Abstract
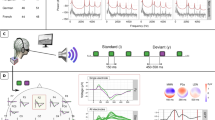
To elucidate the timing and the nature of neural disturbances in dyslexia and to further understand the topographical distribution of these, we examined entire brain regions employing the non-invasive auditory oddball P300 paradigm in children with dyslexia and neurotypical controls. Our findings revealed abnormalities for the dyslexia group in (i) P300 latency, globally, but greatest in frontal brain regions and (ii) decreased P300 amplitude confined to the central brain regions (Fig. 1). These findings reflect abnormalities associated with a diminished capacity to process mental workload as well as delayed processing of this information in children with dyslexia. Furthermore, the topographical distribution of these findings suggests a distinct spatial distribution for the observed P300 abnormalities. This information may be useful in future therapeutic or brain stimulation intervention trials.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alvarenga Kde, F., Araujo, E. S., Ferraz, E., & Crenitte, P. A. (2013). P300 auditory cognitive evoked potential as an indicator of therapeutical evolution in students with developmental dyslexia. Codas, 25(6), 500–505. doi:10.1590/s2317-17822014000100002
Donchin, E. (1981). Surprise!…Surprise? Psychophysiology, 18(5), 493–513.
Donchin, E., & Isreal, J. B. (1980). Event-related potentials and psychological theory. In: H. H. Kornhubek & L. Deecke (Eds.), Progress in brain research (Vol. 54, pp. 697–715). New York: Elsevier.
Donchin, E., Karis, D., Bashore, T. R., Coles, M. G. H., & Gratton, G. (1986). In M. G. H. Coles, E. Donchin, & S. Porges (Eds.), Psychophysiology: Systems, processes, and applications (pp. 244–267). New York: Guilford Press.
Duncan-Johnson, C. C., & Donchin, E. (1982). The P300 component of the event-related brain potential as an index of information processing. Biological Psychology, 14(1-2), 1–52.
Facoetti, A., Trussardi, A. N., Ruffino, M., Lorusso, M. L., Cattaneo, C., Galli, R.,…Zorzi, M. (2010). Multisensory spatial attention deficits are predictive of phonological decoding skills in developmental dyslexia. Journal of Cognitive Neuroscience, 22(5), 1011-1025. doi: 10.1162/jocn.2009.21232
Farmer, M., & Klein, R. (1995). The evidence for a temporal processing deficit linked to dyslexia: a review. Psychonomic Bulletin & Review, 2(4), 460–493. doi:10.3758/BF03210983
Fawcett, A. J., Chattopadhyay, A. K., Kandler, R. H., Jarratt, J. A., Nicolson, R. I., & Proctor, M. (1993). Event-related potentials and dyslexia. Annals of the New York Academy of Sciences, 682(1), 342–345. doi:10.1111/j.1749-6632.1993.tb22988.x
Fawcett, A. J., & Nicolson, R. I. (2004). The dyslexia screening test-Junior. London: Harcourt Assessment.
Gratton, G., Coles, M. G., & Donchin, E. (1983). A new method for off-line removal of ocular artifact. Electroencephalography and Clinical Neurophysiology, 55(4), 468–484.
Heth, I., & Lavidor, M. (2015). Improved reading measures in adults with dyslexia following transcranial direct current stimulation treatment. Neuropsychologia, 70, 107–113. doi:10.1016/j.neuropsychologia.2015.02.022
Hillyard, S. A., & Picton, T. W. (1978). ON and OFF components in the auditory evoked potential. Perception & Psychophysics, 24(5), 391–398. doi:10.3758/BF03199736
Kahneman, D. (1973). Attention and effort. New Jersey: Prentice-Hall.
Kok, A. (1990). Internal and external control: a two-factor model of amplitude change of event-related potentials. Acta Psychologica, 74(2-3), 203–236.
Kok, A. (2001). On the utility of P3 amplitude as a measure of processing capacity. Psychophysiology, 38(3), 557–577.
