Abstract
Purpose
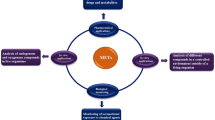
This review article provides a detailed discussion of studies in which microextraction techniques are applied for the determination of new psychoactive substances (NPS) in biological samples. Definitions and classifications of NPS are highlighted as well as the fundamentals of the microextraction techniques used in their analyses.
Methods
A complete literature search was carried out with PubMed, Scopus and the World Wide Web using relevant keywords, e.g., NPS, microextraction and biological fluids.
Results
The determinations of NPS in biological samples remain a challenge for analytical laboratories due to its wide diversity of compounds. The utilization of microextraction techniques in this context is still not many. However, the 96 deep well plate for microextraction and microextraction by packed sorbent (MEPS) can be highlighted as the most explored configurations. Microextraction approaches have the potential to be further improved and optimized to provide rapid and low-cost analyses with reliable results.
Conclusions
There is a wide scope of microextraction techniques to be explored in the field of toxicology and NPS determinations. These techniques are compatible with recent trends of automation and miniaturization, which can enable a straightforward workflow for NPS analyses.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
European Monitoring Centre for Drugs and Drug Addiction and Europol (2019) EU drug markets report 2019. EMCDDA, Lisbon. https://doi.org/10.2810/796253
United Nations Office on Drug and Crime (UNODC) (2019) Early warning advisory on new psychoactive substances. https://www.unodc.org/LSS/Home/NPS. Accessed 10 Apr 2020
Logan BK, Mohr ALA, Friscia M, Krotulski AJ, Papsun DM, Kacinko SL, Ropero-Miller JD, Huestis MA (2017) Reports of adverse events associated with use of novel psychoactive substances, 2013–2016: a review. J Anal Toxicol 41:573–610. https://doi.org/10.1093/jat/bkx031(open access article)
Fagiola M, Hahn T, Avella J (2018) Screening of novel psychoactive substances in postmortem matrices by liquid chromatography–tandem mass spectrometry (LC–MS–MS). J Anal Toxicol 42:562–569. https://doi.org/10.1093/jat/bky050 (open access article)
Rasanen I, Kyber M, Szilvay I, Rintatalo J, Ojanperä I (2019) Single-calibrant quantification of seized synthetic opioids by liquid chromatography-chemiluminescence nitrogen detection. Forensic Sci Int 305:110001. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.forsciint.2019.110001
de Souza BB, Filho JS, Nonemacher K, Schroeder SD, Arbo MD, Rezin KZ (2020) New psychoactive substances (NPS) prevalence over LSD in blotter seized in State of Santa Catarina, Brazil: a six-year retrospective study. Forensic Sci Int 306:110002. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.forsciint.2019.110002
Segawa H, Fukuoka T, Itoh T, Imai Y, Iwata YT, Yamamuro T, Kuwayama K, Tsujikawa K, Kanamori T, Inoue H (2019) Rapid detection of synthetic cannabinoids in herbal highs using surface-enhanced Raman scattering produced by gold nanoparticle co-aggregation in a wet system. Analyst 144:6928–6935. https://doi.org/10.1039/C9AN01512D
Machado Y, Neto JC, Lordeiro RA, Silva MF, Piccin E (2018) Profile of new psychoactive substances (NPS) and other synthetic drugs in seized materials analysed in a Brazilian forensic laboratory. Forensic Toxicol 37:265–271. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11419-018-0456-3
Adamowicz P, Gieroń J, Gil D, Lechowicz W, Skulska A, Tokarczyk B (2016) The prevalence of new psychoactive substances in biological material: a three-year review of casework in Poland. Drug Test Anal 8:63–70. https://doi.org/10.1002/dta.1924
Peacock A, Bruno R, Gisev N, Degenhardt L, Hall W, Sedefov R, White J, Thomas KV, Farrell M, Griffiths P (2019) New psychoactive substances: challenges for drug surveillance, control, and public health responses. Lancet 394:1668–1684. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0140-6736(19)32231-7
