Summary
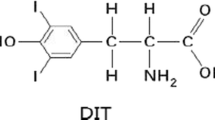
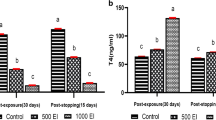
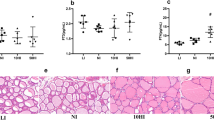
Ammonium perchlorate (AP), mainly used as solid propellants, was reported to interfere with homeostasis via competitive inhibition of iodide uptake. However, detailed mechanisms remain to be elucidated. In this study, AP was administered at 0, 130, 260 and 520 mg/kg every day to 24 male SD rats for 13 weeks. The concentrations of iodine in urine, serum thyroid hormones levels, total iodine, relative iodine and total protein, and malondialdehyde (MDA), superoxide dismutase (SOD) and catalase (CAT) activity in thyroid tissues were measured, respectively. Our results showed that high-dose perchlorate induced a significant increase in urinary iodine and serum thyroid stimulating hormone (TSH), with a decrease of total iodine and relative iodine content. Meanwhile, free thyroxine (FT4) was decreased and CAT activity was remarkably increased. Particularly, the CAT activity was increased in a dose-dependent manner. These results suggested that CAT might be enhanced to promote the synthesis of iodine, resulting in elevated urinary iodine level. Furthermore, these findings suggested that iodine in the urine and CAT activity in the thyroid might be used as biomarkers for exposure to AP, associated with thyroid hormone indicators such as TSH, FT4.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Wolff J. Perchlorateand the thyroid gland. Pharmacol Rev, 1998,50(1):89–105
Charnley G. Perchlorate: Overview of risks and regulation. Food Chem Toxicol, 2008,46(7):2307–2315
Peng KL, Jiang Y, Zhao SL, et al. Toxic effect of ammonium perchlorate on the thyroid gland in rats. Zhonghua Laodong Weisheng Zazhi (Chinese), 2003,21(6):404–407
Greer MA, Goodman G, Pleus RC, et al. Health effects assessment for environmental perchlorate contamination: the dose response for inhibition of thyroidal radioiodine uptake in humans. Environ Health Perspect, 2002,110(9): 927–937
McLanahan ED, Andersen ME, Campbell Jr JL, et al. Competitive inhibition of thyroidal uptake of dietary iodide by perchlorate does not describe perturbations in rat serum total T4 and TSH. Environ Health Perspect, 2009,117(5):731–738
Ye ZK, Sun YN, Lin LX, et al. Effect of different dosage potassium iodate on antioxidative capability of thyroid in rats. Chin J Public Health (Chinese), 2007,23(8):955–956
Lin MF, Peng KL, Guo HX, et al. The effects of ammounium perchlorate on TGF-β, TNF-α expression of lung tissue in rabbit. Zhonghua Laodong Weisheng Zhiyebing Zazhi, 2007,25(10):606–607
Yang HB, Peng KL, Chu QL, et al. Study on the injury effect of ammonium perchlorate to lung. J Hygi Res (Chinese), 2004,33(2):208–210
Wu FH. Guo HX, Lin MF, et al. Biomarker expression in lung of rabbit with pulmonary fibrosis induced by ammonium perchlorate. Toxicol Ind Health, 2011,27(3): 235–241
Zhou X, Wu FH, Zhang R, et al. Effects of ammonium perchlorate on iodine uptake and antioxidant capacity of thyroid. J Environ Occup Med (Chinese), 2011,28(6):347–350
Wu FH, Zhou X, Zhang R, et al. The effects of ammonium perchlorate on thyroid homeostasis and thyroid-specific gene expression in rat. Environ Toxicol, 2012,27(8):445–452
Dunnettt CW. A multiple comparison procedure for comparing several treatments with a control. J Am Stat Assoc, 1955,50(272):1096–1129
Sokal RR, Rohlf FJ. Bartlett’s test of homogeneity of variances In: Biometry, San Francisco: W.H. Freeman and Co, 1969.370–371
Siegel S. Fischer’s exact test In: Nonparametric statistics for the behavioral sciences. New York: McGraw-Hill, 1956.96–105
Dunn OJ. Multiple comparisons using rank sums. Technometrics, 1964,6(3):241–252
Carrasco N. Iodide transport in the thyroid gland. Biochim. Biophys Acta, 1993,1154(1):65–82
Taurog A. Hormone synthesis: Thyroid iodine metabolism. In: Braverman LE, Utiger RD, eds. Werner and Ingbar’s the thyroid: A fundamental and clinical text. 8th ed. Philadelphia: PA: Lippincott Williams & Wilkins, 2000. 61–84
Brabant G, Bergmann P, Kirsch CM, et al. Early adaptation of thyrotropin and thyroglobulin secretion to experimentally decreased iodine supply in man. Metabolism, 1992,41(10):1093–1096
Bürgi H, Benguerel M, Knopp J. et al. Influence of perchlorate on the secretion of non-thyroxine iodine by the normal human thyroid gland. Eur J Clin Invest, 1974,4(1): 65–69
Agency for Toxic Substances and Disease Registry. Toxicological profile for perchlorate. Atlanta, GA: U.S. Department of Health and Human Services, Public Health Service, 2008
Agency for Toxic Substances and Disease Registry. Toxicological profile for iodine. Atlanta, GA: U.S. Department of Health and Human Services, Public Health Service, 2004
Ulianich L, Suzuki K, Mori A, et al. Follicular thyroglobulin (TG) suppression of thyroid restricted genes involves the apical membrane asialoglycoprotein receptor and TG phosphorylation. Biol Chem, 1999,274(35): 25099–25107
Bai Y. Thyroid disease-basic and clinical. Beijing: Scientific and Technical Documents Publishing House, 2003. 167–280 (Chinese).
