Abstract
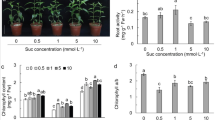
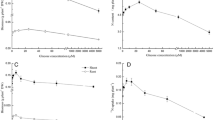
Sucrose is crucial for plant growth, but research about the effect of sucrose on the uptake of different nitrogen (N) and the metabolism of glycine is lacking. The uptake of glycine by pakchoi, when it was in a mixture of glycine, nitrate, and ammonium or acted as the single N source under different sucrose levels were detected in a sterilized environment. The optimal sucrose level for pakchoi growth varied with N supply; it was 6 μM in the single N source of glycine, while it was 15 μM in the mixture. The N contribution of glycine increased under the optimal sucrose, while the N contribution of ammonium decreased. The effect of exogenously supplied sucrose on the uptake and metabolism of glycine is dependent on the N supply. With the single N source, the metabolism of glycine to serine in roots rather than uptake was the limiting step under a high sucrose level (300 μM). In the mixed nitrogen, active uptake and the metabolism of glycine to serine are the limiting steps under high sucrose level. Externally supplied sucrose affects the absorption and metabolism of glycine by pakchoi greatly, and this effect varied with nitrogen supply.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bi YM, Zhang Y, Signorelli T, Rong Zhao, Tong Zhu, Steven R (2005) Genetic analysis of Arabidopsis GATA transcription factor gene family reveals a nitrate-inducible member important for chlorophyll synthesis and glucose sensitivity. Plant J 44:680–692
Bläsing OE, Gibon Y, Günther M, Höhne M, Morcuende R, Osuna D, Thimm O, Usadel B, Scheible WR, Stitt M (2005) Sugars and circadian regulation make major contributions to the global regulation of diurnal gene expression in Arabidopsis. Plant Cell 17:3257–3281
Bloom AJ (2015) The increasing importance of distinguishing among plant nitrogen sources. Curr Opin Plant Biol 25:10–16
Bush DR (2003) Proton-coupled sugar and amino acid transporters in plants. Annu Rev Plant Biol 44:513–542
Chanyarat PL, Lonhienne TGA, Doris R, Nicole R, Michael C, Webb RI, Gamage HK, Carroll BJ, Schenk PM, Susanne S (2008) Plants can use protein as a nitrogen source without assistance from other organisms. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 105:4524–4529
Cross JM, Maria VK, Thomas A, Linda B, Ronan S, Yves G, Natalia P, Mark S (2007) Variation of enzyme activities and metabolite levels in 24 Arabidopsis accessions growing in carbon-limited conditions. Plant Physiol 142:1574–1588
De JF, Thodey K, Lejay LV, Bevan MW (2014) Glucose elevates nitrate transporter2.1 protein levels and nitrate transport activity independently of its hexokinase1-mediated stimulation of nitrate transporter2.1 expression. Plant Physiol 164:308–320
Francesca S, Zwieniecki MA (2012) Analysis of xylem sap from functional (nonembolized) and nonfunctional (embolized) vessels of Populus nigra: chemistry of refilling. Plant Physiol 160:955–964
Francozorrilla JM, Martín AC, Leyva A, Pazares J (2005) Interaction between phosphate-starvation, sugar, and cytokinin signaling in Arabidopsis and the roles of cytokinin receptors CRE1/AHK4 and AHK3. Plant Physiol 138:847–857
Guo JH, Liu XJ, Zhang Y, Shen JL, Han WX, Zhang WF, Christie P, Goulding KWT, Vitousek PM, Zhang FS (2010) Significant acidification in major Chinese croplands. Science 327:1008–1010
Gutiérrez RA, Crawford NM (2007) Insights into the genomic nitrate response using genetics and the Sungear Software System. J Exp Bot 58:2359–2367
Horchani F, Hajri R, Aschi-Smiti S (2010) Effect of ammonium or nitrate nutrition on photosynthesis, growth, and nitrogen assimilation in tomato plants. J Plant Nutr Soil Sci 173:610–617
Jones DL, Hodge A, Kuzyakov Y (2004) Plant and mycorrhizal regulation of rhizodeposition. New Phytol 163:459–480
Jones DL, Healey JR, Willett VB, Farrar JF, Hodge A (2005) Dissolved organic nitrogen uptake by plants—an important N uptake pathway? Soil Biol Biochem 37:413–423
Kielland K, Mcfarland J, Olson K (2006) Amino acid uptake in deciduous and coniferous taiga ecosystems. Plant Soil 288:297–307
Kuzyakov Y, Domanski G (2000) Carbon input by plants into the soil. Review. J Plant Nutr Soil Sci 163:421–431
Lambers H, Veneklaas EJ (2006) Root structure and functioning for efficient acquisition of phosphorus: matching morphological and physiological traits. Ann Bot 98:693–713
Lianghuan W, Shihong J, Qingnan T (1998) The application of colorimetric method on the determination of transaminase activity. Chin J Soil Sci 3:41–43
Lynch JM, Whipps JM (1990) Substrate flow in the rhizosphere. Plant Soil 129:1–10
Ma Q, Cao X, Wu L, Mi W, Feng Y (2016) Light intensity affects the uptake and metabolism of glycine by pakchoi (Brassica chinensis L.). Sci Rep 6:21200
