Abstract
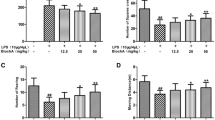
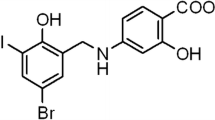
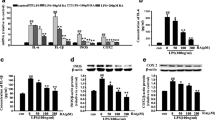
Recent studies have demonstrated a close interaction between neuroinflammatory responses, increased production of inflammatory mediators, and neurodegeneration. Pathological findings in neurological diseases such as Alzheimer’s disease, Parkinson’s disease, and Huntington’s disease have shown common signs of neuroinflammation and neurodegeneration. Lupeol, a natural pentacyclic triterpene, has revealed a number of pharmacological properties including an anti-inflammatory activity. This study aimed to evaluate the effect of lupeol against lipopolysaccharide (LPS)-induced neuroinflammation in the cortex and hippocampus of adult mice. Our results showed that systemic administration of LPS induced glial cell production of proinflammatory cytokines, tumor necrosis factor (TNF)-α, inducible nitric oxide synthase (iNOS), and interleukin (IL)-1β, while co-treatment with lupeol significantly inhibited the LPS-induced activation of microglia and astrocytes, and decreased the LPS-induced generation of TNF-α, iNOS, and IL-1β. The intracellular mechanism involved in the LPS-induced activation of inflammatory responses includes phosphorylation of P38 mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK) and c-Jun N-terminal kinase (JNK), which was significantly inhibited by lupeol. We further elucidated that lupeol inhibited the LPS-induced activation of the mitochondrial apoptotic pathway and reversed the LPS-induced expression of apoptotic markers such as Bax, cytochrome C, caspase-9, and caspase-3. Taken together; our results suggest that lupeol inhibits LPS-induced microglial neuroinflammation via the P38-MAPK and JNK pathways and has therapeutic potential to treat various neuroinflammatory disorders.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ajizan SJ, English BK, Meals EA (1999) Specific inhibitors of p38 and extracellular signal-regulated kinase mitogen-activated protein kinase pathways block inducible nitric oxide synthase and tumor necrosis factor accumulation in murine macrophages stimulated with lipopolysaccharide and interferon-gamma. J Infect Dis 179:939–944
Akihisa T, Yasukawa K, Oinuma H, Kasahara Y, Yamanouchi S, Takido M, Kumaki K, Tamura T (1996) Triterpene alcohols from the flowers of compositae and anti-inflammatory effects. Phytochemistry 43:1255–1260
Aktas O, Ullrich O, Infante-Duarte C, Nitsch R, Zipp F (2007) Neuronal damage in brain inflammation. Arch Neurol 64:185–189
Ali T, Badshah H, Kim TH, Kim MO (2015) Melatonin attenuates D-galactose-induced memory impairment, neuroinflammation and neurodegeneration via RAGE/NF-K B/JNK signaling pathway in aging mouse model. J Pineal Res 58:71–85
Badshah H, Ullah I, Kim SE, Kim TH, Lee HY, Kim MO (2013) Anthocyanins attenuate body weight gain via modulating neuropeptide Y and GABAB1 receptor in rats’ hypothalamus. Neuropeptides 47:347–353
Badshah H, Kim TH, Kim MJ, Ahmad A, Ali T, Yoon GH, Naseer MI, Kim MO (2014) Apomorphine attenuates ethanol-induced neurodegeneration in the adult rat cortex. Neurochem Int 74:8–15
Bani S, Kaul A, Khan B, Ahmad SF, Suri KA, Gupta BD, Satti NK, Qazi GN (2006) Suppression of T lymphocyte activity by lupeol isolated from Crataeva religiosa. Phytother Res 20:279–287
