021) TISCH: a comprehensive web resource enabling interactive single-cell transcriptome visualization of tumor microenvironment. Nucleic Acids Res 49:D1420–D1430. https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gkaa1020
Sun S, Chen S, Liu F, Wu H, McHugh J, Bergin I, Gupta A, Adams D, Guan J (2015) Constitutive activation of mTORC1 in endothelial cells leads to the development and progression of lymphangiosarcoma through VEGF autocrine signaling. Cancer Cell 28(6):758–772. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ccell.2015.10.004
Sung H, Ferlay J, Siegel R, Laversanne M, Soerjomataram I, Jemal A, Bray F (2021) Global cancer statistics 2020: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries. CA: A Cancer Journal for Clinicians 71(3):209–249. https://doi.org/10.3322/caac.21660
Tang H, Zhang X, Xue G, Xu F, Wang Q, Yang P, Hong B, Xu Y, Huang Q, Liu J et al (2021) The biology of bone morphogenetic protein signaling pathway in cerebrovascular system. Chinese Neurosurgical Journal 7(1):36. https://doi.org/10.1186/s41016-021-00254-0
Varn F, Johnson K, Martinek J, Huse J, Nasrallah M, Wesseling P, Cooper L, Malta T, Wade T, Sabedot T et al (2022) Glioma progression is shaped by genetic evolution and microenvironment interactions. Cell. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cell.2022.04.038
Virrey J, Golden E, Sivakumar W, Wang W, Pen L, Schönthal A, Hofman F, Chen T (2009) Glioma-associated endothelial cells are chemoresistant to temozolomide. J Neurooncol 95(1):13–22. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11060-009-9891-7
Wei Q, Singh O, Ekinci C, Gill J, Li M, Mamatjan Y, Karimi S, Bunda S, Mansouri S, Aldape K et al (2021) TNFα secreted by glioma associated macrophages promotes endothelial activation and resistance against anti-angiogenic therapy. Acta Neuropathol Commun 9(1):67. https://doi.org/10.1186/s40478-021-01163-0
Yang T, Sun Y, Lu Z, Leak R, Zhang F (2017) The impact of cerebrovascular aging on vascular cognitive impairment and dementia. Ageing Res Rev 34:15–29. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.arr.2016.09.007
Zhang L, He L, Lugano R, Roodakker K, Bergqvist M, Smits A, Dimberg A (2018) IDH mutation status is associated with distinct vascular gene expression signatures in lower-grade gliomas. Neuro Oncol 20(11):1505–1516. https://doi.org/10.1093/neuonc/noy088
Zhao Z, Zhang K, Wang Q, Li G, Zeng F, Zhang Y, Wu F, Chai R, Wang Z, Zhang C et al (2021) Chinese glioma genome atlas (CGGA): a comprehensive resource with functional genomic data from Chinese glioma patients. Genomics Proteomics Bioinformatics 19(1):1–12. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.gpb.2020.10.005
Funding
This research was supported by the National Health Commission of China (2018ZX-07S-011) the and Translational Medicine Research Fund of Zhongnan Hospital of Wuhan University (ZLYNXM202011, ZNLH201901).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Zhi-Qiang Li and Ze-Fen Wang were involved in the conception or the design of the study. Feng-Ping Li and Xue-Tao Huang performed the experiments. Feng Tang performed bioinformatics analysis. Feng-Ping Li, Xue-Tao Huang, and Guo-Hua Wang participated in the acquisition and analysis of the data. Feng Tang wrote the manuscript. Zhi-Qiang Li and Ze-Fen Wang reviewed the manuscript and made contributions for improvement.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Tang, F., Li, FP., Huang, XT. et al. Anti-Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor Therapy Abolishes Glioma-Associated Endothelial Cell-Induced Tumor Invasion. J Mol Neurosci 73, 104–116 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12031-023-02099-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12031-023-02099-x