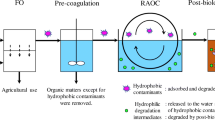
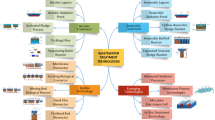
Abstract
Desalination of groundwater and brackish water reverse osmosis is becoming more common worldwide as a means of supplementing and diversifying fresh water supply. However, a key impediment to extensive reverse osmosis desalination adoption, particularly at inland sites, is the lack of economic and ecologically viable reject management alternatives. The reverse osmosis concentrate can harm the ecosystem by causing pH fluctuations, eutrophication, and the proliferation of hazardous metals that can cause various issues in the aquatic ecosystem and subsurface habitat degradation. Several alternative technologies have been explored to enhance reverse osmosis water recovery, limit the reject volume that must be disposed, and eliminate contaminants prior to beneficial uses or discharge. This review examines reject management options and technologies, including disposal, treatment, and beneficial usage. A comparative study reviewing all the plausible methodologies practically employed to economically and feasibly treat varied types of reverse osmosis concentrate is currently unavailable. This review also examines the suitability of the different treatment technologies for different types of reverse osmosis concentrate. The review also identifies important hurdles to a larger usage of desalination procedures, especially for inland applications, by critically reviewing reject management systems, treatment technologies, and beneficial uses. At last, conclusion and future perspectives are provided for researchers working in this field.












Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The authors confirm that this article contains all the data supporting the findings of this study.
References
Acevedo CR, Gardea-Torresdey JL, Tarquin AJ (2010) Silica removal from brine by using ion exchange. World environmental and water resources congress 2010. American Society of Civil Engineers, Reston, pp 3529–3541
Ahmed M, Shayya WH, Hoey D et al (2000) Use of evaporation ponds for brine disposal in desalination plants. Desalination 130:155–168. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0011-9164(00)00083-7
Ahmed M, Arakel A, Hoey D et al (2003) Feasibility of salt production from inland RO desalination plant reject brine: a case study. Desalination 158:109–117. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0011-9164(03)00441-7
Al-Absi RS, Abu-Dieyeh M, Al-Ghouti MA (2021) Brine management strategies, technologies, and recovery using adsorption processes. Environ Technol Innov. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eti.2021.101541
Ali MEA (2021) Nanofiltration process for enhanced treatment of RO brine discharge. Membranes (basel) 11:212. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes11030212
Al-Saad K, El-Azazy M, Issa AA et al (2019) Recycling of date pits into a green adsorbent for removal of heavy metals: a fractional factorial design-based approach. Front Chem. https://doi.org/10.3389/fchem.2019.00552
Amutha K (2017) Sustainable chemical management and zero discharges. In: Muthu SS (ed) Sustainable fibres and textiles. Elsevier, Amsterdam, pp 347–366
Arnal JM, Sancho M, Iborra I et al (2005) Concentration of brines from RO desalination plants by natural evaporation. Desalination 182:435–439. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.desal.2005.02.036
Arola K, Van der Bruggen B, Mänttäri M, Kallioinen M (2019) Treatment options for nanofiltration and reverse osmosis concentrates from municipal wastewater treatment: a review. Crit Rev Environ Sci Technol 49:2049–2116. https://doi.org/10.1080/10643389.2019.1594519
AzadiAghdam M, Achilli A, Snyder SA, Farrell J (2020) Increasing water recovery during reclamation of treated municipal wastewater using bipolar membrane electrodialysis and fluidized bed crystallization. J Water Process Eng 38:101555. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jwpe.2020.101555
Bagastyo AY, Keller J, Batstone DJ (2011a) Size fractionation characterisation of removed organics in reverse osmosis concentrates by ferric chloride. Water Sci Technol 63:1795–1800. https://doi.org/10.2166/wst.2011.379
Bagastyo AY, Radjenovic J, Mu Y et al (2011b) Electrochemical oxidation of reverse osmosis concentrate on mixed metal oxide (MMO) titanium coated electrodes. Water Res 45:4951–4959. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.watres.2011.06.039
Bai H, Liu Z, Sun DD (2011) Highly water soluble and recovered dextran coated Fe3O4 magnetic nanoparticles for brackish water desalination. Sep Purif Technol 81:392–399. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.seppur.2011.08.007