Bendottil C, Tortarolol M, Borsellol T (2006) Stress activated protein kinases, JNK and p38, as new therapeutic approach for neurodegenerative diseases. Cent Nerv Syst Agents Med Chem 6:109
Bjorkqvist M, Wild EJ, Tabrizi SJ (2009) Harnessing immune alterations in neurodegenerative diseases. Neuron 64:21–24
Block ML, Zecca L, Hong JS (2007) Microglia-mediated neurotoxicity: uncovering the molecular mechanisms. Nat Rev Neurosci 8:57–69
Brimson JM, Brimson SJ, Brimson CA, Rakkhitawatthana V, Tencomnao T (2012) Rhinacanthus nasutus extracts prevent glutamate and amyloid-β neurotoxicity in HT-22 mouse hippocampal cells: Possible active compounds include lupeol, stigmasterol, and β-sitosterol. Int J Mol Sci 13:5074–5097
Brown GC, Neher JJ (2010) Inflammatory neurodegeneration and mechanisms of microglial killing of neurons. Mol Neurobiol 41:242–247
Cederbaum AI, Yang L, Wang X, Wu D (2012) CYP2E1 sensitizes the liver to LPS- and Tnf α-induced toxicity via elevated oxidative and nitrosative stress and activation of ASK-1 and JNK mitogen-activated kinases. Int J Hepatol 582790
Chagnon F, Metz CN, Bucala R, Lesur O (2005) Endotoxin-induced myocardial dysfunction. Circ Res 96:1095–1102
Davis RH, DiDonato JJ, Johnson RW, Stewart CB (1994) Aloe vera, hydrocortisone, and sterol influence on wound tensile strength and anti-inflammation. J Am Podiatr Med Assoc 84:614–621
Debatin KM, Poncet D, Kroemer G (2002) Chemotherapy: targeting the mitochondrial cell death pathway. Oncogene 21:8786–8803
Di Filippo M, Chiasserini D, Tozzi A, Picconi B, Calabresi P (2010) Mitochondria and the link between neuroinflammation and neurodegenertion. J Alzheimers Dis 20:369–379
Ding Y, Nguyen HT, Kim SI, Kim HW, Kim YH (2009) The regulation of inflammatory cytokine secretion in macrophage cell line by the chemical constituents of Rhus sylvestris. Chem Lett 19:3607–3610
El-Remessy AB, Tang Y, Zhy G, Matragoon S, Khalifa Y, Liu EK, Liu JY, Hanson E, Mian S, Fatteh N, Liou GI (2008) Neuroprotective effects of cannabidiol in endotoxin-induced uveitis: critical role of p38 MAPK activation. Mol Vis 14:2190–2203
Gao HM, Hong JS (2008) Why neurodegenerative diseases are progressive: uncontrolled inflammation drives disease progression. Trends Immunol 29:357–365
Gebicke-Haerter PJ (2001) Microglia in neurodegeneration: molecular aspects. Microsc Res Tech 54:47–58
Gupta R, Sharma AK, Sharma MC, Dobhal MP, Gupta RS (2012) Evaluation of antidiabetic and antioxidant potential of lupeol in experimental hyperglycemia. Nat Prod Res 26:1125–1129
Han Z, Boyle DL, Chang L, Bennett B, Karin M, Yang L, Manning AM, Firestein GS (2001) C-Jun N-terminal kinase is required for metalloproteinase expression and joint destruction in inflammatory arthritis. Clin Investig 108:73–81
Hattori Y, Takano K, Teramae H, Yamamoto S, Yokoo H, Matsuda N (2010) Inights into sepsis therapeutic design based on the apoptotic death pathway. J Pharmacol Sci 114:354–365
Haydon PG, Carmignoto G (2006) Astrocyte control of synaptic transmission and neurovascular coupling. Physiol Rev 86:1009–1031
He Y, Liu F, Zhang L, Wu Y, Hu B, Zhang Y, Li Y, Liu H (2011) Growth inhibition and apoptosis induced by lupeol, a dietary triterpene, in human hepatocellular carcinoma cells. Biol Pharm Bull 34:517–522
