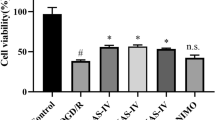
Abstract
Oxidative stress, associated with various neurodegenerative diseases, promotes ROS generation, impairs cellular antioxidant defenses, and finally, triggers both neurons and astroglial cell death by apoptosis. Astrocytes specifically synthesize and release endozepines, a family of regulatory peptides, including the octadecaneuropeptide (ODN). We have previously reported that ODN acts as a potent neuroprotective agent that prevents 6-OHDA-induced apoptotic neuronal death. The purpose of the present study was to investigate the potential glioprotective effect of ODN on 6-OHDA-induced oxidative stress and cell death in cultured rat astrocytes. Incubation of astrocytes with graded concentrations of ODN (10−14 to 10−8 M) inhibited 6-OHDA-evoked cell death in a concentration- and time-dependent manner. In addition, ODN prevented the decrease of mitochondrial activity and caspase-3 activation induced by 6-OHDA. 6-OHDA-treated cells also exhibited enhanced levels of ROS associated with a generation of H2O2 and O2°-, and a reduction of both superoxide dismutase (SOD) and catalase (CAT) activities. Co-treatment of astrocytes with low concentrations of ODN dose-dependently blocked 6-OHDA-evoked production of ROS and inhibition of antioxidant enzyme activities. Concomitantly, ODN stimulated Mn-SOD, CAT, glutathione peroxidase-1, and sulfiredoxin-1 gene transcription and rescued 6-OHDA-associated reduced expression of endogenous antioxidant enzymes. Taken together, these data indicate that, in rat astrocytes, ODN exerts anti-apoptotic and anti-oxidative activities, and hence prevents 6-OHDA-induced oxidative assault and cell death. ODN is thus a potential candidate to delay neuronal damages in various pathological conditions involving oxidative neurodegeneration.






Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- 6-OHDA:
-
6-hydroxydopamine
- CNS:
-
Central nervous system
- DBI:
-
Diazepam-binding inhibitor
- DCFH:
-
2′,7′-dichlorodihydrofluorescein
- JC-1:
-
5,5″,6,6″-tetrachloro-1,1″,3,3″-tetraethylbenzimidazolylcarbocyanine iodide
- DHE:
-
Dihydroethidium
- DHR123:
-
Dihydrorhodamine 123
- FDA:
-
Fluorescein diacetate
- Gpx:
-
Glutathione peroxidase
- H2O2 :
-
Hydrogen peroxide
- LDH:
-
Lactate dehydrogenase
- NBT:
-
Nitrotetrazolium blue chloride
- O2°− :
-
Superoxide anions
- ODN:
-
Octadecaneuropeptide
- PD:
-
Parkinson’s disease
- ROS:
-
Reactive oxygen species
- SOD:
-
Superoxide dismutase
- Srxn:
-
Sulfiredoxin
References
Afshin-Majd S, Bashiri K, Kiasalari Z, Baluchnejadmojarad T, Sedaghat R, Roghani M (2017) Acetyl-l-carnitine protects dopaminergic nigrostriatal pathway in 6-hydroxydopamine-induced model of Parkinson's disease in the rat. Biomed Pharmacother 89:1–9. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biopha.2017.02.007
Alfonso J, Le Magueresse C, Zuccotti A, Khodosevich K, Monyer H (2012) Diazepam binding inhibitor promotes progenitor proliferation in the postnatal SVZ by reducing GABA signaling. Cell Stem Cell 10:76–87. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.stem.2011.11.011
Amri F, Ghouili I, Amri M, Carrier A, Masmoudi-Kouki O (2017) Neuroglobin protects astroglial cells from hydrogen peroxide-induced oxidative stress and apoptotic cell death. J Neurochem 140:151–169. https://doi.org/10.1111/jnc.13876