Bartholomew TV, Mey L, Arena JT et al (2017) Osmotically assisted reverse osmosis for high salinity brine treatment. Desalination 421:3–11. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.desal.2017.04.012
Bell EA, Poynor TE, Newhart KB et al (2017) Produced water treatment using forward osmosis membranes: evaluation of extended-time performance and fouling. J Memb Sci 525:77–88. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.memsci.2016.10.032
Boerlage ŚF, Kennedy MD, Bremere I et al (2000) Stable barium sulphate supersaturation in reverse osmosis. J Memb Sci 179:53–68. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0376-7388(00)00504-4
Burbano AA, Adham SS, Pearce WR (2007) The state of full-scale RO/NF desalination-results from a worldwide survey. J Am Water Works Assoc 99:116–127. https://doi.org/10.1002/j.1551-8833.2007.tb07912.x
De Buren L, Sharbat A (2015) Inland desalination and brine management: Salt recovery and beneficial uses of brine. World environ water resour congr 2015 floods, droughts, ecosyst—proc 2015 world environmental and water resources congress 2015, p1219–1230. https://doi.org/10.1061/9780784479162.120
Cemre Birben N, Bekbolet M (2019) Role of emerging contaminants on solar photocatalytic treatment of organic matter in reverse osmosis concentrate. Catal Today 326:101–107. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cattod.2018.10.048
Chang WS, Tran HT, Park DH, Zhang RH, Ahn DH (2009) Ammonium nitrogen removal characteristics of zeolite media in a Biological Aerated Filter (BAF) for the treatment of textile wastewater. J Ind Eng Chem 15(4):524–528. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jiec.2009.01.009
Chaplin BP, Schrader G, Farrell J (2010) Electrochemical destruction of N -Nitrosodimethylamine in reverse osmosis concentrates using boron-doped diamond film electrodes. Environ Sci Technol 44:4264–4269. https://doi.org/10.1021/es903872p
Choi HJ, Lee SM (2015) Treatment of reverse osmosis concentrate by biological aerated filter. Desalin Water Treat 53:1188–1195. https://doi.org/10.1080/19443994.2013.850449
Choi JY, Kaufmann F, Rahardianto A, Cohen Y (2021) Desupersaturation of RO concentrate and gypsum removal via seeded precipitation in a fluidized bed crystallizer. Water Res 190:116766. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.watres.2020.116766
Crawley J, Jackson WA, Anderson T et al (2012) Evaluating RO performance with biological pretreatment of graywater. J Water Reuse Desalin 2:109–120. https://doi.org/10.2166/wrd.2012.075
de Luna MDG, Rance DPM, Bellotindos LM, Lu M-C (2017) Removal of sulfate by fluidized bed crystallization process. J Environ Chem Eng 5:2431–2439. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jece.2017.04.052
Elazhar F, Elazhar M, El-Ghzizel S et al (2021) Nanofiltration-reverse osmosis hybrid process for hardness removal in brackish water with higher recovery rate and minimization of brine discharges. Process Saf Environ Prot 153:376–383. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.psep.2021.06.025
Ersever I, Ravindran V, Pirbazari M (2007a) Biological denitrification of reverse osmosis brine concentrates: I. Batch reactor and chemostat studies. J Environ Eng Sci 6:503–518. https://doi.org/10.1139/S07-021
Ersever I, Ravindran V, Pirbazari M (2007b) Biological denitrification of reverse osmosis brine concentrates: II. Fluidized bed adsorber reactor studies. J Environ Eng Sci 6:519–532. https://doi.org/10.1139/S07-009
Gabelich CJ, Williams MD, Rahardianto A et al (2007) High-recovery reverse osmosis desalination using intermediate chemical demineralization. J Memb Sci 301:131–141. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.memsci.2007.06.007
Gilron J, Folkman Y, Savliev R et al (2003) WAIV—wind aided intensified evaporation for reduction of desalination brine volume. Desalination 158:205–214. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0011-9164(03)00453-3
Greenlee LF, Lawler DF, Freeman BD et al (2009) Reverse osmosis desalination: water sources, technology, and today’s challenges. Water Res 43:2317–2348. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.watres.2009.03.010
Guan G, Wang R, Wicaksana F et al (2012) Analysis of membrane distillation crystallization system for high salinity brine treatment with zero discharge using aspen flowsheet simulation. Ind Eng Chem Res 51:13405–13413. https://doi.org/10.1021/ie3002183
Hoque S, Alexander T, Gurian PL (2010) Innovative technologies increase evaporation pond efficiency. IDA J Desalin Water Reuse 2:72–78. https://doi.org/10.1179/ida.2010.2.1.72
Hu JY, Song LF, Ong SL et al (2005) Biofiltration pretreatment for reverse osmosis (RO) membrane in a water reclamation system. Chemosphere 59:127–133. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2004.09.096
