Abstract
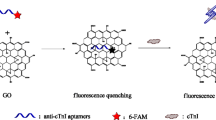
Troponin I, as a cardiac-specific biomarker, is a very valuable tool in the identification of acute coronary syndromes. In this work, an economical technique for easy and sensitive diagnosis of cardiac troponin I (cTnI) was developed nanoprobe on the basis of graphene oxide quenching of the fluorescence of bovine serum albumin–capped fluorescent nickel (BSA@NiNCs) nanoclusters. The developed nanoprobe nickel nanocluster exhibited superparamagnetism. The nanoprobe showed a fluorescence turn-on behavior toward incremental addition of in cTnI, with a detection limit of 0.012 ng/mL. We successfully used the proposed sensing technique for cTnI sensing in serum samples.








Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availability
No datasets were generated or analyzed during the current study.
References
Radha R, Shahzadi SK, Al-Sayah MH (2021) Fluorescent immunoassays for detection and quantification of cardiac troponin i: a short review. Molecules 26:4812. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules26164812
Global status report on noncommunicable diseases 2014: attaining the nine global noncommunicable diseases targets; a shared responsibility - World | ReliefWeb. https://reliefweb.int/report/world/global-status-report-noncommunicable-diseases-2014-attaining-nine-global?psafe_param=1&gclid=CjwKCAjws9ipBhB1EiwAccEi1KUuKTF5iUZqZZjjV_m6KGK2BHF30LMdc9ySygCfFDSVcp0TbL4-lxoC2PwQAvD_BwE. Accessed 23 Oct 2023
Kottwitz J, Bruno KA, Berg J et al (2020) Myoglobin for detection of high-risk patients with acute myocarditis. J Cardiovasc Transl Res 13:853–863. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12265-020-09957-8
Kumar V, Brent JR, Shorie M et al (2016) Nanostructured aptamer-functionalized black phosphorus sensing platform for label-free detection of myoglobin, a cardiovascular disease biomarker. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 8:22860–22868. https://doi.org/10.1021/acsami.6b06488
Tang C, Wang AJ, Feng JJ, Cheang TY (2023) Mulberry-like porous-hollow AuPtAg nanorods for electrochemical immunosensing of biomarker myoglobin. Microchimica Acta. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-023-05802-2
Grabowska I, Sharma N, Vasilescu A et al (2018) Electrochemical aptamer-based biosensors for the detection of cardiac biomarkers. ACS Omega 3:12010–12018. https://doi.org/10.1021/acsomega.8b01558
Maalouf R, Bailey S (2016) A review on B-type natriuretic peptide monitoring: assays and biosensors. Heart Fail Rev 21:567–578. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10741-016-9544-9
Pourali A, Rashidi MR, Barar J et al (2021) Voltammetric biosensors for analytical detection of cardiac troponin biomarkers in acute myocardial infarction. TrAC, Trends Anal Chem 134:116123. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.trac.2020.116123
Takashio S, Yamamuro M, Izumiya Y et al (2018) Diagnostic utility of cardiac troponin T level in patients with cardiac amyloidosis. ESC Heart Fail 5:27–35. https://doi.org/10.1002/ehf2.12203
Varghese S, Madanan AS, Abraham MK et al (2023) “Turn-on” fluorescence sensing of cardiac troponin I based on MnO2 nanosheet quenched mercaptopropionic acid capped Mn2+ doped zinc sulphide quantum dots. Microchem J 194:109327. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.microc.2023.109327
Anju SM, Varghese S, Merin KA et al (2023) Non-enzymatic detection of cardiac troponin − I using polyethylene imine-stabilized fluorescent gold nanoclusters. Sens Actuators B Chem. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.snb.2023.134081
Spain E, Carrara S, Adamson K et al (2018) Cardiac troponin i: ultrasensitive detection using faradaic electrochemical impedance. ACS Omega 3:17116–17124. https://doi.org/10.1021/acsomega.8b01758
Sabek J, Martínez-Pérez P, García-Rupérez J (2019) Computational binding study of cardiac troponin I antibody towards cardiac versus skeletal troponin I. Comput Biol Chem 80:147–151. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.COMPBIOLCHEM.2019.04.002
Camen S, Palosaari T, Reinikainen J et al (2020) Cardiac troponin I and incident stroke in European cohorts: insights from the BiomarCaRE project. Stroke 51:2770–2777. https://doi.org/10.1161/STROKEAHA.120.029452
Mahajan VS, Jarolim P (2011) How to interpret elevated cardiac troponin levels. Circulation 124:2350–2354. https://doi.org/10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.111.023697