Heneka MT, O’Banion MK (2007) Inflammatory processes in Alzheimer’s disease. J Neuroimmunol 184:69–91
Hirsch EC, Hunot S (2009) Neuroinflammation in Parkinson, s disease: a target for neuroprotection? Lancet Neurol 8:382–397
Hotchkiss RS, Swanson PE, Freeman BD, Tinsley KW, Cobb JP, Matuschak GM, Buchman TG, Karl IE (1999) Apoptotic cell death in patients with sepsis, shock, and multiple organ dysfunction. Crit Care Med 27:1230–1251
Huang YN, Lai CC, Lin JJ, Wang JY (2014) L-ascorbate attenuates the endotoxin-induced production of inflammatory mediators by inhibiting MAPK activation and NFκB translocation in cortical neurons/glia cocultures. PLoS ONE 9, e97276
Kacimi R, Giffard RG, Yenari MA (2011) Endotoxin-activated microglia injure brain derived endothelial cells via NF-κB. JAK-STAT and JNK stress kinase pathways. J Inflamm (Lond) 8:7
Kawai T, Akira S (2010) The role of pattern-recognition receptors in innate immunity: update on Toll-like receptors. Nat Immunol 11:373–384
Kumari A, Kakkar P (2012a) Lupeol prevents acetaminophen-induced in vivo hepatotoxicity by altering the Bax/Bcl-2 and oxidative stress-mediated mitochondrial signaling cascade. Life Sci 90:561–570
Kumari A, Kakkar P (2012b) Lupeol protects against acetaminophen-induced oxidative stress and cell death in rat primary hepatocytes. Food Chem Toxicol 50:1781–1789
Kyriakis JM, Ayruch J (2012) Mammalian MAPK signal transduction pathways activated by stress and inflammation: a 10-year update. Physiol Rev 92:689–737
Kyriasis JM, Avruch J (2001) Mammalian mitogen-activated protein kinase signal transduction pathways activated by stress and inflammation. Physiol Rev 81:807–869
Lull ME, Block ML (2010) Microglial activation and chronic neurodegeneration. Neurotherapeutics 7:354–365
Maragakis NJ, Rothstein JD (2006) Mechanism of disease: astrocytes in neurodegenerative disease. Nat Clin Pract Neurol 2:679–689
More SV, Kumar H, Kim IS, Song SY, Choi DK (2013) Cellular and molecular mediators of neuroinflammation in the pathogenesis of Parkinson’s disease. Mediators Inflamm doi: 10.115/2013/952375
Munoz L, Ranaivo HR, Rov SR, Hu W, Craft JM, McNamara LK, Chico LW, Van Eldik LJ, Watterso DM (2007) A novel P38MAPK inhibitor suppresses brain proinflammatory cytokine. J Neuroinflammation 4:21
Munshi N, Fernandis AZ, Cherla RP, Park IW, Ganju RK (2002) Lipopolysaccharide-induced apoptosis of endothelial cells and its inhibition by vascular endothelial growth factor. J Immunol 168:5860–5866
Nakajima K, Tohyama Y, Kohsaka S, Kurihara T (2004) Protien kinase C alpha requirement in the activation of p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase, which is linked to the induction of tumor necrosis factor alpha in lipopolysaccharide-stimulated microglia. Neurochem Int 44:205–214
Nimmerjahn A, Kirchhoff F, Helmchen F (2005) Resting microglial cells are highly dynamic surveillants of brain parenchyma in vivo. Science 308:1314–1318
Palsson-McDermott EM, O’Neill LA (2004) Signal transduction by the lipopolysaccharide receptor, Toll-like receptor-4. Immunology 113:153–162
Papi Reddy K, Singh AB, Puri A, Srivastava AK, Narender T (2009) Synthesis of novel triterpenoid (lupeol) derivatives and their in vivo antihyperglycemic and antidyslipidemic activity. Bioorg Med Chem Lett 4463–6