Ocaña-González JA, Fernández-Torres R, Bello-López MÁ, Ramos-Payán M (2016) New developments in microextraction techniques in bioanalysis. A review. Anal Chim Acta 905:8–23. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aca.2015.10.041
Niu Z, Zhang W, Yu C, Zhang J, Wen Y (2018) Recent advances in biological sample preparation methods coupled with chromatography, spectrometry and electrochemistry analysis techniques. Trends Analyt Chem 102:123–146. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.trac.2018.02.005
Filippou O, Bitas D, Samanidou V (2017) Green approaches in sample preparation of bioanalytical samples prior to chromatographic analysis. J Chromatogr B 1043:44–62. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jchromb.2016.08.040 (open access article)
Sajid M, Płotka-Wasylka J (2018) Combined extraction and microextraction techniques: Recent trends and future perspectives. Trends Analyt Chem 103:74–86. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.trac.2018.03.013
Mafra G, García-Valverde MT, Millán-Santiago J, Carasek E, Lucena R, Cárdenas S (2020) Returning to nature for the design of sorptive phases in solid-phase microextraction. Separations 7:2. https://doi.org/10.3390/separations7010002 (open access article)
Kissoudi M, Samanidou V (2018) Recent advances in applications of ionic liquids in miniaturized microextraction techniques. Molecules 23:1437. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules23061437 (open access article)
Pacheco-Fernández I, Pino V (2019) Green solvents in analytical chemistry. Curr Opin Green Sustain Chem 18:42–50. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cogsc.2018.12.010
Kabir A, Locatelli M, Ulusoy HI (2017) Recent trends in microextraction techniques employed in analytical and bioanalytical sample preparation. Separations 4:36. https://doi.org/10.3390/separations4040036 (open access article)
He Y, Concheiro-Guisan M (2019) Microextraction sample preparation techniques in forensic analytical toxicology. Biomed Chromatogr 33:e4444. https://doi.org/10.1002/bmc.4444
Barroso M, Moreno I, da Fonseca B, Queiroz JA, Gallardo E (2012) Role of microextraction sampling procedures in forensic toxicology. Bioanalysis 4:1805–1826. https://doi.org/10.4155/bio.12.139
de Oliveira SG, Pego AMF, Silva JP, Yonamine M (2019) Green sample preparations for the bioanalysis of drugs of abuse in complex matrices. Bioanalysis 11:295–312. https://doi.org/10.4155/bio-2018-0208
European Monitoring Centre for Drugs and Drug Addiction (2020) European drug report 2020: trends and developments. EMCDDA, Lisbon. https://doi.org/10.2810/420678
Alves VL, Gonçalves JL, Aguiar J, Teixeira HM, Câmara JS (2020) The synthetic cannabinoids phenomenon: from structure to toxicological properties. A review. Crit Rev Toxicol 50:359–382. https://doi.org/10.1080/10408444.2020.1762539
Mechoulam R, Lander N, University A, Zahalka J (1990) Synthesis of the individual, pharmacologically distinct, enantiomers of a tetrahydrocannabinol derivative. Tetrahedron-Asymmetry 1:315–318. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0957-4166(00)86322-3
Ho TC, Tius MA (2019) Synthesis of classical/nonclassical hybrid cannabinoids and related compounds. In: Kobayashi Y (ed) Cutting-edge organic synthesis and chemical biology of bioactive molecules. Springer, Singapore, pp 247–289
Shevyrin VA, Morzherin YY (2015) Cannabinoids: structures, effects, and classification. Russ Chem Bull 64:1249–1266. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11172-015-1008-1
Baumann MH, Walters HM, Niello M, Sitte HH (2018) Neuropharmacology of synthetic cathinones. In: Maurer H, Brandt S (eds) Handbook of experimental pharmacology. Springer, Cham, pp 113–142
Pieprzyca E, Skowronek R, Nižnanský Ľ, Czekaj P (2020) Synthetic cathinones: from natural plant stimulant to new drug of abuse. Eur J Pharmacol 875:173012. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejphar.2020.173012
Valente MJ, de Pinho PG, de Lourdes BM, Carvalho F, Carvalho M (2014) Khat and synthetic cathinones: a review. Arch Toxicol 88:15–45. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00204-013-1163-9