Bahdoudi S, Ghouili I, Hmiden M, do Rego JL, Lefranc B, Leprince J, Chuquet J, do Rego JC, Marcher AB, Mandrup S, Vaudry H, Tonon MC, Amri M, Masmoudi-Kouki O, Vaudry D (2018) Neuroprotective effects of the gliopeptide ODN in an in vivo model of Parkinson’s disease. Cell Mol Life Sci 75:2075–2091. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00018-017-2727-2
Baxter PS, Hardingham GE (2016) Adaptive regulation of the brain’s antioxidant defences by neurons and astrocytes. Free Radic Biol Med 100:147–152. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.freeradbiomed.2016.06.027
Blesa J, Przedborski S (2014) Parkinson’s disease: animal models and dopaminergic cell vulnerability. Front Neuroanat 8:155. https://doi.org/10.3389/fnana.2014.00155
Blum D, Torch S, Nissou MF, Benabid AL, Verna JM (2000) Extracellular toxicity of 6-hydroxydopamine on PC12 cells. Neurosci Lett 283:193–196
Blum D, Torch S, Nissou MF, Verna JM (2001) 6-hydroxydopamine-induced nuclear factor-kappa B activation in PC12 cells. Biochem Pharmacol 62:473–481
Burda JE, Bernstein AM, Sofroniew MV (2016) Astrocyte roles in traumatic brain injury. Exp Neurol 275(Pt 3):305–315. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.expneurol.2015.03.020
Chen LW, Yung KL, Chan YS (2005) Reactive astrocytes as potential manipulation targets in novel cell replacement therapy of Parkinson’s disease. Curr Drug Targets 6:821–833
Dallerac G, Rouach N (2016) Astrocytes as new targets to improve cognitive functions. Prog Neurobiol 144:48–67. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pneurobio.2016.01.003
Dejda A, Sokolowska P, Nowak JZ (2005) Neuroprotective potential of three neuropeptides PACAP, VIP and PHI. Pharmacol Rep 57:307–320
Douiri S, Bahdoudi S, Hamdi Y, Cubi R, Basille M, Fournier A, Vaudry H, Tonon MC, Amri M, Vaudry D, Masmoudi-Kouki O (2016) Involvement of endogenous antioxidant systems in the protective activity of pituitary adenylate cyclase-activating polypeptide against hydrogen peroxide-induced oxidative damages in cultured rat astrocytes. J Neurochem 137:913–930. https://doi.org/10.1111/jnc.13614
Dumitru I, Neitz A, Alfonso J, Monyer H (2017) Diazepam binding inhibitor promotes stem cell expansion controlling environment-dependent neurogenesis. Neuron 94(125–137):e125. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuron.2017.03.003
Dzyubenko E, Gottschling C, Faissner A (2016) Neuron-glia interactions in neural plasticity: contributions of neural extracellular matrix and perineuronal nets. Neural Plast 2016:5214961. https://doi.org/10.1155/2016/5214961
Elkon H, Melamed E, Offen D (2004) Oxidative stress, induced by 6-hydroxydopamine, reduces proteasome activities in PC12 cells: implications for the pathogenesis of Parkinson's disease. J Mol Neurosci 24:387–400. https://doi.org/10.1385/JMN:24:3:387
Espinosa-Oliva AM, de Pablos RM, Sarmiento M, Villaran RF, Carrillo-Jimenez A, Santiago M, Venero JL, Herrera AJ, Cano J, Machado A (2014) Role of dopamine in the recruitment of immune cells to the nigro-striatal dopaminergic structures. Neurotoxicology 41:89–101. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuro.2014.01.006
Ferrero-Gutierrez A, Perez-Gomez A, Novelli A, Fernandez-Sanchez MT (2008) Inhibition of protein phosphatases impairs the ability of astrocytes to detoxify hydrogen peroxide. Free Radic Biol Med 44:1806–1816. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.freeradbiomed.2008.01.029
Ferrero P, Santi MR, Conti-Tronconi B, Costa E, Guidotti A (1986) Study of an octadecaneuropeptide derived from diazepam binding inhibitor (DBI): biological activity and presence in rat brain. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 83:827–831