Ather S, Hira RS, Shenoy M et al (2013) Recurrent low-level troponin I elevation is a worse prognostic indicator than occasional injury pattern in patients hospitalized with heart failure. Int J Cardiol 166:394–398. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijcard.2011.10.113
Farmakis D, Richter D, Chronopoulou G et al (2023) High-sensitivity cardiac troponin I for cardiovascular risk stratification in apparently healthy individuals. Hellenic J Cardiol
Chen D, Gong Y, Jin Y (2022) Detection of cardiac troponin I in serum by CMK-3/AuNPs-based electrochemical sensor. Int J Electrochem Sci. https://doi.org/10.20964/2022.07.31
Feng S, Yan M, Xue Y et al (2021) Electrochemical immunosensor for cardiac troponin I detection based on covalent organic framework and enzyme-catalyzed signal amplification. Anal Chem 93:13572–13579. https://doi.org/10.1021/ACS.ANALCHEM.1C02636/SUPPL_FILE/AC1C02636_SI_001.PDF
Wen R, Zhou C, Tian J, Lu J (2023) Confined catalysis of MOF-818 nanozyme and colorimetric aptasensing for cardiac troponin I. Talanta. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.talanta.2022.123830
Han GR, Kim MG (2020) Highly sensitive chemiluminescence-based lateral flow immunoassay for cardiac troponin I detection in human serum. Sensors (Switzerland). https://doi.org/10.3390/s20092593
Dittmer WU, Evers TH, Hardeman WM et al (2010) Rapid, high sensitivity, point-of-care test for cardiac troponin based on optomagnetic biosensor. Clin Chim Acta 411:868–873. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cca.2010.03.001
Rezaee MA, Rasaee MJ, Mohammadnejad J (2017) Selection of specific inhibitor peptides in enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) of cardiac troponin I using immuno-dominant epitopes as competitor. J Immunoassay Immunochem 38:72–81. https://doi.org/10.1080/15321819.2016.1216444
Song SY, Han YD, Kim K et al (2011) A fluoro-microbead guiding chip for simple and quantifiable immunoassay of cardiac troponin I (cTnI). Biosens Bioelectron 26:3818–3824. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.BIOS.2011.02.036
Du D, Shu J, Guo M et al (2020) Potential-resolved differential electrochemiluminescence immunosensor for cardiac troponin I based on MOF-5-wrapped CdS quantum dot nanoluminophores. Anal Chem 92:14113–14121. https://doi.org/10.1021/ACS.ANALCHEM.0C03131/SUPPL_FILE/AC0C03131_SI_001.PDF
Ni E, Ni E, Fang Y et al (2020) A one-step potentiometric immunoassay for plasma cardiac troponin I using an antibody-functionalized bis-MPA-COOH dendrimer as a competitor with improved sensitivity. Anal Methods 12:2914–2921. https://doi.org/10.1039/d0ay00680g
Campu A, Muresan I, Craciun AM et al (2022) Cardiac troponin biosensor designs: current developments and remaining challenges. Int J Mol Sci 23(3):7728. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms23147728
Pu S, Shi C, Lv C et al (2023) Tb3+-based off-on fluorescent platform for multicolor and dosage-sensitive visualization of bacterial spore marker. Anal Chem 95:8137–8144. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.analchem.3c01542
Zhao Y, Liu H, Jiang Y et al (2018) Detection of various biomarkers and enzymes via a nanocluster-based fluorescence turn-on sensing platform. Anal Chem 90:14578–14585. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.analchem.8b04691
Abraham MK, Anand V, Madanan AS et al (2023) Fluorescence “turn-off-on” detection of heparin and protamine based on bovine serum albumin-stabilized carbon dots (BSA-CDs). ChemNanoMat. https://doi.org/10.1002/cnma.202300115
Anju SM, Asokan AO, Varghese S et al (2023) Ferric ions modulated carbon dots as a fluorescent probe for the detection of neopterin: an inflammatory prognostic marker for risk prediction and severity of Covid-19. Chemistry Select. https://doi.org/10.1002/slct.202300178
Cai Y, Kang K, Li Q et al (2018) Rapid and sensitive detection of cardiac troponin I for point-of-care tests based on red fluorescent microspheres. Molecules 23:1102. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules23051102
Zhao J, Wang S, Lu S et al (2019) Fluorometric and colorimetric dual-readout immunoassay based on an alkaline phosphatase-triggered reaction. Anal Chem 91:7828–7834. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.analchem.9b01553