Sainsbury PD, Kicman AT, Archer RP, King LA, Braithwaite RA (2011) Aminoindanes: the next wave of ‘legal highs’? Drug Test Anal 3:479–482. https://doi.org/10.1002/dta.318
Poulie CBM, Jensen AA, Halberstadt AL, Kristensen JL (2020) DARK classics in chemical neuroscience: NBOMes. ACS Chem Neurosci 11:3860–3869. https://doi.org/10.1021/acschemneuro.9b00528
dos Santos Moreira AM, de Oliveira HL, Filho JFA, Florez DHÂ, Borges MMC, Lacerda V Jr, Romão W, Borges KB (2019) NBOMe compounds: an overview about analytical methodologies aiming their determination in biological matrices. Trends Analyt Chem 114:260–277. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.trac.2019.02.034
Arantes LC, Júnior EF, de Souza LF, Cardoso AC, Alcântara TLF, Lião LM, Machado Y, Lordeiro RA, Neto JC, Andrade AFB (2017) 25-I-NBOH: a new potent serotonin 5-HT2A receptor agonist identified in blotter paper seizures in Brazil. Forensic Toxicol 35:408–414. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11419-017-0357-x (open access article)
Collins M (2011) Some new psychoactive substances: precursor chemicals and synthesis-driven end-products. Drug Test Anal 3:404–416. https://doi.org/10.1002/dta.315
Tabarra I, Soares S, Rosado T, Gonçalves J, Luís Â, Malaca S, Barroso M, Keller T, Restolho J, Gallardo E (2019) Novel synthetic opioids: toxicological aspects and analysis. Forensic Sci Res 4:111–140. https://doi.org/10.1080/20961790.2019.1588933 (open access article)
El Balkhi S, Monchaud C, Herault F, Géniaux H, Saint-Marcoux F (2020) Designer benzodiazepines’ pharmacological effects and potencies: how to find the information. J Psychopharmacol 34:1021–1029. https://doi.org/10.1177/0269881119901096
Kokosa JM (2019) Selecting an extraction solvent for a greener liquid phase microextraction (LPME) mode-based analytical method. Trends Analyt Chem 118:238–247. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.trac.2019.05.012
Hansen FA, Pedersen-Bjergaard S (2020) Emerging extraction strategies in analytical chemistry. Anal Chem 92:2–15. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.analchem.9b04677
Wei G, Li Y, Wang X (2007) Application of dispersive liquid-liquid microextraction combined with high-performance liquid chromatography for the determination of methomyl in natural waters. J Sep Sci 30:3262–3267. https://doi.org/10.1002/jssc.200700291
Liu Y, Zhao E, Zhu W, Gao H, Zhou Z (2009) Determination of four heterocyclic insecticides by ionic liquid dispersive liquid–liquid microextraction in water samples. J Chromatogr A 1216:885–891. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chroma.2008.11.076
Zohrabi P, Shamsipur M, Hashemi M, Hashemi B (2016) Liquid-phase microextraction of organophosphorus pesticides using supramolecular solvent as a carrier for ferrofluid. Talanta 160:340–346. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.talanta.2016.07.036
González-Curbelo MÁ, Hernández-Borges J, Borges-Miquel TM, Rodríguez-Delgado MÁ (2013) Determination of organophosphorus pesticides and metabolites in cereal-based baby foods and wheat flour by means of ultrasound-assisted extraction and hollow-fiber liquid-phase microextraction prior to gas chromatography with nitrogen phosphorus detection. J Chromatogr A 1313:166–174. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chroma.2013.05.081
Daneshfar A, Khezeli T, Lotfi HJ (2009) Determination of cholesterol in food samples using dispersive liquid–liquid microextraction followed by HPLC–UV. J Chromatogr B 877:456–460. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jchromb.2008.12.050 (open access article)
Rezaei F, Yamini Y, Moradi M, Daraei B (2013) Supramolecular solvent-based hollow fiber liquid phase microextraction of benzodiazepines. Anal Chim Acta 804:135–142. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aca.2013.10.026
Rezaee M, Assadi Y, Hosseini M-RM, Aghaee E, Ahmadi F, Benrijani S (2006) Determination of organic compounds in water using dispersive liquid-liquid microextraction. J Chromatogr A 1116:1–9. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chroma.2006.03.007