Gandolfo P, Patte C, Thoumas JL, Leprince J, Vaudry H, Tonon MC (1999) The endozepine ODN stimulates [3H]thymidine incorporation in cultured rat astrocytes. Neuropharmacology 38:725–732
Gardaneh M, Gholami M, Maghsoudi N (2011) Synergy between glutathione peroxidase-1 and astrocytic growth factors suppresses free radical generation and protects dopaminergic neurons against 6-hydroxydopamine. Rejuvenation Res 14:195–204. https://doi.org/10.1089/rej.2010.1080
Garzon D, Cabezas R, Vega N, Avila-Rodriguez M, Gonzalez J, Gomez RM, Echeverria V, Aliev G, Barreto GE (2016) Novel approaches in astrocyte protection: from experimental methods to computational approaches. J Mol Neurosci 58:483–492. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12031-016-0719-6
Ghouili I, Bahdoudi S, Morin F, Amri F, Hamdi Y, Coly PM, Walet-Balieu ML, Leprince J, Zekri S, Vaudry H, Vaudry D, Castel H, Amri M, Tonon MC, Masmoudi-Kouki O (2018) Endogenous expression of ODN-related peptides in astrocytes contributes to cell protection against oxidative stress: astrocyte-neuron crosstalk relevance for neuronal survival. Mol Neurobiol 55:4596–4611. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12035-017-0630-3
Gomide VC, Silveira GA, Chadi G (2005) Transient and widespread astroglial activation in the brain after a striatal 6-OHDA-induced partial lesion of the nigrostriatal system. Int J Neurosci 115:99–117
Goswami P, Gupta S, Biswas J, Sharma S, Singh S (2016) Endoplasmic reticulum stress instigates the rotenone induced oxidative apoptotic neuronal death: a study in rat brain. Mol Neurobiol 53:5384–5400. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12035-015-9463-0
Gu XL, Long CX, Sun L, Xie C, Lin X, Cai H (2010) Astrocytic expression of Parkinson's disease-related A53T alpha-synuclein causes neurodegeneration in mice. Mol Brain 3:12. https://doi.org/10.1186/1756-6606-3-12
Guidotti A, Forchetti CM, Corda MG, Konkel D, Bennett CD, Costa E (1983) Isolation, characterization, and purification to homogeneity of an endogenous polypeptide with agonistic action on benzodiazepine receptors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 80:3531–3535
Hamdi Y, Kaddour H, Vaudry D, Bahdoudi S, Douiri S, Leprince J, Castel H, Vaudry H, Tonon MC, Amri M, Masmoudi-Kouki O (2012) The octadecaneuropeptide ODN protects astrocytes against hydrogen peroxide-induced apoptosis via a PKA/MAPK-dependent mechanism. PLoS One 7:e42498. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0042498
Hamdi Y, Kaddour H, Vaudry D, Leprince J, Zarrouk A, Hammami M, Vaudry H, Tonon MC, Amri M, Masmoudi-Kouki O (2015) Octadecaneuropeptide ODN prevents hydrogen peroxide-induced oxidative damage of biomolecules in cultured rat astrocytes. Peptides 71:56–65. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.peptides.2015.06.010
Hamdi Y, Masmoudi-Kouki O, Kaddour H, Belhadj F, Gandolfo P, Vaudry D, Mokni M, Leprince J, Hachem R, Vaudry H, Tonon MC, Amri M (2011) Protective effect of the octadecaneuropeptide on hydrogen peroxide-induced oxidative stress and cell death in cultured rat astrocytes. J Neurochem 118:416–428. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1471-4159.2011.07315.x
Han X, Zhu S, Wang B, Chen L, Li R, Yao W, Qu Z (2014) Antioxidant action of 7,8-dihydroxyflavone protects PC12 cells against 6-hydroxydopamine-induced cytotoxicity. Neurochem Int 64:18–23. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuint.2013.10.018