Parajuli B, Sonobe Y, Kawanokuchi J, Doi Y, Noda M, Takeuchi H, Mizuno T, Suzumura A (2012) GM-CSF increase LPS-induced production of proinflammatory mediators via upregulation of TLR4 and CD14 in murine microglia. J Neuroinflammation 9:268
Putcha GV, Le S, Frank S, Besirli CG, Clark K, Chu B, Alix S, Youle RJ, LaMarche A, Maroney AC, Johnson EM Jr (2003) JNK-mediated BIM phosphorylation potentiates BAX-dependent apoptosis. Neuron 19:899–914
Saeed MA, Sabir AW (2002) Irritant potential of triterpenoids from Ficus carica leaves. Fitoterapia 73:417–420
Schmued LC, Hopkins KJ (2000) Fluoro-Jade B: a high affinity fluorescent marker for the localization of neuronal degeneration. Brain Res 874:123–130
Shah SA, Lee HY, Bressan RA, Yun DJ, Kim MO (2014) Novel osmotin attenuates glutamate-induced synaptic dysfunction and neurodegeneration via the JNK/PI3K/Akt pathway in postnatal rat brain. Cell Death Dis 5:1026
Shaulian E, Karin M (2002) AP-1 as a regulator of cell life and death. Nat Cell Biol 4:131–136
Siddique HR, Saleem M (2011) Beneficial health effects of lupeol triterpene: a review of preclinical studies. Life Sci 88:285–293
Siddique HR, Mishra SK, Karnes RJ, Saleem M (2011) Lupeol, a novel androgen receptor inhibitor: implications in prostate cancer therapy. Cancer Res 17:5379–5391
Skaper SD (2007) The brain as a target for inflammatory processes and neuroprotective strategies. Ann N Y Acad Sci 1122:23–34
Stambe C, Atkins RC, Hill PA, Nikolic-Paterson DJ (2003) Activation and cellular localization of the p38 and JNK MAPK pathways in rat crescentic glomerulonephritis. Kidney Int 64:2121–2132
Tansey M, Tran T, Lee JK (2009) Neuroinflammation in Parkinson’s disease. J Neuroimmune Pharmacol 4:419–429
Tournier C, Hess P, Yang DD, Xu J, Turner TK, Nimnual A, Bar-Sagi D, Jones SN, Flavell RA, Davis RJ (2000) Requirement of JNK for stress-induced activation of the cytochrome c-mediated death pathway. Science 288:870–874
Wang LW, Tu YF, Huang CC, Ho CJ (2012) JNK signaling is the shared pathway linking neuroinflammation, blood–brain barrier disruption, and oligodendroglial apoptosis in the white matter injury of the immature brain. J Neuroinflammation 9:175
Xing B, Bachstetter AD, Van Eldik LJ (2011) Microglial p38α MAPK is critical for LPS-induced neuron degeneration, through a mechanism involving TNFα. Mol Neurodegener 6:84
Yasuda S, Sugiura H, Tanaka H, Takigami S, Yamagata K (2011) p38 MAP kinase inhibitors as potential therapeutic drugs for neural diseases. Cent Nerv Syst Agents Med Chem 11:45–59
Zarubin T, Han J (2005) Activation and signaling of p38 MAP kinase pathway. Cell Res 15:11–18
Acknowledgments
This research was supported by the Commercializations Promotion Agency for R&D outcome (COMPA) and Pioneer Research Center Program through the National Research Foundation of Korea funded by the Ministry of Science, ICT & Future Planning (2012–0009521).
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Haroon Badshah and Tahir Ali contributed equally to this work.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Badshah, H., Ali, T., Rehman, Su. et al. Protective Effect of Lupeol Against Lipopolysaccharide-Induced Neuroinflammation via the p38/c-Jun N-Terminal Kinase Pathway in the Adult Mouse Brain. J Neuroimmune Pharmacol 11, 48–60 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11481-015-9623-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11481-015-9623-z