Rezaee M, Yamini Y, Faraji M (2010) Evolution of dispersive liquid–liquid microextraction method. J Chromatogr A 1217:2342–2357. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chroma.2009.11.088
Zgoła-Grześkowiak A, Grześkowiak T (2011) Dispersive liquid-liquid microextraction. Trends Analyt Chem 30:1382–1399. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.trac.2011.04.014
Odoardi S, Fisichella M, Romolo FS, Strano-Rossi S (2015) High-throughput screening for new psychoactive substances (NPS) in whole blood by DLLME extraction and UHPLC–MS/MS analysis. J Chromatogr B 1000:57–68. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jchromb.2015.07.007 (open access article)
Fernández P, Regenjo M, Ares A, Fernández AM, Lorenzo RA, Carro AM (2019) Simultaneous determination of 20 drugs of abuse in oral fluid using ultrasound-assisted dispersive liquid–liquid microextraction. Anal Bioanal Chem 411:193–203. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00216-018-1428-5
Vincenti F, Montesano C, Celluci L, Gregori A, Fanti F, Compagnone D, Curini R, Sergi M (2019) Combination of pressurized liquid extraction with dispersive liquid liquid micro extraction for the determination of sixty drugs of abuse in hair. J Chromatogr A 1605:360348. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chroma.2019.07.002
Pedersen-Bjergaard S, Rasmussen KE (2006) Electrokinetic migration across artificial liquid membranes: new concept for rapid sample preparation of biological fluids. J Chromatogr A 1109:183–190. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chroma.2006.01.025
Hansen F, Jaghl F, Øiestad EL, Jensen H, Pedersen-Bjergaard S, Huang C (2020) Impact of ion balance in electromembrane extraction. Anal Chim Acta 1124:129–136. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aca.2020.05.039
Gjelstad A, Rasmussen KE, Pedersen-Bjergaard S (2006) Electrokinetic migration across artificial liquid membranes: tuning the membrane chemistry to different types of drug substances. J Chromatogr A 1124:29–34. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chroma.2006.04.039
Rezazadeh M, Yamini Y, Seidi S (2011) Electromembrane extraction of trace amounts of naltrexone and nalmefene from untreated biological fluids. J Chromatogr B 879:1143–1148. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jchromb.2011.03.043 (open access article)
Vårdal L, Øiestad EL, Gjelstad A, Jensen H, Pedersen-Bjergaard S (2019) Electromembrane extraction with solvent modification of the acceptor solution: improved mass transfer of drugs of abuse from human plasma. Bioanalysis 11:755–771. https://doi.org/10.4155/bio-2018-0308
Gjelstad A, Rasmussen KE, Parmer MP, Pedersen-Bjergaard S (2013) Parallel artificial liquid membrane extraction: micro-scale liquid–liquid–liquid extraction in the 96-well format. Bioanalysis 5:1377–1385. https://doi.org/10.4155/BIO.13.59
Gjelstad A (2019) Three-phase hollow fiber liquid-phase microextraction and parallel artificial liquid membrane extraction. Trends Analyt Chem 113:25–31. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.trac.2019.01.007
Ask KS, Bardakci T, Parmer MP, Halvorsen TG, Øiestad EL, Pedersen-Bjergaard S, Gjelstad A (2016) Parallel artificial liquid membrane extraction as an efficient tool for removal of phospholipids from human plasma. J Pharm Biomed Anal 129:229–236. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jpba.2016.07.011
Ask KS, Øiestad EL, Pedersen-Bjergaard S, Gjelstad A (2018) Dried blood spots and parallel artificial liquid membrane extraction: a simple combination of microsampling and microextraction. Anal Chim Acta 1009:56–64. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aca.2018.01.024
Ask KS, Lid M, Øiestad EL, Pedersen-Bjergaard S, Gjelstad A (2019) Liquid-phase microextraction in 96-well plates: calibration and accurate quantification of pharmaceuticals in human plasma samples. J Chromatogr A 1602:117–123. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chroma.2019.06.013
Vårdal L, Askildsen H-M, Gjelstad A, Øiestad EL, Edvardsen HME, Pedersen-Bjergaard S (2017) Parallel artificial liquid membrane extraction of new psychoactive substances in plasma and whole blood. J Chromatogr B 1048:77–84. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jchromb.2017.02.010 (open access article)