Huang H, Shi M, Ge X (1999) The effect of a black insulation sheet on the evaporation rate from a shallow salt pond. Int J Energy Res 23:31–39. https://doi.org/10.1002/(SICI)1099-114X(199901)23:1%3c31::AID-ER449%3e3.0.CO;2-F
Istirokhatun T, Dewi MN, Ilma HI, Susanto H (2018) Separation of antiscalants from reverse osmosis concentrates using nanofiltration. Desalination 429:105–110. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.desal.2017.12.018
Jamil S, Jeong S, Vigneswaran S (2016) Application of pressure assisted forward osmosis for water purification and reuse of reverse osmosis concentrate from a water reclamation plant. Sep Purif Technol 171:182–190. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.seppur.2016.07.036
Jamil S, Loganathan P, Kandasamy J et al (2019) Removal of dissolved organic matter fractions from reverse osmosis concentrate: comparing granular activated carbon and ion exchange resin adsorbents. J Environ Chem Eng 7:103126. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jece.2019.103126
Jeppesen T, Shu L, Keir G, Jegatheesan V (2009) Metal recovery from reverse osmosis concentrate. J Clean Prod 17:703–707. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2008.11.013
Ji X, Curcio E, Al Obaidani S et al (2010) Membrane distillation-crystallization of seawater reverse osmosis brines. Sep Purif Technol 71:76–82. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.seppur.2009.11.004
Jiang J-Q (2015) The role of coagulation in water treatment. Curr Opin Chem Eng 8:36–44. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.coche.2015.01.008
Jiang C, Wang Y, Zhang Z, Xu T (2014) Electrodialysis of concentrated brine from RO plant to produce coarse salt and freshwater. J Memb Sci 450:323–330. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.memsci.2013.09.020
Jiang N, Shang R, Heijman SGJ, Rietveld LC (2018) High-silica zeolites for adsorption of organic micro-pollutants in water treatment: a review. Water Res 144:145–161. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.watres.2018.07.017
Jiang X, Shao Y, Sheng L et al (2021) Membrane crystallization for process intensification and control: a review. Engineering 7:50–62. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eng.2020.06.024
Kazner C, Jamil S, Phuntsho S et al (2014) Forward osmosis for the treatment of reverse osmosis concentrate from water reclamation: process performance and fouling control. Water Sci Technol 69:2431–2437. https://doi.org/10.2166/wst.2014.138
Kim IH, Il LS, Kim DK (2016) Biological treatment of reverse osmosis concentrate from low salinity water. Desalin Water Treat 57:7667–7678. https://doi.org/10.1080/19443994.2015.1043593
Korngold E, Aronov L, Daltrophe N (2009) Electrodialysis of brine solutions discharged from an RO plant. Desalination 242:215–227. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.desal.2008.04.008
Kress N, Gertner Y, Shoham-Frider E (2020) Seawater quality at the brine discharge site from two mega size seawater reverse osmosis desalination plants in Israel (Eastern Mediterranean). Water Res 171:115402. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.watres.2019.115402
Labhasetwar PK, Yadav A (2023) Membrane based point-of-use drinking water treatment systems. IWA Publishing, London
Lee LY, Ng HY, Ong SL et al (2009a) Integrated pretreatment with capacitive deionization for reverse osmosis reject recovery from water reclamation plant. Water Res 43:4769–4777. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.watres.2009.08.006
Lee LY, Ng HY, Ong SL et al (2009b) Ozone-biological activated carbon as a pretreatment process for reverse osmosis brine treatment and recovery. Water Res 43:3948–3955. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.watres.2009.06.016
Lee S, Choi J, Park YG et al (2019) Hybrid desalination processes for beneficial use of reverse osmosis brine: current status and future prospects. Desalination 454:104–111. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.desal.2018.02.002
Leong J, Tan J, Heitz A, Ladewig BP (2016) Use of vibratory shear enhanced processing to treat magnetic ion exchange concentrate: a techno-economic analysis. Desalination 383:46–52. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.desal.2016.01.002
Liu J, Yuan J, Ji Z et al (2016) Concentrating brine from seawater desalination process by nanofiltration-electrodialysis integrated membrane technology. Desalination 390:53–61. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.desal.2016.03.012
Llenas L, Martínez-Lladó X, Yaroshchuk A et al (2011) Nanofiltration as pretreatment for scale prevention in seawater reverse osmosis desalination. Desalin Water Treat 36:310–318. https://doi.org/10.5004/dwt.2011.2767
