Abstract
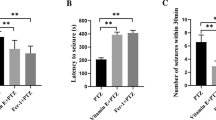
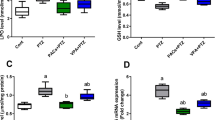
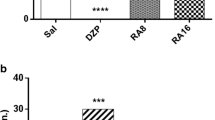
Epilepsy is a common neurological disorder that leads to neuronal excitability and provoke various forms of cellular reorganization in the brain. In this study, we investigate the anti-convulsant and neuroprotective effects of thymoquinone (TQ) and vitamin C against pentylenetetrazole (PTZ)-induced generalized seizures. Epileptic seizures were induced in adult rats using systemic intraperitoneal injections of PTZ (50 mg/kg) for 7 days. Animals pretreated with either TQ or vitamin C or in combination attenuated PTZ-induced seizures and mortality in rats as well neurodegeneration in the cells. Compared to PTZ, TQ and vitamin C significantly prolonged the onset of seizures (p > 0.05) as well decrease the high-grade seizures. Analysis of electroencephalogram (EEG) recordings revealed that TQ or vitamin C supplementation significantly reduced polyspike and epileptiform discharges. Epileptic seizures caused a decline in expression of gamma-aminobutyric acid B1 receptor (GABAB1R) (p > 0.05), unchanged expression of protein kinase A (PKA), decreased calcium/calmodulin-dependent protein kinase II (CaMKII) (p > 0.05) and inhibit the phosphorylation of cAMP response element-binding protein (CREB) (p > 0.05) in cortex and hippocampus, respectively, compared with control. Changes in expression of GABAB1R, CaMKII and CREB by PTZ were reversed by TQ and vitamin C supplementation. Moreover, PTZ significantly increased Bax, decreased Bcl-2 expression and finally the activation of caspase-3. TQ and vitamin C pretreatment reversed all these deleterious effects induced by PTZ. TQ and vitamin C showed anticonvulsant effects via activation of GABAB1R/CaMKII/CREB pathway and suggest a potential therapeutic role in epilepsy.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abdel-Fattah, A. M., Matsumoto, K., & Watanabe, H. (2000). Antinociceptive effects of Nigella sativa oil and its major component, thymoquinone, in mice. European Journal of Pharmacology, 400, 89–97.
Akhondian, J., Kianifar, H., Raoofziaee, M., Moayedpour, A., Toosi, M. B., & Khajedaluee, M. (2011). The effect of thymoquinone on intractable pediatric seizures (pilot study). Epilepsy Research, 93, 39–43.
Al-Majed, A. A., Al-Omar, F. A., & Nagi, M. N. (2006). Neuroprotective effects of thymoquinone against transient forebrain Ischemia in the rat hippocampus. European Journal of Pharmacology, 543, 40–47.
Anderson, K. J., Miller, K. M., Fugaccia, I., & Scheff, S. W. (2005). Regional distribution of Fluoro-Jade B staining in the hippocampus following traumatic brain injury. Experimental Neurology, 193, 125–130.
Andrade, D. M., & Minassian, B. A. (2007). Genetics of epilepsies. Expert Review of Neurotherapeutics, 7, 727–734.
Bouilleret, V., Nehlig, A., Marescaux, C., & Namer, I. J. (2000). Magnetic resonance imaging follow-up of progressive hippocampal changes in a mouse model of mesial temporal lobe epilepsy. Epilepsia, 41, 642–650.
Brown, J. T., Gill, C. H., Farmer, C. E., Lanneau, C., Randall, A. D., Pangalos, M. N., et al. (2003). Mechanism contributing to the exacerbated epileptiform activity in hippocampal slices of GABAB1 receptor subunit knockout mice. Epilepsy Research, 57, 121–136.
Carey, K., & Fuchs, S. (2001). Pediatric pharmacology. What you need to know for the next pediatric call. Emergency Medical Services, 30, 27–34.