Vårdal L, Wong G, Øiestad AML, Pedersen-Bjergaard S, Gjelstad A, Øiestad EL (2018) Rapid determination of designer benzodiazepines, benzodiazepines, and Z-hypnotics in whole blood using parallel artificial liquid membrane extraction and UHPLC-MS/MS. Anal Bioanal Chem 410:4967–4978. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00216-018-1147-y
Spietelun A, Marcinkowski L, de la Guardia M, Namieśnik J (2013) Recent developments and future trends in solid phase microextraction techniques towards green analytical chemistry. J Chromatogr A 1321:1–13. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chroma.2013.10.030
Arthur CL, Pawliszyn J (1990) Solid phase microextraction with thermal desorption using fused silica optical fibers. Anal Chem 62:2145–2148. https://doi.org/10.1021/ac00218a019
De Giovanni N, Marchetti D (2019) A systematic review of solid-phase microextraction applications in the forensic context. J Anal Toxicol 44:268–297. https://doi.org/10.1093/jat/bkz077
Kataoka H, Saito K (2011) Recent advances in SPME techniques in biomedical analysis. J Pharm Biomed Anal 54:926–950. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jpba.2010.12.010
Risticevic S, Niri VH, Vuckovic D, Pawliszyn J (2009) Recent developments in solid-phase microextraction. Anal Bioanal Chem 393:781–795. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00216-008-2375-3
Kremser A, Jochmann MA, Schmidt TC (2016) PAL SPME Arrow–evaluation of a novel solid-phase microextraction device for freely dissolved PAHs in water. Anal Bioanal Chem 408:943–952. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00216-015-9187-z (open access article)
Montesano C, Sergi M (2016) Microextraction techniques in illicit drug testing: present and future. Bioanalysis 8:863–866. https://doi.org/10.4155/bio-2016-0008
Queiroz MEC, Melo LP (2014) Selective capillary coating materials for in-tube solid-phase microextraction coupled to liquid chromatography to determine drugs and biomarkers in biological samples: a review. Anal Chim Acta 826:1–11. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aca.2014.03.024
Kataoka H (2015) SPME techniques for biomedical analysis. Bioanalysis 7:2135–2144. https://doi.org/10.4155/bio.15.145
Roszkowska A, Miękus N, Bączek T (2019) Application of solid-phase microextraction in current biomedical research. J Sep Sci 42:285–302. https://doi.org/10.1002/jssc.201800785
Pragst F (2007) Application of solid-phase microextraction in analytical toxicology. Anal Bioanal Chem 388:1393–1414. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00216-007-1289-9
Anzillotti L, Marezza F, Calò L, Andreoli R, Agazzi S, Bianchi F, Careri M, Cecchi R (2019) Determination of synthetic and natural cannabinoids in oral fluid by solid-phase microextraction coupled to gas chromatography/mass spectrometry: a pilot study. Talanta 201:335–341. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.talanta.2019.04.029
Alsenedi KA, Morrison C (2018) Determination of amphetamine-type stimulants (ATSs) and synthetic cathinones in urine using solid phase micro-extraction fibre tips and gas chromatography-mass spectrometry. Anal Methods 10:1431–1440. https://doi.org/10.1039/C8AY00041G
Abdel-Rehim M (2004) New trend in sample preparation: on-line microextraction in packed syringe for liquid and gas chromatography applications. I. Determination of local anaesthetics in human plasma samples using gas chromatography–mass spectrometry. J Chromatogr B 801:317–321. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jchromb.2003.11.042(open access article)
Moein MM, Abdel-Rehim A, Abdel-Rehim M (2015) Microextraction by packed sorbent (MEPS). Trends Analyt Chem 67:34–44. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.trac.2014.12.003
De Boeck M, Dehaen W, Tytgat J, Cuypers E (2019) Microextractions in forensic toxicology: the potential role of ionic liquids. Trends Analyt Chem 111:73–84. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.trac.2018.11.036