Macedonio F, Katzir L, Geisma N et al (2011) Wind-Aided Intensified Evaporation (WAIV) and Membrane Crystallizer (MCr) integrated brackish water desalination process: advantages and drawbacks. Desalination 273:127–135. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.desal.2010.12.002
Macedonio F, Quist-Jensen CA, Al-Harbi O et al (2013) Thermodynamic modeling of brine and its use in membrane crystallizer. Desalination 323:83–92. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.desal.2013.02.009
Martinetti CR, Childress AE, Cath TY (2009) High recovery of concentrated RO brines using forward osmosis and membrane distillation. J Memb Sci 331:31–39. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.memsci.2009.01.003
McCutcheon JR, McGinnis RL, Elimelech M (2006) Desalination by ammonia–carbon dioxide forward osmosis: influence of draw and feed solution concentrations on process performance. J Memb Sci 278:114–123. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.memsci.2005.10.048
Mericq JP, Laborie S, Cabassud C (2010) Vacuum membrane distillation of seawater reverse osmosis brines. Water Res 44:5260–5273. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.watres.2010.06.052
Mickley MC (2006) Membrane concentrate disposal: practices and regulation. Desalin Water Purif Res Dev Progr 123:298
Mousavi SS, Kargari A (2022) Water recovery from reverse osmosis concentrate by commercial nanofiltration membranes: a comparative study. Desalination 528:115619. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.desal.2022.115619
Naidu G, Jeong S, Choi Y, Vigneswaran S (2017) Membrane distillation for wastewater reverse osmosis concentrate treatment with water reuse potential. J Memb Sci 524:565–575. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.memsci.2016.11.068
Ng HY, Lee LY, Ong SL et al (2008) Treatment of RO brine–towards sustainable water reclamation practice. Water Sci Technol 58:931–936. https://doi.org/10.2166/wst.2008.713
Ning RY, Tarquin A, Trzcinski M, Patwardhan G (2006) Recovery optimization of RO concentrate from desert wells. Desalination 201:315–322. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.desal.2006.06.006
Oren Y (2008) Capacitive deionization (CDI) for desalination and water treatment—past, present and future (a review). Desalination 228:10–29. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.desal.2007.08.005
Oren Y, Korngold E, Daltrophe N et al (2010) Pilot studies on high recovery BWRO-EDR for near zero liquid discharge approach. Desalination 261:321–330. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.desal.2010.06.010
Pan S-Y, Haddad AZ, Kumar A, Wang S-W (2020) Brackish water desalination using reverse osmosis and capacitive deionization at the water-energy nexus. Water Res 183:116064. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.watres.2020.116064
Park Y-S, Lee C-K, Kim S-K et al (2013) Effect of temperature difference on performance of membrane crystallization-based membrane distillation system. Desalin Water Treat 51:1362–1365. https://doi.org/10.1080/19443994.2012.705052
Pérez-González A, Urtiaga AM, Ibáñez R, Ortiz I (2012) State of the art and review on the treatment technologies of water reverse osmosis concentrates. Water Res 46:267–283. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.watres.2011.10.046
Petersen KL, Frank H, Paytan A, Bar-Zeev E (2018) Impacts of seawater desalination on coastal environments. Sustain Desalin Handb Plant Sel Des Implement. https://doi.org/10.1016/B978-0-12-809240-8.00011-3
Qu D, Wang J, Fan B et al (2009a) Study on concentrating primary reverse osmosis retentate by direct contact membrane distillation. Desalination 247:540–550. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.desal.2008.08.004
Qu D, Wang J, Wang L et al (2009b) Integration of accelerated precipitation softening with membrane distillation for high-recovery desalination of primary reverse osmosis concentrate. Sep Purif Technol 67:21–25. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.seppur.2009.02.021
Qu D, Wang J, Hou D et al (2010) Concentrating primary reverse osmosis concentrate by direct contact membrane distillation. Water Sci Technol Water Supply 10:403–410. https://doi.org/10.2166/ws.2010.121
Rahardianto A, McCool BC, Cohen Y (2008) Reverse osmosis desalting of inland brackish water of high gypsum scaling propensity: kinetics and mitigation of membrane mineral scaling. Environ Sci Technol 42:4292–4297. https://doi.org/10.1021/es702463a