Li Y, Dai W, Lv X, Deng Y (2018) Aptamer-based rolling circle amplification coupled with graphene oxide-based fluorescence resonance energy transfer for sensitive detection of cardiac troponin i. Anal Methods 10:1767–1773. https://doi.org/10.1039/c8ay00309b
Raj V, Alex S (2021) Non-enzymatic colorimetric sensor for cardiac Troponin I (cTnI) based on self-assembly of gold nanorods on heparin. Gold Bull 54:1–7. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13404-020-00287-w
Wang Y, Mu Y, Hu J et al (2019) Rapid, one-pot, protein-mediated green synthesis of water-soluble fluorescent nickel nanoclusters for sensitive and selective detection of tartrazine. Spectrochim Acta A Mol Biomol Spectrosc 214:445–450. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.saa.2019.02.055
Marcano DC, Kosynkin DV, Berlin JM et al (2010) Improved synthesis of graphene oxide. ACS Nano 4:4806–4814. https://doi.org/10.1021/nn1006368
Habibi MH, Fakhri F (2017) Hydrothermal synthesis of nickel iron oxide nano-composite and application as magnetically separable photocatalyst for degradation of Solar Blue G dye. J Mater Sci: Mater Electron 28:14091–14096. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-017-7261-3
Ali SR, De M (2022) Superparamagnetic nickel nanocluster-embedded MoS2 nanosheets for Gram-selective bacterial adhesion and antibacterial activity. ACS Biomater Sci Eng 8:2932–2942. https://doi.org/10.1021/acsbiomaterials.2c00257
Bhatnagar D, Kumar V, Kumar A, Kaur I (2016) Graphene quantum dots FRET based sensor for early detection of heart attack in human. Biosens Bioelectron 79:495–499. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bios.2015.12.083
Taniselass S, Arshad MKM, Gopinath SCB (2019) Graphene-based electrochemical biosensors for monitoring noncommunicable disease biomarkers. Biosens Bioelectron 130:276–292
Marston S, Zamora JE (2020) Troponin structure and function: a view of recent progress. J Muscle Res Cell Motil 41:71–89. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10974-019-09513-1
Tuteja SK, Priyanka BV et al (2014) Graphene-gated biochip for the detection of cardiac marker troponin I. Anal Chim Acta 809:148–154. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aca.2013.11.047
Tuteja SK, Kukkar M, Suri CR et al (2015) One step in-situ synthesis of amine functionalized graphene for immunosensing of cardiac marker cTnI. Biosens Bioelectron 66:129–135. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bios.2014.10.072
Sun D, Luo Z, Lu J et al (2019) Electrochemical dual-aptamer-based biosensor for nonenzymatic detection of cardiac troponin I by nanohybrid electrocatalysts labeling combined with DNA nanotetrahedron structure. Biosens Bioelectron 134:49–56. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bios.2019.03.049
Abraham MK, Anju SM, Varghese S et al (2023) NaYF4: Yb/Ho upconversion nanoprobe incorporated gold nanoparticle (AuNP) based FRET immunosensor for the “turn-on” detection of cardiac troponin I. Analyst. https://doi.org/10.1039/d3an01405c
Acknowledgements
The authors thank the Head of the Chemistry Department at the University of Kerala in Thiruvananthapuram, Kerala, for his support and the use of the department’s laboratory and instruments and University of Kerala and CLIF, University of Kerala, for the sophisticated instrumental analysis offered. The authors Ali Ibrahim Shkhair and Geneva Indongo thank the Government of India for the Indian Council for Cultural Relationship (ICCR) scholarship.
Funding
This research was funded by the Indian Council for Cultural Relations ICCR with Ref. No. RBI0072494658807.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
All authors contributed to the study. The author, Anju S Madanan, conceived the idea of the work. Ali Ibrahim Shkhair performed design, material preparation, data collection, and analysis. Ali Ibrahim Shkhair wrote the original manuscript draft, and Susan Varghese, Merin K. Abraham, Geneva Indongo, Greeshma Rajeevan, and Arathy B. K and Sara Muneer Abbas commented on previous versions. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing Interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Shkhair, A.I., Madanan, A.S., Varghese, S. et al. Nickel Nanocluster as a Fluorescent Probe for the Non-enzymatic Detection of Cardiac Troponin I. Plasmonics (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11468-024-02311-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11468-024-02311-7