Abdel-Rehim M (2010) Recent advances in microextraction by packed sorbent for bioanalysis. J Chromatogr A 1217:2569–2580. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chroma.2009.09.053
Abdel-Rehim M (2011) Microextraction by packed sorbent (MEPS): a tutorial. Anal Chim Acta 701:119–128. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aca.2011.05.037
Scientific Instruments Services (SIS) (2019) SGE MEPS™‐micro extraction by packed sorbent. https://www.sisweb.com/lc/sge-meps.htm. Accessed 27 May 2020
Bianchi F, Agazzi S, Riboni N, Erdal N, Hakkarainen M, Ilag LL, Anzillotti L, Andreoli R, Marezza F, Moroni F, Cecchi R, Careri M (2019) Novel sample-substrates for the determination of new psychoactive substances in oral fluid by desorption electrospray ionization-high resolution mass spectrometry. Talanta 202:136–144. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.talanta.2019.04.057
Sorribes-Soriano A, Monedero A, Esteve-Turrillas FA, Armenta S (2019) Determination of the new psychoactive substance dichloropane in saliva by microextraction by packed sorbent ion mobility spectrometry. J Chromatogr A 1603:61–66. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chroma.2019.06.054
Sorribes-Soriano A, Verdeguer J, Pastor A, Armenta S, Esteve-Turrillas FA (2021) Determination of third generation synthetic cannabinoids in oral fluids. J Anal Toxicol 45:331–336. https://doi.org/10.1093/jat/bkaa091
Ares AM, Fernández P, Regenjo M, Fernández AM, Carro AM, Lorenzo RA (2017) A fast bioanalytical method based on microextraction by packed sorbent and UPLC–MS/MS for determining new psychoactive substances in oral fluid. Talanta 174:454–461. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.talanta.2017.06.022
Rocchi R, Simeoni MC, Montesano C, Vannutelli G, Curini R, Sergi M, Compagnone D (2018) Analysis of new psychoactive substances in oral fluids by means of microextraction by packed sorbent followed by ultra-high-performance liquid chromatography–tandem mass spectrometry. Drug Test Anal 10:865–873. https://doi.org/10.1002/dta.2330
Fernández P, González M, Regenjo M, Ares AM, Fernández AM, Lorenzo RA, Carro AM (2017) Analysis of drugs of abuse in human plasma using microextraction by packed sorbents and ultra-high-performance liquid chromatography. J Chromatogr A 1485:8–19. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chroma.2017.01.021
Basheer C, Alnedhary AA, Rao BSM, Valliyaveettil S, Lee HK (2006) Development and application of porous membrane-protected carbon nanotube micro-solid-phase extraction combined with gas chromatography/mass spectrometry. Anal Chem 78:2853–2858. https://doi.org/10.1021/ac060240i
Płotka-Wasylka J, Szczepańska N, de la Guardia M, Namieśnik J (2015) Miniaturized solid-phase extraction techniques. Trends Analyt Chem 73:19–38. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.trac.2015.04.026
Seidi S, Tajik M, Baharfar M, Rezazadeh M (2019) Micro solid-phase extraction (pipette tip and spin column) and thin film solid-phase microextraction: miniaturized concepts for chromatographic analysis. Trends Analyt Chem 118:810–827. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.trac.2019.06.036
Montesano C, Vannutelli G, Piccirilli V, Sergi M, Compagnone D, Curini R (2017) Application of a rapid μ-SPE clean-up for multiclass quantitative analysis of sixteen new psychoactive substances in whole blood by LC–MS/MS. Talanta 167:260–267. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.talanta.2017.02.019
Sánchez-González J, Odoardi S, Bermejo AM, Bermejo-Barrera P, Romolo FS, Moreda-Piñeiro A, Strano-Rossi S (2019) HPLC-MS/MS combined with membrane-protected molecularly imprinted polymer micro-solid-phase extraction for synthetic cathinones monitoring in urine. Drug Test Anal 11:33–44. https://doi.org/10.1002/dta.2448
Morés L, Dias AN, Carasek E (2018) Development of a high-throughput method based on thin-film microextraction using a 96-well plate system with a cork coating for the extraction of emerging contaminants in river water samples. J Sep Sci 41:697–703. https://doi.org/10.1002/jssc.201700774
