Abstract
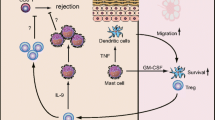
Mast cells secrete a wide spectrum of stored or newly synthesized pro-inflammatory, anti-inflammatory, and/or immunosuppressive mediators and express several costimulatory and inhibitory surface molecules. Mast cells finely tune activities of T cells, B cells, and regulatory cells and effectively contribute to the development of different T cell-associated responses by influencing their recruitment, activation, proliferation, and differentiation. The interaction between mast cells and T cells, with regard to cellular functionality and immune responses, can be assessed in both activating and inhibitory regulations. While Th2 cytokines, including IL-5 and IL-9, stimulate stem cell factor (SCF)-dependent proliferation of mast cells, Th1 cytokine IFN-γ suppresses SCF-mediated differentiation of mast cell progenitors. Mast cell mediators such as CCL5 have a role in the recruitment of CD8+ T cells to viral infection sites where their ability in clearance of viral reservoirs is needed. The capacity of mast cells in presenting antigens by classes I and II MHC molecules to CD4+ and CD8+ T cells respectively is considered one of the main antigen-dependent interactions of mast cells with T cells. Interestingly, Tregs recruit mast cells to different sites through secretion of IL-9, while the OX40L (expressed on mast cell)-OX40(expressed on T cell) interaction inhibits the extent of the mast cell degranulation. Recently, the capability of exosomes to carry regulatory receptors of the mast cell surface and their role in T cell activation has been investigated. Functional interplay between mast cells and T cell subsets has been suggested primarily by investigating their co-localization in inflamed tissues and involvement of mast cells in autoimmune diseases. In this review, the interactions of mast cells with T cells are reviewed in cell-to-cell, cytokine, and exosome categories.







Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- RANKL:
-
Receptor activator of NF-κB ligand
- LTs:
-
Leukotrienes
- PGs:
-
Prostaglandins
- PAF:
-
Platelet activating factor
- MCs:
-
Mast cells
- iDCs:
-
Immature DCs
References
Gri G, Frossi B, D'Inca F, Danelli L, Betto E, Mion F, Sibilano R, Pucillo C (2012) Mast cell: an emerging partner in immune interaction. Front Immunol 3:120. https://doi.org/10.3389/fimmu.2012.00120
Wernersson S, Pejler G (2014) Mast cell secretory granules: armed for battle. Nat Rev Immunol 14(7):478–494. https://doi.org/10.1038/nri3690
Kalesnikoff J, Galli SJ (2008) New developments in mast cell biology. Nat Immunol 9(11):1215–1223. https://doi.org/10.1038/ni.f.216
Migalovich-Sheikhet H, Friedman S, Mankuta D, Levi-Schaffer F (2012) Novel identified receptors on mast cells. Front Immunol 3:238. https://doi.org/10.3389/fimmu.2012.00238
Komi DEA, Rambasek T, Wohrl S (2017) Mastocytosis: from a molecular point of view. Clin Rev Allergy Immunol. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12016-017-8619-2
Okayama Y, Kawakami T (2006) Development, migration, and survival of mast cells. Immunol Res 34(2):97–115. https://doi.org/10.1385/ir:34:2:97
Krystel-Whittemore M, Dileepan KN, Wood JG (2015) Mast cell: a multi-functional master cell. Front Immunol 6:620. https://doi.org/10.3389/fimmu.2015.00620
Campillo-Navarro M, Chavez-Blanco AD, Wong-Baeza I, Serafin-Lopez J, Flores-Mejia R, Estrada-Parra S, Estrada-Garcia I, Chacon-Salinas R (2014) Mast cells in lung homeostasis: beyond type I hypersensitivity. Curr Respir Med Rev 10(2):115–123. https://doi.org/10.2174/1573398x10666141024220151