Ramdin M, Morrison ART, De Groen M et al (2019) High pressure electrochemical reduction of co2 to formic acid/formate: a comparison between bipolar membranes and cation exchange membranes. Ind Eng Chem Res 58:1834–1847. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.iecr.8b04944
Randall DG, Nathoo J (2015) A succinct review of the treatment of reverse osmosis brines using freeze crystallization. J Water Process Eng 8:186–194. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jwpe.2015.10.005
Randall DG, Nathoo J, Lewis AE (2011) A case study for treating a reverse osmosis brine using eutectic freeze crystallization-approaching a zero waste process. Desalination 266:256–262. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.desal.2010.08.034
Salvador Cob S, Genceli Güner FE, Hofs B et al (2014) Three strategies to treat reverse osmosis brine and cation exchange spent regenerant to increase system recovery. Desalination 344:36–47. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.desal.2014.03.009
Sanmartino JA, Khayet M, García-Payo MC et al (2017) Treatment of reverse osmosis brine by direct contact membrane distillation: chemical pretreatment approach. Desalination 420:79–90. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.desal.2017.06.030
Shane Walker W, Kim Y, Lawler DF (2014) Treatment of model inland brackish groundwater reverse osmosis concentrate with electrodialysis—Part III: sensitivity to composition and hydraulic recovery. Desalination 347:158–164. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.desal.2014.05.034
Shanmuganathan S, Johir MAH, Listowski A et al (2016) Sustainable processes for treatment of waste water reverse osmosis concentrate to achieve zero waste discharge: a detailed study in water reclamation plant. Procedia Environ Sci 35:930–937. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.proenv.2016.07.076
Shanmuganathan S, Loganathan P, Kazner C et al (2017) Submerged membrane filtration adsorption hybrid system for the removal of organic micropollutants from a water reclamation plant reverse osmosis concentrate. Desalination 401:134–141. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.desal.2016.07.048
Sluys JTM, Verdoes D, Hanemaaijer JH (1996) Water treatment in a membrane-assisted crystallizer (MAC). Desalination 104:135–139. https://doi.org/10.1016/0011-9164(96)00036-7
Stylianou SK, Szymanska K, Katsoyiannis IA, Zouboulis AI (2015) Novel water treatment processes based on hybrid membrane-ozonation systems: a novel ceramic membrane contactor for bubbleless ozonation of emerging micropollutants. J Chem 2015:1–12. https://doi.org/10.1155/2015/214927
Su J, Chung T-S, Helmer BJ, de Wit JS (2012) Enhanced double-skinned FO membranes with inner dense layer for wastewater treatment and macromolecule recycle using Sucrose as draw solute. J Memb Sci 396:92–100. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.memsci.2012.01.001
Subramani A, Jacangelo JG (2014) Treatment technologies for reverse osmosis concentrate volume minimization: a review. Sep Purif Technol 122:472–489. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.seppur.2013.12.004
Subramani A, DeCarolis J, Pearce W, Jacangelo JG (2012) Vibratory shear enhanced process (VSEP) for treating brackish water reverse osmosis concentrate with high silica content. Desalination 291:15–22. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.desal.2012.01.020
Tanaka Y (2007) Chapter 3 Bipolar membrane electrodialysis. pp 405–436
Tao G, Viswanath B, Kekre K et al (2011) RO brine treatment and recovery by biological activated carbon and capacitive deionization process. Water Sci Technol 64:77–82. https://doi.org/10.2166/wst.2011.604
Tawfik A, Alalm MG, Awad HM et al (2022) Solar photo-oxidation of recalcitrant industrial wastewater: a review. Environ Chem Lett 20:1839–1862. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10311-022-01390-4
Torma CZ, Cséfalvay E (2018) Nanofiltration and electrodialysis: alternatives in heavy metal containing high salinity process water treatment. Chem Pap 72:1115–1124. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11696-018-0433-7
Tun CM, Fane AG, Matheickal JT, Sheikholeslami R (2005) Membrane distillation crystallization of concentrated salts—flux and crystal formation. J Memb Sci 257:144–155. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.memsci.2004.09.051
Turek M (2004) Electrodialytic desalination and concentration of coal-mine brine. Desalination 162:355–359. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0011-9164(04)00069-4
van der Ham F, Seckler MM, Witkamp GJ (2004) Eutectic freeze crystallization in a new apparatus: the cooled disk column crystallizer. Chem Eng Process Process Intensif 43:161–167. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0255-2701(03)00018-7