Ma Q, Cao X, Xie Y, Gu Y, Feng Y, Mi W, Yang X, Wu L (2017a) Effect of pH on the uptake and metabolism of glycine in pakchoi (Brassica chinensis L.). Environ Exp Bot 133:139–150
Ma Q, Cao X, Tan X, Si L, Wu L (2017b) Effects of cadmium stress on pakchoi (Brassica chinensis L.) growth and uptake of inorganic and organic nitrogenous compounds. Environ Exp Bot. doi:10.1016/j.envexpbot.2017.02.001
Mason MG, Ross JJ, Babst BA, Wienclaw BN, Beveridge CA (2014) Sugar demand, not auxin, is the initial regulator of apical dominance. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 111:6092–6097
Miller AE, Bowman WD (2003) Alpine plants show species-level differences in the uptake of organic and inorganic nitrogen. Plant Soil 250:283–292
Mimmo T, Hann S, Jaitz L, Cesco S, Gessa CE, Puschenreiter M (2011) Time and substrate dependent exudation of carboxylates by Lupinus albus L. and Brassica napus L. Plant Physio Biochem 49:1272–1278
Nero D, Krouk G, Tranchina D, Coruzzi GM (2009) A system biology approach highlights a hormonal enhancer effect on regulation of genes in a nitrate responsive “biomodule”. BMC Syst Biol 3:59
Pearse SJ, Veneklaas EJ, Cawthray GR, Bolland MDA, Lambers H (2006) Carboxylate release of wheat, canola and 11 grain legume species as affected by phosphorus status. Plant Soil 288:127–139
Persson J, Gardeström P, Näsholm T (2006) Uptake, metabolism and distribution of organic and inorganic nitrogen sources by Pinus sylvestris. J Exp Bot 57:2651–2659
Persson J, Gardeström P, Näsholm T (2002) Regulation of amino acid uptake in conifers by exogenous and endogenous nitrogen. Planta 215:639–644
Ruan YL (2014) Sucrose metabolism: gateway to diverse carbon use and sugar signaling. Annu Rev Plant Biol 65:33–67
Ruffel S, Gojon A, Lejay L (2014) Signal interactions in the regulation of root nitrate uptake. J Exp Bot 65:5509–5517
Sauheitl L, Glaser B, Weigelt A (2009) Uptake of intact amino acids by plants depends on soil amino acid concentrations. Environ Exp Bot 66:145–152
Schmidt S, Stewart GR (1999) Glycine metabolism by plant roots and its occurrence in Australian plant communities. Aust J Plant Physiol 26:253–264
Schofield RA, Bi YM, Kant S, Rothstein SJ (2009) Over-expression of STP13, a hexose transporter, improves plant growth and nitrogen use in Arabidopsis thaliana seedlings. Plant Cell Environ 32:271–285
Secchi F, Zwieniecki MA (2012) Analysis of xylem sap from functional (nonembolized) and nonfunctional (embolized) vessels of Populus nigra: chemistry of refilling. Plant Physiol 160:955–964
Susanne S, Torgny N, Doris R (2014) Organic nitrogen. New Phytol 203:29–31
Tegeder M (2012) Transporters for amino acids in plant cells: some functions and many unknowns. Curr Opin Plant Biol 15:315–321
Thornton B (2004) Inhibition of nitrate influx by glutamine in Lolium perenne depends upon the contribution of the HATS to the total influx. J Exp Bot 55:761–769
Thornton B, Robinson D (2005) Uptake and assimilation of nitrogen from solutions containing multiple N sources. Plant, Cell Environ 28:813–821
Torgny NS, Knut K, Ulrika G (2009) Uptake of organic nitrogen by plants. New Phytol 182:31–48
Wang L, Ruan YL (2015) Shoot–root carbon allocation, sugar signalling and their coupling with nitrogen uptake and assimilation. Funct Plant Biol 43(2):105–113
Warren CR (2012) Post-uptake metabolism affects quantification of amino acid uptake. New Phytol 193:522–531
Warren CR (2013) Quaternary ammonium compounds can be abundant in some soils and are taken up as intact molecules by plants. New Phytol 198:476–485
Warren CR (2014) Organic N molecules in the soil solution: what is known, what is unknown and the path forwards. Plant Soil 375:1–19
Wu LH, Mo LY, Fan ZL, Tao QN, Zhang FS (2005) Absorption of glycine by three agricultural species under sterile sand culture conditions. Pedosphere 15:286–292
Xu G, Fan X, Miller AJ (2011) Plant nitrogen assimilation and use efficiency. Annu Rev Plant Biol 63:153–182
Zerihun A, Mckenzie BA, Morton JD (1998) Photosynthate costs associated with the utilization of different nitrogen–forms: influence on the carbon balance of plants and shoot-root biomass partitioning. New Phytol 138:1–11
Zhang F, Cui Z, Chen X, Ju X, Shen J, Chen Q, Liu X, Zhang W, Mi G, Fan M (2012) 1 integrated nutrient management for food security and environmental quality in China. Adv Agron 116:1
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Communicated by J Gao.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ma, Q., Ma, J., Sun, Y. et al. Effects of external supplied sucrose on the uptake and metabolism of glycine by pakchoi (Brassica chinensis L.). Acta Physiol Plant 39, 170 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11738-017-2459-9
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11738-017-2459-9