Hanrott K, Gudmunsen L, O'Neill MJ, Wonnacott S (2006) 6-hydroxydopamine-induced apoptosis is mediated via extracellular auto-oxidation and caspase 3-dependent activation of protein kinase Cdelta. J Biol Chem 281:5373–5382. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M511560200
Hernandez-Baltazar D, Mendoza-Garrido ME, Martinez-Fong D (2013) Activation of GSK-3beta and caspase-3 occurs in nigral dopamine neurons during the development of apoptosis activated by a striatal injection of 6-hydroxydopamine. PLoS One 8:e70951. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0070951
Huertas A, Wessinger WD, Kucheryavykh YV, Sanabria P, Eaton MJ, Skatchkov SN, Rojas LV, Maldonado-Martinez G, Inyushin MY (2015) Quinine enhances the behavioral stimulant effect of cocaine in mice. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 129:26–33. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pbb.2014.11.021
Ishii T, Takanashi Y, Sugita K, Miyazawa M, Yanagihara R, Yasuda K, Onouchi H, Kawabe N, Nakata M, Yamamoto Y, Hartman PS, Ishii N (2017) Endogenous reactive oxygen species cause astrocyte defects and neuronal dysfunctions in the hippocampus: a new model for aging brain. Aging Cell 16:39–51. https://doi.org/10.1111/acel.12523
Jakel RJ, Townsend JA, Kraft AD, Johnson JA (2007) Nrf2-mediated protection against 6-hydroxydopamine. Brain Res 1144:192–201. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.brainres.2007.01.131
Johnson JA, Johnson DA, Kraft AD, Calkins MJ, Jakel RJ, Vargas MR, Chen PC (2008) The Nrf2-ARE pathway: an indicator and modulator of oxidative stress in neurodegeneration. Ann N Y Acad Sci 1147:61–69. https://doi.org/10.1196/annals.1427.036
Jordan J, Galindo MF, Tornero D, Gonzalez-Garcia C, Cena V (2004) Bcl-x L blocks mitochondrial multiple conductance channel activation and inhibits 6-OHDA-induced death in SH-SY5Y cells. J Neurochem 89:124–133. https://doi.org/10.1046/j.1471-4159.2003.02299.x
Kaddour H, Hamdi Y, Vaudry D, Basille M, Desrues L, Leprince J, Castel H, Vaudry H, Tonon MC, Amri M, Masmoudi-Kouki O (2013) The octadecaneuropeptide ODN prevents 6-hydroxydopamine-induced apoptosis of cerebellar granule neurons through a PKC-MAPK-dependent pathway. J Neurochem 125:620–633. https://doi.org/10.1111/jnc.12140
Khan MM, Ahmad A, Ishrat T, Khan MB, Hoda MN, Khuwaja G, Raza SS, Khan A, Javed H, Vaibhav K, Islam F (2010) Resveratrol attenuates 6-hydroxydopamine-induced oxidative damage and dopamine depletion in rat model of Parkinson’s disease. Brain Res 1328:139–151. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.brainres.2010.02.031
Kiasalari Z, Khalili M, Baluchnejadmojarad T, Roghani M (2016) Protective effect of oral hesperetin againstunilateral striatal 6-hydroxydopamine damage in the rat. Neurochem Res 41:1065–1072. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11064-015-1796-6
Kuruvilla KP, Nandhu MS, Paul J, Paulose CS (2013) Oxidative stress mediated neuronal damage in the corpus striatum of 6-hydroxydopamine lesioned Parkinson’s rats: neuroprotection by serotonin, GABA and bone marrow cells supplementation. J Neurol Sci 331:31–37. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jns.2013.04.020
L' Episcopo F, Tirolo C, Testa N, Caniglia S, Morale MC, Marchetti B (2010) Glia as a turning point in the therapeutic strategy of Parkinson’s disease. CNS Neurol Disord Drug Targets 9:349–372
