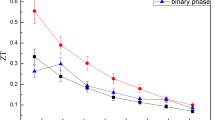
Bulk thermoelectric materials are of interest for commercial application in both power generation and Peltier refrigeration. Various synthesis approaches have been developed by our group for high performance bulk thermoelectric materials, such as solvo- or hydrothermal synthesis for nanopowders, hot-pressing, and spark plasma sintering for nanostructured bulk materials, and rapid solidification for metal silicides. In this article we report some of our recent results in the development of high ZT thermoelectric materials, including Bi2Te3-Sb2Te3 nanocomposites and CoSb3 micro/nanocomposites prepared by a powder blending route, and GeTe-AgSbTe2 and Mg2Si-Mg2Sn nanocomposites prepared by an in situ route. The results show various possibilities for improved microstructures and therefore enhanced properties of bulk thermoelectric materials through optimization of the preparation processing based on simple synthesis routes. A high ZT of approximately 1.5 has been obtained in both Bi2Te3-Sb2Te3 and GeTe-AgSbTe2 nanocomposites. Further ZT enhancement of the materials should be possible through the control of the nanopowder morphology during synthesis and the hindering of␣grain growth during sintering, as well as through the optimization of composition and doping.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
M.S. Dresselhaus, G. Chen, M.Y. Tang, R.G. Yang, H. Lee, D.Z. Wang, Z.F. Ren, J.P. Fleurial, and P. Gogna, Adv. Mater. 19, 1043 (2007). doi:10.1002/adma.200600527
X. Sun, Z. Zhang, and M.S. Dresselhaus, Appl. Phys. Lett. 74, 4005 (1999). doi:10.1063/1.123242
R. Venkatasubramanian, E. Siivola, T. Colpitts, and B. O’Quinn, Nature 413, 597 (2001). doi:10.1038/35098012
X.F. Tang, W.J. Xie, H. Li, W.Y. Zhao, Q.J. Zhang, and M. Niino, Appl. Phys. Lett. 90, 012102 (2007). doi:10.1063/1.2425007
B. Poudel, Q. Hao, Y. Ma, Y.C. Lan, A. Minnich, B. Yu, X. Yan, D.Z. Wang, A. Muto, D. Vashaee, X.Y. Chen, J.M. Liu, M.S. Dresselhaus, G. Chen, and Z. Ren, Science 320, 634 (2008). doi:10.1126/science.1156446
Y.Q. Cao, X.B. Zhao, T.J. Zhu, X.B. Zhang, and J.P. Tu, Appl. Phys. Lett. 92, 143106 (2008). doi:10.1063/1.2900960
R.G. Yang, G. Chen, and M.S. Dresselhaus, Phys. Rev. B 72, 125418 (2005). doi:10.1103/PhysRevB.72.125418
W. Kim, J. Zide, A. Gossard, D. Klenov, S. Stemmer, A. Shakouri, and A. Majumdar, Phys. Rev. Lett. 96, 045901 (2006). doi:10.1103/PhysRevLett.96.045901
X.B. Zhao, X.H. Ji, Y.H. Zhang, T.J. Zhu, J.P. Tu, and X.B. Zhang, Appl. Phys. Lett. 86, 062111 (2005). doi:10.1063/1.1863440
K.F. Hsu, S. Loo, F. Guo, W. Chen, J.S. Dyck, C. Uher, T. Hogan, E.K. Polychroniadis, and M.G. Kanatzidis, Science 303, 818 (2004). doi:10.1126/science.1092963
T.C. Harman, M.P. Walsh, B.E. Laforge, and G.W. Turner, J. Electron. Mater. 34, L19 (2005). doi:10.1007/s11664-005-0083-8
X.B. Zhao, X.H. Ji, Y.H. Zhang, G.S. Cao, and J.P. Tu, Appl. Phys. A 80, 1567 (2005). doi:10.1007/s00339-004-2956-8
X.B. Zhao, T. Sun, T.J. Zhu, and J.P. Tu, J. Mater. Chem. 15, 1621 (2005). doi:10.1039/b500759c
J.L. Mi, X.B. Zhao, T.J. Zhu, J.P. Tu, and G.S. Cao, J. Alloy. Compd. 417, 269 (2006). doi:10.1016/j.jallcom.2005.09.033
J.L. Mi, X.B. Zhao, T.J. Zhu, J.P. Tu, and G.S. Cao, J. Alloy. Compd. 399, 260 (2005). doi:10.1016/j.jallcom.2005.03.013
J.L. Mi, T.J. Zhu, X.B. Zhao, and J. Ma, J. Appl. Phys. 101, 054314 (2007). doi:10.1063/1.2436927
D.G. Ebling, A. Jacquot, M. Jagle, H. Bottner, U. Kuhn, and L. Kirste, Phys. Status Solidi-Rapid Res. Lett. 1, 238 (2007)
E. Quarez, K.F. Hsu, R. Pcionek, N. Frangis, E.K. Polychroniadis, and M.G. Kanatzidis, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 127, 9177 (2005). doi:10.1021/ja051653o
J. Androulakis, C.H. Lin, H.J. Kong, C. Uher, C.I. Wu, T. Hogan, B.A. Cook, T. Caillat, K.M. Paraskevopoulos, and M.G. Kanatzidis, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 129, 9780 (2007). doi:10.1021/ja071875h
J. Androulakis, K.F. Hsu, R. Pcionek, H. Kong, C. Uher, J.J. Dangelo, A. Downey, T. Hogan, and M.G. Kanatzidis, Adv. Mater. 18, 1170 (2006). doi:10.1002/adma.200502770
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhao, X.B., Yang, S.H., Cao, Y.Q. et al. Synthesis of Nanocomposites with Improved Thermoelectric Properties. J. Electron. Mater. 38, 1017–1024 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11664-009-0698-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11664-009-0698-2