Sandig H, Bulfone-Paus S (2012) TLR signaling in mast cells: common and unique features. Front Immunol 3:185. https://doi.org/10.3389/fimmu.2012.00185
Hirahara K, Nakayama T (2016) CD4+ T-cell subsets in inflammatory diseases: beyond the Th1/Th2 paradigm. Int Immunol 28(4):163–171. https://doi.org/10.1093/intimm/dxw006
Luckheeram RV, Zhou R, Verma AD, Xia B (2012) CD4(+)T cells: differentiation and functions. Clin Dev Immunol 2012:925135. https://doi.org/10.1155/2012/925135
Caza T, Landas S (2015) Functional and phenotypic plasticity of CD4(+) T cell subsets. Biomed Res Int 2015:521957. https://doi.org/10.1155/2015/521957
Kalesnikoff J, Galli SJ (2011) Antiinflammatory and immunosuppressive functions of mast cells. Methods in molecular biology (Clifton, NJ) 677:207–220. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-60761-869-0_15
Nakano N, Nishiyama C, Yagita H, Koyanagi A, Ogawa H, Okumura K (2011) Notch1-mediated signaling induces MHC class II expression through activation of class II transactivator promoter III in mast cells. J Biol Chem 286(14):12042–12048. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M110.138966
Malaviya R, Twesten NJ, Ross EA, Abraham SN, Pfeifer JD (1996) Mast cells process bacterial Ags through a phagocytic route for class I MHC presentation to T cells. J Immunol (Baltimore, Md : 1950) 156(4):1490–1496
Gilfillan AM, Beaven MA (2011) Regulation of mast cell responses in health and disease. Crit Rev Immunol 31(6):475–529
Cardamone C, Parente R, Feo GD, Triggiani M (2016) Mast cells as effector cells of innate immunity and regulators of adaptive immunity. Immunol Lett 178:10–14. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.imlet.2016.07.003
Valitutti S, Espinosa E (2010) Cognate interactions between mast cells and helper T lymphocytes. Self 1(2):114–122. https://doi.org/10.4161/self.1.2.11795
Gaudenzio N, Espagnolle N, Mars LT, Liblau R, Valitutti S, Espinosa E (2009) Cell-cell cooperation at the T helper cell/mast cell immunological synapse. Blood 114(24):4979–4988. https://doi.org/10.1182/blood-2009-02-202648
de Vries VC, Noelle RJ (2010) Mast cell mediators in tolerance. Curr Opin Immunol 22(5):643–648. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.coi.2010.08.015
Hershko AY, Rivera J (2010) Mast cell and T cell communication; amplification and control of adaptive immunity. Immunol Lett 128(2):98–104. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.imlet.2009.10.013
Yeatman CF 2nd, Jacobs-Helber SM, Mirmonsef P, Gillespie SR, Bouton LA, Collins HA, Sawyer ST, Shelburne CP, Ryan JJ (2000) Combined stimulation with the T helper cell type 2 cytokines interleukin (IL)-4 and IL-10 induces mouse mast cell apoptosis. J Exp Med 192(8):1093–1103
Bulanova E, Bulfone-Paus S (2010) P2 receptor-mediated signaling in mast cell biology. Purinergic signalling 6(1):3–17. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11302-009-9173-z
Kulka M, Metcalfe DD (2005) High-resolution tracking of cell division demonstrates differential effects of TH1 and TH2 cytokines on SCF-dependent human mast cell production in vitro: correlation with apoptosis and Kit expression. Blood 105(2):592–599. https://doi.org/10.1182/blood-2004-07-2838
Suurmond J, van Heemst J, van Heiningen J, Dorjee AL, Schilham MW, van der Beek FB, Huizinga TW, Schuerwegh AJ, Toes RE (2013) Communication between human mast cells and CD4(+) T cells through antigen-dependent interactions. Eur J Immunol 43(7):1758–1768. https://doi.org/10.1002/eji.201243058
