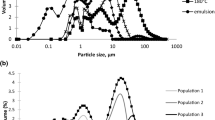
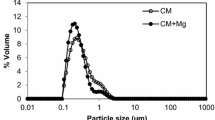
Abstract
This study investigated effects of enzyme-modified soy lecithin (ESL) on freeze thaw stability and heat stability of coconut oil-in-water emulsions and coconut milk emulsions. Addition of ESL improved freeze thaw stability of coconut oil-in-water emulsions and coconut milk emulsions. Mean droplet sizes of coconut oil-in-water emulsions contained 20 wt% oil and 9 wt% ESL did not significantly alter after emulsions being frozen at -20 °C for 22 h and thawed at room temperature. Relatively similar fat crystallization patterns obtained from differential scanning calorimetry after three cooling-heating cycles (40 °C to -40 °C to 40 °C at 5 °C/min) confirmed high freeze thaw stability of coconut oil-in-water emulsions. Increasing concentrations of ESL to 9 wt% reduced amounts of destabilized oil in freeze thawed coconut milk emulsions substantially. Heat stability study shows that coconut oil-in-water emulsions and coconut milk emulsions stabilized by 9 wt% ESL remained remarkably stable after heating at 121 °C for 1 h observed by microscopy and mean droplet sizes. This work reveals that ESL contained mostly of unsaturated lysophospholipids reduced partial coalescence during freeze thawing process and reduced protein coagulation, droplets flocculation, and coalescence during heating process. ESL partially displaced and possibly interacted with interfacial coconut proteins which increased stability of coconut milk emulsions.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
C.C. Seow, C.N. Gwee, Int. J. Food Sci. Technol. 32, 189 (1997)
N. Tangsuphoom, J.N. Coupland, J. Food Sci. 70(8), 466 (2005)
N. Tangsuphoom, J.N. Coupland, J. Food Sci. 73(6), 274 (2008)
N. Tangsuphoom, J.N. Coupland, Food Hydrocolloids 22(7), 1233 (2008)
N. Tangsuphoom, J.N. Coupland, Food Hydrocolloids 23(7), 1792 (2009)
N. Tangsuphoom, J.N. Coupland, Food Hydrocolloids 23(7), 1801 (2009)
S. Ariyaprakai, L. Tanachote, P. Pradipasena, Food Hydrocolloids 30, 358 (2013)
S. Ariyaprakai, K. Tananuwong, J. Food Eng. 152, 57 (2015)
J. Yang, C. Qiu, G. Li, W.J. Lee, C.P. Tan, O.M. Lai, Y. Wang. Food Chem. 327, 127014 (2020)
S. Ghosh, D. Rousseau, J. Colloid Interface Sci. 339(1), 91 (2009)
Q.-Q. Yang, Z. Sui, W. Lu, H. Corke, Food Chem. 338, 128071 (2021)
Z. Ma, N. Khalid, G. Shu, Y. Zhao, I. Kobayashi, M.A. Neves, A. Tuwo, M. Nakajima, ACS Omega 4(6), 10502 (2019)
L. Cui, J. Fan, Y. Sun, Z. Zhu, J. Yi, Food Chem. 252, 28 (2018)
D.J. McClements, E.A. Decker, S.J. Choi, J. Agric. Food Chem. 62(14), 3257 (2014)
D. Wu, J. Lu, S. Zhong, P. Schwarz, B. Chen, J. Rao, LWT Food Sci. Technol. 106, 98 (2019)
I. Dammak, P.J. do Amaral Sobral, J. Food Eng., 229, 12 (2018)
A.M. Chuah, T. Kuroiwa, I. Kobayashi, M. Nakajima, Food Hydrocolloids 23(3), 600 (2009)
M.I. Moran-Valero, V.M.P. Ruiz-Henestrosa, A.M.R. Pilosof, Colloids Surf., B, 151, 68 (2017)
J. Palanuwech, R. Potineni, R.F. Roberts, J.N. Coupland, Food Hydrocolloids 17(1), 55 (2003)
P. Thanasukarn, R. Pongsawatmanit, D.J. McClements, Food Hydrocolloids 18(6), 1033 (2004)
K. Matsumiya, W. Takahashi, T. Inoue, Y. Matsumura, J. Food Eng. 96(2), 185 (2010)
M. Schmiele, S. Busch, H. Morhenn, T. Schindler, T. Schmutzler, R. Schweins, P. Lindner, P. Boesecke, M. Westermann, F. Steiniger, S.S. Funari, T. Unruh, J. Phys. Chem. 120(24), 5513 (2016)
M. Schmiele, T. Schindler, T. Unruh, S. Busch, H. Morhenn, M. Westermann, F. Steiniger, A. Radulescu, P. Lindner, R. Schweins, P. Boesecke, Phys. Rev. E: Stat. Nonlinear Soft Matter Phys. 87 (6), 062316 (2013)
M. Schmiele, T. Schindler, M. Westermann, F. Steiniger, A. Radulescu, A. Kriele, R. Gilles, T. Unruh, J. Phys. Chem. B 118(29), 8808 (2014)
T. Tran Le, P. Sabatino, B. Heyman, M. Kasinos, H.H. Dinh, K. Dewettinck, J. Martins, P. Van der Meeren, Food Hydrocolloids. 25 (4), 594 (2011)
Acknowledgements
Enzyme-modified soy lecithin (ESL) used in this study were kindly donated by Rama Production., Ltd.
This research did not receive any specific grant from funding agencies in the public, commercial, or not-for-profit sectors.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The author declared that having no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
11483_2021_9711_MOESM1_ESM.docx
Supplementary file1 Supplementary Figure 1 Oil droplet size distributions of initial and freeze thawed coconut oil-in-water emulsions contained 20 wt% oil with addition of 1-9 wt% enzyme-modified soy lecithin. (DOCX 31 KB)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ariyaprakai, S. Freeze Thaw Stability and Heat Stability of Coconut Oil-in-Water Emulsions and Coconut Milk Emulsions Stabilized by Enzyme-Modified Soy Lecithin. Food Biophysics 17, 557–567 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11483-021-09711-w
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11483-021-09711-w