Kujala, T., Myllyviita, K., Tervaniemi, M., Alho, K., Kallio, J., & Näätänen, R. (2000). Basic auditory dysfunction in dyslexia as demonstrated by brain activity measurements. Psychophysiology, 37(2), 262–266.
Kutas, M., McCarthy, G., & Donchin, E. (1977). Augmenting mental chronometry: the P300 as a measure of stimulus evaluation time. Science, 197(4305), 792–795.
Leong, V., & Goswami, U. (2014). Impaired extraction of speech rhythm from temporal modulation patterns in speech in developmental dyslexia. Frontiers in Human Neuroscience, 8, 96. doi:10.3389/fnhum.2014.00096
Maciejewska, B., Wiskirska-Woznica, B., Swidzinski, P., & Michalak, M. (2013). Assessing auditory processing disorders in children with developmental dyslexia using auditory cognitive event-related potentials. Folia Phoniatrica et Logopedica, 65(3), 129–135. doi:10.1159/000354167
Magliero, A., Bashore, T. R., Coles, M. G., & Donchin, E. (1984). On the dependence of P300 latency on stimulus evaluation processes. Psychophysiology, 21(2), 171–186.
Mendonca, E. B., Muniz, L. F., Leal, M. D., & Diniz, A. D. (2013). Applicability of the P300 frequency pattern test to assess auditory processing. Brazilian Journal of Otorhinolaryngology, 79(4), 512–521. doi:10.5935/1808-8694.20130091
Nicolson, R. I. (1994). Reaction times and dyslexia. The Quarterly Journal of Experimental Psychology Section A, 47(1), 29–48. doi:10.1080/14640749408401142
Nicolson, R. I., & Fawcett, A. J. (1990). Automaticity: a new framework for dyslexia research? Cognition, 35(2), 159–182.
Oliveira, J. C., Murphy, C. F., & Schochat, E. (2013). Auditory processing in children with dyslexia: electrophysiological and behavior evaluation. Codas, 25(1), 39–44.
Ortiz Alonso, T., Navarro, M., & Vila Abad, E. (1990). P300 component of the auditory event-related potentials and dyslexia. Functional Neurology, 5(4), 333–338.
Polich, J. (1987). Task difficulty, probability, and inter-stimulus interval as determinants of P300 from auditory stimuli. Electroencephalography and Clinical Neurophysiology, 68(4), 311–320.
Polich, J. (2007). Updating P300: an integrative theory of P3a and P3b. Clinical Neurophysiology, 118(10), 2128–2148. doi:10.1016/j.clinph.2007.04.019
Polich, J., & Kok, A. (1995). Cognitive and biological determinants of P300: an integrative review. Biological Psychology, 41(2), 103–146.
Pribram, K. H., & McGuinness, D. (1975). Arousal, activation, and effort in the control of attention. Psychological Review, 82(2), 116–149.
Shaywitz, S. E., & Shaywitz, B. A. (2005). Dyslexia (specific reading disability). Biological Psychiatry, 57(11), 1301–1309. doi:10.1016/j.biopsych.2005.01.043
Sperling, A. J., Lu, Z. L., Manis, F. R., & Seidenberg, M. S. (2005). Deficits in perceptual noise exclusion in developmental dyslexia. Nature Neuroscience, 8(7), 862–863. doi:10.1038/nn1474
Sutton, S., Braren, M., Zubin, J., & John, E. R. (1965). Evoked-potential correlates of stimulus uncertainty. Science, 150(3700), 1187–1188.
Tallal, P. (1980). Auditory temporal perception, phonics, and reading disabilities in children. Brain and Language, 9(2), 182–198.
Thomson, J. M., & Goswami, U. (2008). Rhythmic processing in children with developmental dyslexia: auditory and motor rhythms link to reading and spelling. Journal of Physiology, Paris, 102(1-3), 120–129. doi:10.1016/j.jphysparis.2008.03.007
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Papagiannopoulou, E.A., Lagopoulos, J. P300 event-related potentials in children with dyslexia. Ann. of Dyslexia 67, 99–108 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11881-016-0122-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11881-016-0122-6