Kambayashi T, Laufer TM (2014) Atypical MHC class II-expressing antigen-presenting cells: can anything replace a dendritic cell? Nat Rev Immunol 14(11):719–730. https://doi.org/10.1038/nri3754
Nakano N, Nishiyama C, Yagita H, Koyanagi A, Akiba H, Chiba S, Ogawa H, Okumura K (2009) Notch signaling confers antigen-presenting cell functions on mast cells. J Allergy Clin Immunol 123(1):74–81.e71. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jaci.2008.10.040
Hong GU, Kim NG, Kim TJ, Ro JY (2014) CD1d expressed in mast cell surface enhances IgE production in B cells by up-regulating CD40L expression and mediator release in allergic asthma in mice. Cell Signal 26(5):1105–1117. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cellsig.2014.01.029
Lee YK, Mukasa R, Hatton RD, Weaver CT (2009) Developmental plasticity of Th17 and Treg cells. Curr Opin Immunol 21(3):274–280. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.coi.2009.05.021
Weaver CT, Harrington LE, Mangan PR, Gavrieli M, Murphy KM (2006) Th17: an effector CD4 T cell lineage with regulatory T cell ties. Immunity 24(6):677–688. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.immuni.2006.06.002
Bi Y, Liu G, Yang R (2007) Th17 cell induction and immune regulatory effects. J Cell Physiol 211(2):273–278. https://doi.org/10.1002/jcp.20973
Suurmond J, Habets KL (2016) Expansion of Th17 cells by human mast cells is driven by inflammasome-independent IL-1beta. J Immunol 197(11):4473–4481
Ishii N, Takahashi T, Soroosh P, Sugamura K (2010) OX40-OX40 ligand interaction in T-cell-mediated immunity and immunopathology. Adv Immunol 105:63–98. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0065-2776(10)05003-0
Cho KA, Suh JW, Sohn JH, Park JW, Lee H, Kang JL, Woo SY, Cho YJ (2012) IL-33 induces Th17-mediated airway inflammation via mast cells in ovalbumin-challenged mice. Am J Physiol Lung Cell mol physiol 302(4):L429–L440. https://doi.org/10.1152/ajplung.00252.2011
Carroll-Portillo A, Cannon JL, te Riet J, Holmes A, Kawakami Y, Kawakami T, Cambi A, Lidke DS (2015) Mast cells and dendritic cells form synapses that facilitate antigen transfer for T cell activation. J Cell Biol 210(5):851–864. https://doi.org/10.1083/jcb.201412074
Dudeck A, Suender CA, Kostka SL, von Stebut E, Maurer M (2011) Mast cells promote Th1 and Th17 responses by modulating dendritic cell maturation and function. Eur J Immunol 41(7):1883–1893. https://doi.org/10.1002/eji.201040994
Liu ZQ, Song JP, Liu X, Jiang J, Chen X, Yang L, Hu T, Zheng PY, Liu ZG, Yang PC (2014) Mast cell-derived serine proteinase regulates T helper 2 polarization. Sci Rep 4:4649. https://doi.org/10.1038/srep04649
Shelburne CP, Ryan JJ (2001) The role of Th2 cytokines in mast cell homeostasis. Immunol Rev 179:82–93
Bailey DP, Kashyap M, Mirmonsef P, Bouton LA, Domen J, Zhu J, Dessypris EN, Ryan JJ (2004) Interleukin-4 elicits apoptosis of developing mast cells via a Stat6-dependent mitochondrial pathway. Exp Hematol 32(1):52–59
Yanagida M, Fukamachi H, Ohgami K, Kuwaki T, Ishii H, Uzumaki H, Amano K, Tokiwa T, Mitsui H, Saito H, Iikura Y, Ishizaka T, Nakahata T (1995) Effects of T-helper 2-type cytokines, interleukin-3 (IL-3), IL-4, IL-5, and IL-6 on the survival of cultured human mast cells. Blood 86(10):3705–3714
Hu ZQ, Zhao WH, Shimamura T, Galli SJ (2006) Interleukin-4-triggered, STAT6-dependent production of a factor that induces mouse mast cell apoptosis. Eur J Immunol 36(5):1275–1284. https://doi.org/10.1002/eji.200526275
