Abstract
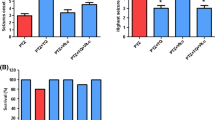
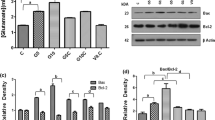
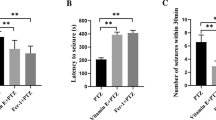
The regulation of programmed cell death in the nervous system of vertebrates is a complex mechanism aimed to remove superfluous or damaged cells. Epileptic seizures can lead to an activation of pathways resulting in neuronal cell death. B-vitamins might have a neuroprotective potential reducing cell death following appropriate stimulation. Here, the role of the B-vitamins B1 (thiamine), B6 (pyridoxine), and B12 (cobalamine) was investigated in a mouse model of experimental epilepsy induced by kainate. B-vitamin pre-treated animals showed a significantly reduced epileptic score during the first 15 min after kainate injection. The molecular response to kainate showed a bi-phased time course with early induction of Bcl-2 expression within 12 h and a second induction after 7 days of kainate exposure. B-vitamin pre-treatment resulted in significant higher Bcl-2 expression in control animals (no kainate) and at 12 h within the early phase. Bcl-2 expression was not affected by B-vitamins within the second phase. BAX expression was not significantly influenced during the whole experiment. Three days after kainate stimulation, the number of TdT-mediated dUTP-biotin nick end labeling-positive cells in the hippocampal region was lower in B-vitamin-treated animals. Therefore, B-vitamin pre-treatment may attenuate the response to epileptic stimulation.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ananth C, Thameem Dheen S, Gopalakrishnakone P, Kaur C (2001) Domoic acid-induced neuronal damage in the rat hippocampus: changes in apoptosis related genes (bcl-2, bax, caspase-3) and microglial response. J Neurosci Res 66:177–190
Apeland T, Froyland ES, Kristensen O, Strandjord RE, Mansoor MA (2008) Drug-induced pertubation of the aminothiol redox-status in patients with epilepsy: improvement by B-vitamins. Epilepsy Res 82:1–6
Balk E, Chung M, Raman G, Tatsioni A, Chew P, Ip S et al (2006) B vitamins and berries and age-related neurodegenerative disorders. Evid Rep/Technol Assess 134:1–161
Chuang JI, Chen ST, Chang YH, Jen LS (2001) Alteration of Bcl-2 expression in the nigrostriatal system after kainate injection with or without melatonin co-treatment. J Chem Neuroanat 21:215–223
Dakshinamurti K, Sharma SK, Bonke D (1990) Influence of B vitamins on binding properties of serotonin receptors in the CNS of rats. Klin Wochenschr 68:142–145
Dominguez YL, Hernandez M, Matos CM, Zhou D (2006) Is B vitamins deficiency associated with prevalence of Alzheimer’s disease in Cuban elderly? Nutr Health 18:103–118
Gavrieli Y, Sherman Y, Ben Sasson SA (1992) Identification of programmed cell death in situ via specific labeling of nuclear DNA fragmentation. J Cell Biol 119:493–501
Gillardon F, Wickert H, Zimmermann M (1995) Up-regulation of bax and down-regulation of bcl-2 is associated with kainate-induced apoptosis in mouse brain. Neurosci Lett 192:85–88
Hockenbery D, Nunez G, Milliman C, Schreiber RD, Korsmeyer SJ (1990) Bcl-2 is an inner mitochondrial membrane protein that blocks programmed cell death. Nature 348:334–336
LeBlanc AC (2003) Natural cellular inhibitors of caspases. Prog Neuropsychopharmacol Biol Psychiatry 27:215–229
Lopez E, Pozas E, Rivera R, Ferrer I (1999) Bcl-2, Bax and Bcl-x expression following kainic acid administration at convulsant doses in the rat. Neuroscience 91:1461–1470
Mikati MA, Zeinieh M, Habib RA, El Hokayem J, Rahmeh A, El Sabban M et al (2008) Changes in sphingomyelinases, ceramide, Bax, Bcl(2), and caspase-3 during and after experimental status epilepticus. Epilepsy Res 81:161–166
Mooney S, Leuendorf JE, Hendrickson C, Hellmann H (2009) Vitamin B6: a long known compound of surprising complexity. Molecules 14:329–351
Mori F, Okada M, Tomiyama M, Kaneko S, Wakabayashi K (2005) Effects of ryanodine receptor activation on neurotransmitter release and neuronal cell death following kainic acid-induced status epilepticus. Epilepsy Res 65:59–70
Obeid R, McCaddon A, Herrmann W (2007) The role of hyperhomocysteinemia and B-vitamin deficiency in neurological and psychiatric diseases. Clin Chem Lab Med 45:1590–1606