Cendes, F. (2005). Progressive hippocampal and extrahippocampal atrophy in drug resistant epilepsy. Current Opinion in Neurology, 18, 173–177.
Chang, Y. C., Huang, A. M., Kuo, Y. M., Wang, S. T., Chang, Y. Y., & Huang, C. C. (2003). Febrile seizures impair memory and cAMP response-element binding protein activation. Annals of Neurology, 54, 706–718.
Chebib, M., & Johnston, G. A. (1999). The ABC of GABA receptors: A brief review. Clinical and Experimental Pharmacology, 26, 937–940.
Cheng, C. Y., Su, S. Y., Tang, N. Y., Ho, T. Y., Lo, W. Y., & Hsieh, C. L. (2010). Ferulic acid inhibits nitric oxide-induced apoptosis by enhancing GABAB1 receptor expression in transient focal cerebral ischemia in rats. Acta Pharmacologica Sinica, 31, 898–899.
Costello, D. J., & Delanty, N. (2004). Oxidative injury in epilepsy: Potential for antioxidant therapy? Expert Review of Neurotherapeutics, 4, 541–553.
Dong, Y. U., & Rosenberg, H. C. (2004). Prolonged changes in Ca2 +/calmodulin-dependent protein kinase II after a brief pentylenetetrazol seizure; potential role in kindling. Epilepsy Research, 58, 107–117.
Duncan, J. S., Sander, J. W., Sisodiya, S. M., & Walker, M. C. (2006). Adult epilepsy. Lancet, 367, 1087–1100.
Engel, T., & Henshall, D. C. (2009). Apoptosis, Bcl-2 family proteins and caspases: The ABCs of seizure-damage and epileptogenesis? International Journal of Physiology, Pathophysiology and Pharmacology, 1, 97–115.
Erakovic, V., Zupan, G., Varljen, J., Laginja, J., & Simonic, A. (2001). Altered activities of rat brain metabolic enzymes caused by pentylenetetrazol kindling and pentylenetetrazol-induced seizures. Epilepsy Research, 43, 165–173.
Fujikawa, D. G. (2005). Prolonged seizures and cellular injury: Understanding the connection. Epilepsy & Behavior, 7(Suppl 3), S3–S11.
Gonzalez-Ramirez, M., Razo-Juarez, L., Sauer-Ramirez, J. L., Gonzalez-Trujano, M. E., et al. (2010). Anticonvulsive effect of vitamin C on pentylenetetrazol-induced seizures in immature rats. Pharmacology Biochemistry and Behavior, 97, 267–272.
Greggio, S., Rosa, R. M., Dolganov, A., Oliveira, L. M., & Menegat, F. D. (2009). NAP prevents hippocampal oxidative damage in neonatal rats subjected to hypoxia-induced seizures. Neurobiology of Disease, 36, 435–444.
Haut, S. R., Bigal, M. E., & Lipton, R. B. (2006). Chronic disorders with episodic manifestations: Focus on epilepsy and migraine. Lancet Neurology, 5, 148–157.
Haut, S. R., Velískova, J., & Moshé, S. L. (2004). Susceptibility of immature and adult brains to seizure effects. Lancet Neurology, 3, 608–617.
Hosford, D. A., Clark, S., Cao, Z., Wilson, W. A., Lin, F. H., Morrisett, R. A., & Huin, A. (1992). The role of GABA receptor activation in absence seizures of lethargic (lh/lh) mice. Science, 257, 398–401.
Hosseinzadeh, H., & Parvardeh, S. (2004). Anticonvulsant effects of thymoquinone, the major constituent of Nigella Sativa seeds, in mice. Phytomedicine, 11, 56–64.
Houghton, P. J., Zarka, R., de las Heras, B., & Hoult, J. R. (1995). Fixed oil of Nigella sativa and derived thymoquinone inhibit eicosanoid generation in leukocytes and membrane lipid peroxidation. Planta Medica, 611, 33–36.