Metz M, Maurer M (2007) Mast cells—key effector cells in immune responses. Trends Immunol 28(5):234–241. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.it.2007.03.003
McLachlan JB, Hart JP, Pizzo SV, Shelburne CP, Staats HF, Gunn MD, Abraham SN (2003) Mast cell-derived tumor necrosis factor induces hypertrophy of draining lymph nodes during infection. Nat Immunol 4(12):1199–1205. https://doi.org/10.1038/ni1005
Nakae S, Suto H, Iikura M, Kakurai M, Sedgwick JD, Tsai M, Galli SJ (2006) Mast cells enhance T cell activation: importance of mast cell costimulatory molecules and secreted TNF. J Immunol(Baltimore, Md : 1950) 176(4):2238–2248
Huang B, Lei Z, Zhang GM, Li D, Song C, Li B, Liu Y, Yuan Y, Unkeless J, Xiong H, Feng ZH (2008) SCF-mediated mast cell infiltration and activation exacerbate the inflammation and immunosuppression in tumor microenvironment. Blood 112(4):1269–1279. https://doi.org/10.1182/blood-2008-03-147033
Khazaie K, Blatner NR, Khan MW, Gounari F, Gounaris E, Dennis K, Bonertz A, Tsai FN, Strouch MJ, Cheon E, Phillips JD, Beckhove P, Bentrem DJ (2011) The significant role of mast cells in cancer. Cancer Metastasis Rev 30(1):45–60. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10555-011-9286-z
Galli SJ, Grimbaldeston M, Tsai M (2008) Immunomodulatory mast cells: negative, as well as positive, regulators of immunity. Nat Rev Immunol 8(6):478–486. https://doi.org/10.1038/nri2327
Wasiuk A, de Vries VC, Hartmann K, Roers A, Noelle RJ (2009) Mast cells as regulators of adaptive immunity to tumours. Clin Exp Immunol 155(2):140–146. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-2249.2008.03840.x
Ganeshan K, Bryce PJ (2012) Regulatory T cells enhance mast cell production of IL-6 via surface-bound TGF-beta. J Immunol (Baltimore, Md : 1950) 188(2):594–603. https://doi.org/10.4049/jimmunol.1102389
Frossi B, Gri G, Tripodo C, Pucillo C (2010) Exploring a regulatory role for mast cells: ‘MCregs’? Trends Immunol 31(3):97–102. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.it.2009.12.007
Xu Y, Chen G (2015) Mast cell and autoimmune diseases. Mediat Inflamm 2015:246126. https://doi.org/10.1155/2015/246126
Piconese S, Gri G, Tripodo C, Musio S, Gorzanelli A, Frossi B, Pedotti R, Pucillo CE, Colombo MP (2009) Mast cells counteract regulatory T-cell suppression through interleukin-6 and OX40/OX40L axis toward Th17-cell differentiation. Blood 114(13):2639–2648. https://doi.org/10.1182/blood-2009-05-220004
Yang Z, Zhang B, Li D, Lv M, Huang C, Shen GX, Huang B (2010) Mast cells mobilize myeloid-derived suppressor cells and Treg cells in tumor microenvironment via IL-17 pathway in murine hepatocarcinoma model. PLoS One 5(1):e8922. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0008922
Groot Kormelink T, Abudukelimu A, Redegeld FA (2009) Mast cells as target in cancer therapy. Curr Pharm Des 15(16):1868–1878
Christy AL, Brown MA (2007) The multitasking mast cell: positive and negative roles in the progression of autoimmunity. J Immunol (Baltimore, Md : 1950) 179(5):2673–2679
Walker ME, Hatfield JK, Brown MA (2012) New insights into the role of mast cells in autoimmunity: evidence for a common mechanism of action? Biochim Biophys Acta 1822(1):57–65. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbadis.2011.02.009
Akdis CA, Akdis M (2014) Mechanisms of immune tolerance to allergens: role of IL-10 and Tregs. J Clin Invest 124(11):4678–4680. https://doi.org/10.1172/jci78891