L'Episcopo F, Tirolo C, Testa N, Caniglia S, Morale MC, Cossetti C, D'Adamo P, Zardini E, Andreoni L, Ihekwaba AE, Serra PA, Franciotta D, Martino G, Pluchino S, Marchetti B (2011) Reactive astrocytes and Wnt/beta-catenin signaling link nigrostriatal injury to repair in 1-methyl-4-phenyl-1,2,3,6-tetrahydropyridine model of Parkinson’s disease. Neurobiol Dis 41:508–527. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.nbd.2010.10.023
Leprince J, Oulyadi H, Vaudry D, Masmoudi O, Gandolfo P, Patte C, Costentin J, Fauchere JL, Davoust D, Vaudry H, Tonon MC (2001) Synthesis, conformational analysis and biological activity of cyclic analogs of the octadecaneuropeptide ODN: design of a potent endozepine antagonist. Eur J Biochem 268:6045–6057
Lev N, Barhum Y, Ben-Zur T, Melamed E, Steiner I, Offen D (2013) Knocking out DJ-1 attenuates astrocytes neuroprotection against 6-hydroxydopamine toxicity. J Mol Neurosci 50:542–550. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12031-013-9984-9
Li Q, Yu S, Wu J, Zou Y, Zhao Y (2013) Sulfiredoxin-1 protects PC12 cells against oxidative stress induced by hydrogen peroxide. J Neurosci Res 91:861–870. https://doi.org/10.1002/jnr.23218
Lin CH, Wang CH, Hsu SL, Liao LY, Lin TA, Hsueh CM (2016) Molecular mechanisms responsible for neuron-derived conditioned medium (NCM)-mediated protection of ischemic brain. PLoS One 11:e0146692. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0146692
Liu L, Liu L, Shi J, Tan M, Xiong J, Li X, Hu Q, Yi Z, Mao D (2016) MicroRNA-34b mediates hippocampal astrocyte apoptosis in a rat model of recurrent seizures. BMC Neurosci 17:56. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12868-016-0291-6
Liu Z, Chopp M (2016) Astrocytes, therapeutic targets for neuroprotection and neurorestoration in ischemic stroke. Prog Neurobiol 144:103–120. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pneurobio.2015.09.008
Masaki Y, Izumi Y, Matsumura A, Akaike A, Kume T (2017) Protective effect of Nrf2-ARE activator isolated from green perilla leaves on dopaminergic neuronal loss in a Parkinson’s disease model. Eur J Pharmacol 798:26–34. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejphar.2017.02.005
Masmoudi-Kouki O, Douiri S, Hamdi Y, Kaddour H, Bahdoudi S, Vaudry D, Basille M, Leprince J, Fournier A, Vaudry H, Tonon MC, Amri M (2011) Pituitary adenylate cyclase-activating polypeptide protects astroglial cells against oxidative stress-induced apoptosis. J Neurochem 117:403–411. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1471-4159.2011.07185.x
Masmoudi-Kouki O, Gandolfo P, Castel H, Leprince J, Fournier A, Dejda A, Vaudry H, Tonon MC (2007) Role of PACAP and VIP in astroglial functions. Peptides 28:1753–1760. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.peptides.2007.05.015
Michel PP, Toulorge D, Guerreiro S, Hirsch EC (2013) Specific needs of dopamine neurons for stimulation in order to survive: implication for Parkinson disease. FASEB J 27:3414–3423. https://doi.org/10.1096/fj.12-220418
Mirza B, Hadberg H, Thomsen P, Moos T (2000) The absence of reactive astrocytosis is indicative of a unique inflammatory process in Parkinson’s disease. Neuroscience 95:425–432
Mladenovic A, Perovic M, Raicevic N, Kanazir S, Rakic L, Ruzdijic S (2004) 6-Hydroxydopamine increases the level of TNFalpha and bax mRNA in the striatum and induces apoptosis of dopaminergic neurons in hemiparkinsonian rats. Brain Res 996:237–245
Mullett SJ, Di Maio R, Greenamyre JT, Hinkle DA (2013) DJ-1 expression modulates astrocyte-mediated protection against neuronal oxidative stress. J Mol Neurosci 49:507–511. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12031-012-9904-4