Huang, R. Q., Bell-Horner, C. L., Dibas, M. I., Covey, D. F., Drewe, J. A., & Dillon, G. H. (2001). Pentylenetetrazole-induced inhibition of recombinant gamma-aminobutyric acid type A (GABA (A)) receptors: Mechanism and site of action. Journal of Pharmacology and Experimental Therapeutics, 298, 986–995.
Ilhan, A., Gurel, A., Armutcu, F., Kamisli, S., & Iraz, M. (2005). Antiepileptogenic and antioxidant effects of Nigella sativa oil against pentylenetetrazol-induced kindling in mice. Neuropharmacology, 49, 456–464.
Jancic, D., Armentia, M. L., Valor, L. M., Olivares, R., & Barco, A. (2009). Inhibition of cAMP response element-binding protein reduces neuronal excitability and plasticity, and triggers neurodegeneration. Cerebral Cortex, 19, 2535–2547.
Kanter, M. (2008). Nigella sativa and derived thymoquinone prevents hippocampal neurodegeneration after chronic toluene exposure in rats. Neurochemical Research, 33, 579–588.
Kulik, A., Vida, I., Fukazawa, Y., Guetg, N., Kasugai, Y., Marker, C. L., et al. (2006). Compartment dependent colocalization of Kir3.2-containing K+ channels and GABAB receptors in hippocampal pyramidal cells. Journal of Neuroscience, 26, 4289–4297.
Leung, L. S., Canning, K. J., & Shen, B. (2005). Hippocampal after discharges after GABA (B)-receptor blockade in freely moving rat. Epilepsia, 46, 203–216.
Li, J., Olinger, A. B., Dassow, M. S., & Abel, M. S. (2003). Up-regulation of GABA (B) receptor mRNA and protein in the hippocampus of cocaine- and lidocaine-kindled rats. Neuroscience, 118, 451–462.
Liu, Z., Vergnes, M., Depaulis, A., & Marescaux, C. (1992). Involvement of intrathalamic GABAB neurotransmission in the control of absence seizures in the rat. Neuroscience, 48, 87–93.
Macdonald, R. L., & Barker, J. L. (1978). Specific antagonism of GABA-mediated postsynaptic inhibition in cultured mammalian spinal cord neurons: A common mode of convulsant action. Neurology, 28, 325–330.
Mousavi, S. H., Tayarani-Najaran, Z., Asghari, M., & Sadeghnia, H. R. (2010). Protective effect of Nigella sativa extract and thymoquinone on serum/glucose deprivation-induced PC12 cells death. Cellular and Molecular Neurobiology, 30, 591–598.
Nagi, M. N., & Mansour, M. A. (2000). Protective effect of thymoquinone against doxorubicin–induced cardiotoxicity in rats: A possible mechanism of protection. Pharmacological Research, 41, 283–289.
Naseer, M. I., Li, S., & Kim, M. O. (2009). Maternal epileptic seizure induced by pentylenetetrazol: Apoptotic neurodegeneration and decreased GABAB1 receptor expression in prenatal rat brain. Mol Brain, 2, 1–20.
Naseer, M. I., Ullah, I., Al-Qahtani, M. H., Karim, S., Ullah, N., Ansari, S. A., et al. (2013). Decreased GABABR expression and increased neuronal cell death in developing rat brain after PTZ-induced seizure. Neurological Sciences, 4, 497–503.
Oblak, A. L., Gibbs, T. T., & Blatt, G. J. (2010). Decreased GABAB receptors in the cingulate cortex and fusiform gyrus in autism. Journal of Neurochemistry, 114, 1414–1423.
Patsoukis, N., Zervoudakis, G., Georgiou, C. D., Angelatou, F., Matsokis, N. A., & Panagopoulos, N. T. (2005). Thiol redox state and lipid and protein oxidation in the mouse striatum after pentylenetetrazol-induced epileptic seizure. Epilepsia, 46, 1205–1211.