Palomares O, Martin-Fontecha M, Lauener R (2014) Regulatory T cells and immune regulation of allergic diseases: roles of IL-10 and TGF-beta. Genes Immun 15(8):511–520. https://doi.org/10.1038/gene.2014.45
Bulfone-Paus S, Bahri R (2015) Mast cells as regulators of T cell responses. Front Immunol 6:394. https://doi.org/10.3389/fimmu.2015.00394
McAlpine SM, Issekutz TB, Marshall JS (2012) Virus stimulation of human mast cells results in the recruitment of CD56(+) T cells by a mechanism dependent on CCR5 ligands. FASEB J : Off Publ Fed Am Soc Exp Biol 26(3):1280–1289. https://doi.org/10.1096/fj.11-188979
Podlech J, Ebert S, Becker M, Reddehase MJ, Stassen M, Lemmermann NA (2015) Mast cells: innate attractors recruiting protective CD8 T cells to sites of cytomegalovirus infection. Med Microbiol Immunol 204(3):327–334. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00430-015-0386-1
Ebert S, Becker M, Lemmermann NA, Buttner JK, Michel A, Taube C, Podlech J, Bohm V, Freitag K, Thomas D, Holtappels R, Reddehase MJ, Stassen M (2014) Mast cells expedite control of pulmonary murine cytomegalovirus infection by enhancing the recruitment of protective CD8 T cells to the lungs. PLoS Pathog 10(4):e1004100. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.ppat.1004100
Ott VL, Cambier JC, Kappler J, Marrack P, Swanson BJ (2003) Mast cell-dependent migration of effector CD8+ T cells through production of leukotriene B4. Nat Immunol 4(10):974–981. https://doi.org/10.1038/ni971
Stelekati E, Bahri R, D'Orlando O, Orinska Z, Mittrucker HW, Langenhaun R, Glatzel M, Bollinger A, Paus R, Bulfone-Paus S (2009) Mast cell-mediated antigen presentation regulates CD8+ T cell effector functions. Immunity 31(4):665–676. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.immuni.2009.08.022
Li YS, Luo W, Zhu SA, Lei GH (2017) T cells in osteoarthritis: alterations and beyond. Front Immunol 8:356. https://doi.org/10.3389/fimmu.2017.00356
Woolley DE, Tetlow LC (2000) Mast cell activation and its relation to proinflammatory cytokine production in the rheumatoid lesion. Arthritis Res 2(1):65–74. https://doi.org/10.1186/ar70
Rivellese F, Nerviani A, Rossi FW, Marone G, Matucci-Cerinic M, de Paulis A, Pitzalis C (2017) Mast cells in rheumatoid arthritis: friends or foes? Autoimmun Rev 16(6):557–563. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.autrev.2017.04.001
Schuerwegh AJ, Dombrecht EJ, Stevens WJ, Van Offel JF, Bridts CH, De Clerck LS (2003) Influence of pro-inflammatory (IL-1 alpha, IL-6, TNF-alpha, IFN-gamma) and anti-inflammatory (IL-4) cytokines on chondrocyte function. Osteoarthr Cartil 11(9):681–687
Frenzel L, Hermine O (2013) Mast cells and inflammation. Joint, bone, spine : revue du rhumatisme 80 (2):141–145. doi:https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jbspin.2012.08.013
Shaik-Dasthagirisaheb YB, Conti P (2016) The role of mast cells in Alzheimer’s disease. Adv Clin Exp Med : Off Organ Wroclaw Med Univ 25(4):781–787. 10.17219/acem/61914
Folch J, Petrov D, Ettcheto M, Pedros I, Abad S, Beas-Zarate C, Lazarowski A, Marin M, Olloquequi J, Auladell C, Camins A (2015) Masitinib for the treatment of mild to moderate Alzheimer's disease. Expert Rev Neurother 15(6):587–596. https://doi.org/10.1586/14737175.2015.1045419
Xu D, Jiang HR, Kewin P, Li Y, Mu R, Fraser AR, Pitman N, Kurowska-Stolarska M, McKenzie AN, McInnes IB, Liew FY (2008) IL-33 exacerbates antigen-induced arthritis by activating mast cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 105(31):10913–10918. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.0801898105