Murakami S, Miyazaki I, Asanuma M (2018) Neuroprotective effect of fermented papaya preparation by activation of Nrf2 pathway in astrocytes. Nutr Neurosci 21:176–184. https://doi.org/10.1080/1028415X.2016.1253171
Osborn LM, Kamphuis W, Wadman WJ, Hol EM (2016) Astrogliosis: an integral player in the pathogenesis of Alzheimer's disease. Prog Neurobiol 144:121–141. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pneurobio.2016.01.001
Patte C, Vaudry H, Desrues L, Gandolfo P, Strijdveen I, Lamacz M, Tonon MC (1995) The endozepine ODN stimulates polyphosphoinositide metabolism in rat astrocytes. FEBS Lett 362:106–110
Pekny M, Pekna M, Messing A, Steinhauser C, Lee JM, Parpura V, Hol EM, Sofroniew MV, Verkhratsky A (2016) Astrocytes: a central element in neurological diseases. Acta Neuropathol 131:323–345. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00401-015-1513-1
Perfeito R, Cunha-Oliveira T, Rego AC (2013) Reprint of: revisiting oxidative stress and mitochondrial dysfunction in the pathogenesis of Parkinson disease-resemblance to the effect of amphetamine drugs of abuse. Free Radic Biol Med 62:186–201. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.freeradbiomed.2013.05.042
Podkletnova I, Rothstein JD, Helen P, Alho H (2001) Microglial response to the neurotoxicity of 6-hydroxydopamine in neonatal rat cerebellum. Int J Dev Neurosci 19:47–52
Raicevic N, Mladenovic A, Perovic M, Harhaji L, Miljkovic D, Trajkovic V (2005a) Iron protects astrocytes from 6-hydroxydopamine toxicity. Neuropharmacology 48:720–731. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuropharm.2004.12.003
Raicevic N, Mladenovic A, Perovic M, Miljkovic D, Trajkovic V (2005b) The mechanisms of 6-hydroxydopamine-induced astrocyte death. Ann N Y Acad Sci 1048:400–405. https://doi.org/10.1196/annals.1342.049
Sandhu JK, Gardaneh M, Iwasiow R, Lanthier P, Gangaraju S, Ribecco-Lutkiewicz M, Tremblay R, Kiuchi K, Sikorska M (2009) Astrocyte-secreted GDNF and glutathione antioxidant system protect neurons against 6OHDA cytotoxicity. Neurobiol Dis 33:405–414. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.nbd.2008.11.016
Sari Y, Gozes I (2006) Brain deficits associated with fetal alcohol exposure may be protected, in part, by peptides derived from activity-dependent neurotrophic factor and activity-dependent neuroprotective protein. Brain Res Rev 52:107–118. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.brainresrev.2006.01.004
Soto-Otero R, Mendez-Alvarez E, Hermida-Ameijeiras A, Munoz-Patino AM, Labandeira-Garcia JL (2000) Autoxidation and neurotoxicity of 6-hydroxydopamine in the presence of some antioxidants: potential implication in relation to the pathogenesis of Parkinson’s disease. J Neurochem 74:1605–1612
Tong H, Zhang X, Meng X, Lu L, Mai D, Qu S (2018) Simvastatin inhibits activation of NADPH oxidase/p38 MAPK pathway and enhances expression of antioxidant protein in Parkinson disease models. Front Mol Neurosci 11:165. https://doi.org/10.3389/fnmol.2018.00165
Tonon MC, Desy L, Nicolas P, Vaudry H, Pelletier G (1990) Immunocytochemical localization of the endogenous benzodiazepine ligand octadecaneuropeptide (ODN) in the rat brain. Neuropeptides 15:17–24
Tonon MC, Leprince J, Gandolfo P, Compère V, Pelletier G, Malagon MM, Vaudry H (2006) Endozepines.In handbook of biologically active peptides,. ed A J Kastin (New York: Elsevier):813–819
Tonon MC, Leprince J, Morin F, Gandolfo P, Compère V, Pelletier G, Malagon M, Vaudry H (2013) Endozepines. In: Kastin AJ (ed) Handbook of biological active peptides, 2nd edn. Elsevier, Oxford, UK, pp 760–765