Van Hege K, Verhaege M, Verstraete W (2002) Indirect electrochemical oxidation of reverse osmosis membrane concentrates at boron-doped diamond electrodes. Electrochem Commun 4:296–300. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1388-2481(02)00276-X
Virapan SR, Murugaiyan V (2017) Treatment of reverse osmosis reject water from industries. Int J Appl Environ Sci 12:489–503
Vyas BG, Labhasetwar PK, Yadav A, Paital AR (2022) A compendium of evaporation techniques for salt production from seawater and sub-soil brine. Chem Pap 2022:1–16. https://doi.org/10.1007/S11696-022-02363-1
Waite T, Fane A, Schäfer A (2005) Nanofiltration: principles and applications. Elsevier, Amsterdam
Woisetschläger D, Humpl B, Koncar M, Siebenhofer M (2013) Electrochemical oxidation of wastewater - Opportunities and drawbacks. Water Sci Technol 68:1173–1179. https://doi.org/10.2166/wst.2013.366
Woo SY, Lee HS, Ji H et al (2019) Silica gel-based adsorption cooling cum desalination system: focus on brine salinity, operating pressure, and its effect on performance. Desalination 467:136–146. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.desal.2019.06.016
Xevgenos D, Vidalis A, Moustakas K et al (2015) Sustainable management of brine effluent from desalination plants: the SOL-BRINE system. Desalin Water Treat 53:3151–3160. https://doi.org/10.1080/19443994.2014.933621
Xu P, Cath TY, Robertson AP et al (2013) Critical review of desalination concentrate management, treatment and beneficial use. Environ Eng Sci 30:502–514. https://doi.org/10.1089/ees.2012.0348
Xu X, Lin L, Ma G et al (2018) Study of polyethyleneimine coating on membrane permselectivity and desalination performance during pilot-scale electrodialysis of reverse osmosis concentrate. Sep Purif Technol 207:396–405. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.seppur.2018.06.070
Yadav A, Sinha N (2022) Organic polymers for drinking water purification. In: Hashmi MSJ (ed) Encyclopedia of materials: plastics and polymers. Elsevier, Amsterdam, pp 997–1003
Yadav A, Labhasetwar PK, Shahi VK (2021) Membrane distillation using low-grade energy for desalination: a review. J Environ Chem Eng 9:105818. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jece.2021.105818
Yadav A, Labhasetwar PK, Shahi VK (2021) Fabrication and optimization of tunable pore size poly(ethylene glycol) modified poly(vinylidene-co-hexafluoropropylene) membranes in vacuum membrane distillation for desalination. Sep Purif Technol 271:118840. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.seppur.2021.118840
Yadav A, Labhasetwar PK, Shahi VK (2022) Membrane distillation crystallization technology for zero liquid discharge and resource recovery: opportunities, challenges and futuristic perspectives. Sci Total Environ 806:150692. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2021.150692
Yan Z, Yang H, Qu F et al (2017) Reverse osmosis brine treatment using direct contact membrane distillation: effects of feed temperature and velocity. Desalination 423:149–156. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.desal.2017.09.010
Zhang Y, Van der Bruggen B, Pinoy L, Meesschaert B (2009) Separation of nutrient ions and organic compounds from salts in RO concentrates by standard and monovalent selective ion-exchange membranes used in electrodialysis. J Memb Sci 332:104–112. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.memsci.2009.01.030
Zhi J-F, Wang H-B, Nakashima T et al (2003) Electrochemical incineration of organic pollutants on boron-doped diamond electrode. Evidence for direct electrochemical oxidation pathway. J Phys Chem B 107:13389–13395. https://doi.org/10.1021/jp030279g
Zhou T, Lim T-T, Chin S-S, Fane AG (2011) Treatment of organics in reverse osmosis concentrate from a municipal wastewater reclamation plant: feasibility test of advanced oxidation processes with/without pretreatment. Chem Eng J 166:932–939. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2010.11.078
Acknowledgements
CSIR-CSMCRI PRIS no 170/2022.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
RVP, RG, BGV, PL, AY—conceptualization, methodology, data curation, writing—original draft, visualization, investigation, writing—review & editing.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Ethics approval
Not applicable.
Consent to participate
Not applicable.
Consent for publication
We consent to publish the paper in this journal.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Patel, R.V., Gajera, R., Vyas, B.G. et al. Compendium of technologies for the treatment of reverse osmosis concentrate from inland desalination plants. Chem. Pap. 77, 5623–5639 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11696-023-02867-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11696-023-02867-4