Saluja R, Kumar A, Jain M, Goel SK, Jain A (2017) Role of Sphingosine-1-phosphate in mast cell functions and asthma and its regulation by non-coding RNA. Front Immunol 8:587. https://doi.org/10.3389/fimmu.2017.00587
Cahill KN, Katz HR, Cui J, Lai J, Kazani S, Crosby-Thompson A, Garofalo D, Castro M, Jarjour N, DiMango E, Erzurum S, Trevor JL, Shenoy K, Chinchilli VM, Wechsler ME, Laidlaw TM, Boyce JA, Israel E (2017) KIT inhibition by imatinib in patients with severe refractory asthma. N Engl J Med 376(20):1911–1920. https://doi.org/10.1056/NEJMoa1613125
Franceschini B, Ceva-Grimaldi G, Russo C, Dioguardi N, Grizzi F (2006) The complex functions of mast cells in chronic human liver diseases. Dig Dis Sci 51(12):2248–2256. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10620-006-9082-8
Bischoff SC (2016) Mast cells in gastrointestinal disorders. Eur J Pharmacol 778:139–145. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejphar.2016.02.018
Boeckxstaens G (2015) Mast cells and inflammatory bowel disease. Curr Opin Pharmacol 25:45–49. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.coph.2015.11.005
Gan PY, O'Sullivan KM, Ooi JD, Alikhan MA, Odobasic D, Summers SA, Kitching AR, Holdsworth SR (2016) Mast cell stabilization ameliorates autoimmune anti-myeloperoxidase glomerulonephritis. J Am Soc Nephrol : JASN 27(5):1321–1333. https://doi.org/10.1681/asn.2014090906
Elieh-Ali-Komi D, Cao Y (2017) Role of mast cells in the pathogenesis of multiple sclerosis and experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis. Clin Rev Allergy Immunol 52(3):436–445. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12016-016-8595-y
Kolkhir P, Church MK, Weller K, Metz M, Schmetzer O, Maurer M (2017) Autoimmune chronic spontaneous urticaria: what we know and what we do not know. J Allergy Clin Immunol 139(6):1772–1781.e1771. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jaci.2016.08.050
Rojanapremsuk T, Kasprowicz S, Schafer E, Story R, Clarke MS, Walls T, Snyder V, Gleason BC, Thomas AB, Cibull T (2015) Clinicopathologic findings in (anti-FcepsilonR1alpha) autoimmune-related chronic urticaria. J Cutan Pathol 42(5):329–332. https://doi.org/10.1111/cup.12471
Zebrowska A, Wagrowska-Danilewicz M (2014) Mediators of mast cells in bullous pemphigoid and dermatitis. Herpetiformis 2014:936545. https://doi.org/10.1155/2014/936545
Chen R, Ning G, Zhao ML, Fleming MG, Diaz LA, Werb Z, Liu Z (2001) Mast cells play a key role in neutrophil recruitment in experimental bullous pemphigoid. J Clin Invest 108(8):1151–1158. https://doi.org/10.1172/jci11494
Ujiie H, Nishie W, Shimizu H (2012) Pathogenesis of bullous pemphigoid. Immunol Allergy Clin N Am 32(2):207–215, v. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.iac.2012.04.001
Betto E, Usuelli V, Mandelli A, Badami E, Sorini C, Capolla S, Danelli L, Frossi B, Guarnotta C, Ingrao S, Tripodo C, Pucillo C, Gri G, Falcone M (2017) Mast cells contribute to autoimmune diabetes by releasing interleukin-6 and failing to acquire a tolerogenic IL-10+ phenotype. Clin Immunol (Orlando, Fla) 178:29–38. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.clim.2015.12.013
Conti P, Kempuraj D (2016) Important role of mast cells in multiple sclerosis. Mult sclerosis and Relat Disord 5:77–80. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.msard.2015.11.005