Scalabrino G, Veber D, Mutti E (2008) Experimental and clinical evidence of the role of cytokines and growth factors in the pathogenesis of acquired cobalamin-deficient leukoneuropathy. Brains Res Rev 59:42–54
Schenkel J (2004) Activation of the c-Jun transcription factor following neurodegeneration in vivo. Neurosci Lett 361:36–39
Schulz RJ (2007) Homocysteine as a biomarker for cognitive dysfunction in the elderly. Curr Opin Clin Nutr Metab Care 10:718–723
Sinha S, Patil SA, Jayalekshmy V, Satishchandra P (2008) Do cytokines have any role in epilepsy? Epilepsy Res 82:171–176
Tagscherer KE, Fassl A, Campos B, Farhadi M, Kraemer A, Bock BC et al (2008) Apoptosis-based treatment of glioblastomas with ABT-737, a novel small molecule inhibitor of Bcl-2 family proteins. Oncogene 27:6646–6656
Trovero F, Gobbi M, Weil-Fuggaza J, Besson MJ, Brochet D, Pirot S (2000) Evidence for a modulatory effect of sulbutiamine on glutamatergic and dopaminergic cortical transmissions in the rat brain. Neurosci Lett 292:49–53
Tuunanen J, Lukasiuk K, Halonen T, Pitkanen A (1999) Status epilepticus-induced neuronal damage in the rat amygdaloid complex: distribution, time-course and mechanisms. Neuroscience 94:473–495
Vezzani A, Balosso S, Ravizza T (2008) The role of cytokines in the pathophysiology of epilepsy. Brain Behav Immun 22:797–803
Vogel J, Weigand MA, Behrens A, Wagner EF, Schorpp-Kistner M, Zimmermann M et al (2007) Infarct volume after transient middle cerebral artery occlusion (MCAo) can be reduced by attenuation but not by inactivation of c-Jun action. Brain Res 1151:12–19
Vyas S, Javoy-Agid F, Herrero MT, Strada O, Boissiere F, Hibner U et al (1997) Expression of Bcl-2 in adult human brain regions with special reference to neurodegenerative disorders. J Neurochem 69:223–231
Wang L, Liu YH, Huang YG, Chen LW (2008) Time-course of neuronal death in the mouse pilocarpine model of chronic epilepsy using Fluoro-Jade C staining. Brain Res 1241:157–167
Winter C, Weiss C, Martin-Villalba A, Zimmermann M, Schenkel J (2002) JunB and Bcl-2 overexpression results in protection against cell death of nigral neurons following axotomy. Brain Res Mol Brain Res 104:194–202
Wu G, Lu ZH, Wang J, Wang Y, Xie X, Meyenhofer MF et al (2005) Enhanced susceptibility to kainate-induced seizures, neuronal apoptosis, and death in mice lacking gangliotetraose gangliosides: protection with LIGA 20, a membrane-permeant analog of GM1. J Neurosci 25:11014–11022
Yalcin A, Kanit L, Sozmen EY (2004) Altered gene expressions in rat hippocampus after kainate injection with or without melatonin pre-treatment. Neurosci Lett 359:65–68
Youle RJ, Strasser A (2008) The BCL-2 protein family: opposing activities that mediate cell death. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 9:47–59
Zaczek R, Simonton S, Coyle JT (1980) Local and distant neuronal degeneration following intrastriatal injection of kainic acid. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol 39:245–264
Zhong LT, Sarafian T, Kane DJ, Charles AC, Mah SP, Edwards RH et al (1993) bcl-2 inhibits death of central neural cells induced by multiple agents. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 90:4533–4537
Zucchini S, Buzzi A, Barbieri M, Rodi D, Paradiso B, Binaschi A et al (2008) Fgf-2 overexpression increases excitability and seizure susceptibility but decreases seizure-induced cell loss. J Neurosci 28:13112–13124
Acknowledgements
The authors thank Inge Keller for her expert technical assistance. This work was supported by Merck KGaA, Darmstadt, Germany.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Tamer Rabie and Wolfgang Mühlhofer, as well as Hugo H. Marti and Johannes Schenkel contributed equally to this paper.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Rabie, T., Mühlhofer, W., Bruckner, T. et al. Transient Protective Effect of B-Vitamins in Experimental Epilepsy in the Mouse Brain. J Mol Neurosci 41, 74–79 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12031-009-9286-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12031-009-9286-4