Braverman LE. Clinical Studies of Exposure to Perchlorate in the United States. Thyroid, 2007,17(9):819–822
Dohan O, Portulano C, Basquin C, et al. The NaI/symporter (NIS) mediates electroneutral active transport of the environmental pollutant perchlorate. Proc Nat Acad Sci U S A, 2007,104(51):20250–20255
Cianchetta S, Bernardo JD, Romeo G, et al. Perchlorate transport and inhibition of the sodium iodide symporter measured with the yellow fluorescent protein variant YFPH148Q/I152L. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol, 2010,243(3):372–380
York RG, Funk KA, Girard MF, et al. Oral (drinking water) developmental toxicity study of ammonium perchlorate in Sprague-Dawley rats. Int J Toxicol, 2003, 22(6):453–464
Blount BC, Pirkle JL, Osterloh JD, et al. Urinary perchlorate and thyroid hormone levels in adolescent and adult men and women living in the United States. Environ Health Perspect, 2006,114(12):1865–1871
Ye Y, Wang K, Zhang L. Effects of different iodine intake on iodine metabolism and thyroid function in rats. Chin J Public Health (Chinese), 2007,23(6):714–716
Tran N, Valentin-Blasini L, Blount BC, et al. Thyroid-stimulating hormone increases active transport of perchlorate into thyroid cells. Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab, 2008,294(4):802–806
Pearce EN, Andersson M, Zimmermann MB. Global Iodine Nutrition: Where Do We Stand in 2013? Thyroid, 2013,6(23):523–528
McDougal JN, Jones KL, Fatuyi B, et al. The effects of perchlorate on thyroidal gene expression are different from the effects of iodide deficiency. J Toxicol Environ Health A, 2011,74(14):917–926
Braverman LE, He XM, Pino S, et al. The Effect of perchlorate, thiocyanate,and nitrate on thyroid function in workers exposed to perchlorate long-term. J Clin Endocrinol Metab, 2005,90(2):700–706
NRC (National Research Council). Committee to assess the health implications of perchlorate ingestion. Washington, DC: National Academies Press, 2005.104–105
Ohye H, Sugawara M. Dual oxidase, hydrogen peroxide and thyroid diseases. Exp Biol Med, 2010,235(4): 424–433
Braverman LE, Utiger RD. Werner and Ingbar’s the thyroid: A fundamental and clinical text. 8th ed. Philadelphia: PA: Lippincott Williams & Wilkins, 2000:227–233
Kogai T, Endo T, Saito T, et al. Regulation by thyroid stimulating hormone of sodium/iodide symporter gene expression and protein levels in FRTL-5 cells. Endocrinology, 1997,138(6):2227–2232
Saito T, Endo T, Kawaguchi A, et al. Increased expression of the Na/I-symporter in cultured human thyroid cells exposed to thyrotropin and in Graves’ thyroid tissue. J Clin Endocrinol Metab, 1997,82(10):3331–3336
Selmi-Ruby S, Watrin C, Trouttet-Masson S, et al. The porcine sodium/iodide symporter gene exhibits an uncommon expression pattern related to the use of alternative splice sites not present in the human or murine species. Endocrinology, 2003,144(3):1074–1085
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
This project was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 30972452).
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chen, Hx., Ding, Mh., Liu, Q. et al. Change of iodine load and thyroid homeostasis induced by ammonium perchlorate in rats. J. Huazhong Univ. Sci. Technol. [Med. Sci.] 34, 672–678 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11596-014-1335-8
Received:
Revised:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11596-014-1335-8