Pavlova, T. V., Yakovlev, A. A., Stepanichev, M. Y., Mendzheritskii, A. M., & Gulyaeva, N. V. (2004). Pentylenetetrazole kindling induces activation of caspase-3 in the rat brain. Neuroscience and Behavioral Physiology, 34, 45–47.
Pi, X., Lee, J., Li, F., & Rosenber, H. C. (2004). Decreased expression of cAMP response element-binding protein gene following pentylenetetrazole seizure. Molecular Brain Research, 127, 60–67.
Pin, J. P., Kniazeff, J., Binet, V., Liu, J., Maurel, D., Galvez, T., et al. (2004). Activation mechanism of the heterodimeric GABA(B) receptor. Biochemical Pharmacology, 68, 1565–1572.
Racine, R. J. (1972). Modification of seizure activity by electrical stimulation: II. Motor seizure. Electroencephalography and Clinical Neurophysiology, 32, 281–294.
Santos, L. F. S., Freitas, R. L. M., Xavier, S. M. L., Saldanha, G. B., & Freitas, R. M. (2008). Neuroprotective actions of vitamin C to decreased lipid peroxidation and increased catalase activity in adult rats after pilocarpine-induced seizures. Pharmacology, Biochemistry and Behavior, 89, 1–5.
Sas, K., Robotka, H., Rozsa, E., Agoston, M., Szenasi, G., Gigler, G., et al. (2008). Kynurenine diminishes the ischemia-induced histological and electrophysiological deficits in the rat hippocampus. Neurobiology of Disease, 32, 302–308.
Schuler, V., Luscher, C., et al. (2001). Epilepsy, hyperalgesia, impaired memory, and loss of pre- and postsynaptic GABAB responses in mice lacking GABAB(1). Neuron, 31, 47–58.
Sudha, K., Ashalatha, V. R., & Anjali, R. (2001). Oxidative Stress and antioxidants in epilepsy. Clinica Chimica Acta, 303, 19–24.
Tu, H., Xu, C., Zhang, W., Liu, Q., Rondard, P., Pin, J. P., & Liu, J. (2010). GABAB receptor activation protects neurons from apoptosis via IGF-1 receptor transactivatio. Journal of Neuroscience, 30, 749–759.
Ullah, N., Naseer, M. I., Ullah, I., Lee, H. Y., Koh, P. O., & Kim, M. O. (2011). Protective effect of pyruvate against ethanol-induced apoptotic neurodegeneration in the developing rat brain. Neuropharmacology, 61, 1248–1255.
Vollenweider, F., Bendfeldt, K., Maetzler, W., Otten, U., & Nitsch, C. (2006). GABA(B) receptor expression and cellular localization in gerbil hippocampus after transient global ischemia. Neuroscience Letters, 395, 118–123.
Wei, X. W., Yan, H., Xo, B. O., Wu, Y. P., Li, C., & Zhang, G. Y. (2012). Neuroprotection of co-activation of GABA receptors by preventing caspase-3 denitrosylation in KA-induced seizures. Brain Research Bulletin, 88, 617–623.
Xu, K., & Stringer, J. L. (2008). Antioxidants and free radical scavengers do not consistently delay seizure onset in animal models of acute seizures. Epilepsy & Behavior, 13, 77–82.
Zeng, L. H., Xu, L., Rensing, N. R., Sinatra, P. M., Rothman, S. M., & Wong, M. (2007). Kainate seizures cause acute dendritic injury and actin depolymerization in vivo. Journal of Neuroscience, 27, 11604–11613.
Acknowledgments
This research was supported by the Pioneer Research Center Program through the National Research Foundation of Korea funded by the Ministry of Science, ICT & Future Planning (2012-0009521).
Conflict of interest
The authors have no competing interest to declare.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ullah, I., Badshah, H., Naseer, M.I. et al. Thymoquinone and Vitamin C Attenuates Pentylenetetrazole-Induced Seizures Via Activation of GABAB1 Receptor in Adult Rats Cortex and Hippocampus. Neuromol Med 17, 35–46 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12017-014-8337-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12017-014-8337-3