Kawikova I, Askenase PW (2015) Diagnostic and therapeutic potentials of exosomes in CNS diseases. Brain Res 1617:63–71. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.brainres.2014.09.070
Carroll-Portillo A, Surviladze Z, Cambi A, Lidke DS, Wilson BS (2012) Mast cell synapses and exosomes: membrane contacts for information exchange. Front Immunol 3:46. https://doi.org/10.3389/fimmu.2012.00046
Lenassi M, Cagney G, Liao M, Vaupotic T, Bartholomeeusen K, Cheng Y, Krogan NJ, Plemenitas A, Peterlin BM (2010) HIV Nef is secreted in exosomes and triggers apoptosis in bystander CD4+ T cells. Traffic (Copenhagen, Denmark) 11(1):110–122. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1600-0854.2009.01006.x
Li F, Wang Y, Lin L, Wang J, Xiao H, Li J, Peng X, Dai H, Li L (2016) Mast cell-derived exosomes promote Th2 cell differentiation via OX40L-OX40 ligation. J Immunol Res 2016:3623898. https://doi.org/10.1155/2016/3623898
Grimbaldeston MA, Metz M, Yu M, Tsai M, Galli SJ (2006) Effector and potential immunoregulatory roles of mast cells in IgE-associated acquired immune responses. Curr Opin Immunol 18(6):751–760. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.coi.2006.09.011
Hong GU, Lim JY, Kim NG, Shin JH, Ro JY (2015) IgE and IgA produced by OX40-OX40L or CD40-CD40L interaction in B cells-mast cells re-activate FcepsilonRI or FcalphaRI on mast cells in mouse allergic asthma. Eur J Pharmacol 754:199–210. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejphar.2015.02.023
Hong GU, Park BS, Park JW, Kim SY, Ro JY (2013) IgE production in CD40/CD40L cross-talk of Band mast cells and mediator release via TGase 2 in mouse allergic asthma. Cell Signal 25(6):1514–1525. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cellsig.2013.03.010
Mekori YA, Hershko AY (2012) T cell-mediated modulation of mast cell function: heterotypic adhesion-induced stimulatory or inhibitory effects. Front Immunol 3:6. https://doi.org/10.3389/fimmu.2012.00006
Mekori YA, Hershko AY, Frossi B, Mion F, Pucillo CE (2016) Integrating innate and adaptive immune cells: mast cells as crossroads between regulatory and effector B and T cells. Eur J Pharmacol 778:84–89. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejphar.2015.03.087
Gong J, Yang NS, Croft M, Weng IC, Sun L, Liu FT, Chen SS (2010) The antigen presentation function of bone marrow-derived mast cells is spatiotemporally restricted to a subset expressing high levels of cell surface FcepsilonRI and MHC II. BMC Immunol 11:34. https://doi.org/10.1186/1471-2172-11-34
Shefler I, Mekori YA, Mor A (2008) Stimulation of human mast cells by activated T cells leads to N-Ras activation through Ras guanine nucleotide releasing protein 1. J Allergy Clin Immunol 122(6):1222–1225. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jaci.2008.07.024
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
I hereby state that none of the coauthors and the corresponding author of this paper have a conflict of interest, and it has been prepared for publication without using any funding. Moreover, the paper does not contain any studies with human participants or animals performed by any of the authors.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Elieh Ali Komi, D., Grauwet, K. Role of Mast Cells in Regulation of T Cell Responses in Experimental and Clinical Settings. Clinic Rev Allerg Immunol 54, 432–445 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12016-017-8646-z
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12016-017-8646-z