Toulorge D, Schapira AH, Hajj R (2016) Molecular changes in the postmortem parkinsonian brain. J Neurochem 139 Suppl 1:27–58. https://doi.org/10.1111/jnc.13696
Tronel C, Rochefort GY, Arlicot N, Bodard S, Chalon S, Antier D (2013) Oxidative stress is related to the deleterious effects of heme oxygenase-1 in an in vivo neuroinflammatory rat model. Oxidative Med Cell Longev 2013:264935. https://doi.org/10.1155/2013/264935
Tuncel N, Korkmaz OT, Tekin N, Sener E, Akyuz F, Inal M (2012) Antioxidant and anti-apoptotic activity of vasoactive intestinal peptide (VIP) against 6-hydroxy dopamine toxicity in the rat corpus striatum. J Mol Neurosci 46:51–57. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12031-011-9618-z
Wachter B, Schurger S, Rolinger J, von Ameln-Mayerhofer A, Berg D, Wagner HJ, Kueppers E (2010) Effect of 6-hydroxydopamine (6-OHDA) on proliferation of glial cells in the rat cortex and striatum: evidence for de-differentiation of resident astrocytes. Cell Tissue Res 342:147–160. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00441-010-1061-x
Wu J, Chen Y, Yu S, Li L, Zhao X, Li Q, Zhao J, Zhao Y (2017) Neuroprotective effects of sulfiredoxin-1 during cerebral ischemia/reperfusion oxidative stress injury in rats. Brain Res Bull 132:99–108. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.brainresbull.2017.05.012
Yang CM, Lin CC, Hsieh HL (2017) High-glucose-derived oxidative stress-dependent heme oxygenase-1 expression from astrocytes contributes to the neuronal apoptosis. Mol Neurobiol 54:470–483. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12035-015-9666-4
Yu S, Wang X, Lei S, Chen X, Liu Y, Zhou Y, Zhou Y, Wu J, Zhao Y (2015) Sulfiredoxin-1 protects primary cultured astrocytes from ischemia-induced damage. Neurochem Int 82:19–27. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuint.2015.01.005
Zhou Y, Duan S, Zhou Y, Yu S, Wu J, Wu X, Zhao J, Zhao Y (2015a) Sulfiredoxin-1 attenuates oxidative stress via Nrf2/ARE pathway and 2-Cys Prdxs after oxygen-glucose deprivation in astrocytes. J Mol Neurosci 55:941–950. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12031-014-0449-6
Zhou Y, Zhou Y, Yu S, Wu J, Chen Y, Zhao Y (2015b) Sulfiredoxin-1 exerts anti-apoptotic and neuroprotective effects against oxidative stress-induced injury in rat cortical astrocytes following exposure to oxygen-glucose deprivation and hydrogen peroxide. Int J Mol Med 36:43–52. https://doi.org/10.3892/ijmm.2015.2205
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the France-Tunisia CMCU-Campus France/PHC Utique 16G0820/34940PK exchange program (to Olfa Masmoudi-Kouki and David Vaudry), Alternance scholarship of Tunisian Higher Education Ministry and the Laboratory of Neurophysiology, Cellular Physiopathology and Biomolecules Valorisation. LR18ES03, INSERM (U1239), the European Regional Development Fund (PACT-CBS and PHEDERCPG projects), and the Region Normandy. Europe gets involved in Normandy with European Regional Development Fund (ERDF). The funders had no role in study design, data collection and analysis, decision to publish, or preparation of the manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kaddour, H., Hamdi, Y., Amri, F. et al. Antioxidant and Anti-Apoptotic Activity of Octadecaneuropeptide Against 6-OHDA Toxicity in Cultured Rat Astrocytes. J Mol Neurosci 69, 1–16 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12031-018-1181-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12031-018-1181-4