Mafra G, Vieira AA, Merib J, Anderson JL, Carasek E (2019) Single drop microextraction in a 96-well plate format: a step toward automated and high-throughput analysis. Anal Chim Acta 31:159–166. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aca.2019.02.013(open access article)
Mafra G, Birk L, Scheid C, Eller S, Brognoli R, de Oliveira TF, Carasek E, Merib J (2020) A straightforward and semiautomated membrane-based method as efficient tool for the determination of cocaine and its metabolites in urine samples using liquid chromatography coupled to quadrupole time-of-flight-mass spectrometry. J Chromatogr A 21:461088. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chroma.2020.461088(open access article)
Ohcho K, Saito K, Kataoka H (2008) Automated analysis of non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs in environmental water by on-line in-tube solid-phase microextraction coupled with liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry. J Environ Chem 18:511–520. https://doi.org/10.5985/jec.18.511
Fleischer H, Drews RR, Janson J, Chinna Patlolla BR, Chu X, Klos M, Thurow K (2016) Application of a dual-arm robot in complex sample preparation and measurement processes. J Lab Autom 21:671–681. https://doi.org/10.1177/2211068216637352(open access article)
Medina DAV, Cabal LFR, Lanças FM, Santos-Neto AJ (2019) Sample treatment platform for automated integration of microextraction techniques and liquid chromatography analysis. HardwareX 5:e00056. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ohx.2019.e00056
Kocúrová L, Balogh IS, Andruch V (2013) Solvent microextraction: a review of recent efforts at automation. Microchem J 110:599–607. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.microc.2013.07.009
Alexovič M, Horstkotte B, Šrámková I, Solich P, Sabo J (2017) Automation of dispersive liquid-liquid microextraction and related techniques. Approaches based on flow, batch, flow-batch and in-syringe modes. Trends Analyt Chem 86:39–55. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.trac.2016.10.003
Drouin N, Kubáň P, Rudaz S, Pedersen-Bjergaard S, Schappler J (2019) Electromembrane extraction: overview of the last decade. Trends Analyt Chem 113:357–363. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.trac.2018.10.024
Hutchinson JP, Setkova L, Pawliszyn J (2007) Automation of solid-phase microextraction on a 96-well plate format. J Chromatogr A 1149:127–137. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chroma.2007.02.117
Serenjeh FN, Hashemi P, Ghiasvand AR, Rasolzadeh F, Heydari N, Badiei A (2020) Cooling assisted headspace microextraction by packed sorbent coupled to HPLC for the determination of volatile polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in soil. Anal Chim Acta 1125:128–134. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aca.2020.05.067
Lockwood TE, Talebi M, Minett A, Mills S, Doble PA, Bishop DP (2019) Micro solid-phase extraction for the analysis of per- and polyfluoroalkyl substances in environmental waters. J Chromatogr A 1604:460495. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chroma.2019.460495
Ciceri D, Perera JM, Stevens GW (2014) The use of microfluidic devices in solvent extraction. J Chem Technol Biotechnol 89:771–786. https://doi.org/10.1002/jctb.4318
Petersen NJ, Jensen H, Hansen SH, Foss ST, Snakenborg D, Pedersen-Bjergaard S (2010) On-chip electro membrane extraction. Microfluid Nanofluid 9:881–888. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10404-010-0603-6
Santigosa E, Maspoch S, Payán MR (2019) Liquid phase microextraction integrated into a microchip device for the extraction of fluoroquinolones from urine samples. Microchem J 145:280–286. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.microc.2018.10.051
Payán MR, Murillo ES, Coello J, López MÁB (2018) A comprehensive study of a new versatile microchip device based liquid phase microextraction for stopped-flow and double-flow conditions. J Chromatogr A 1556:29–36. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chroma.2018.04.051
Acknowledgements
The authors would like to acknowledge the financial support from Coordination of Improvement of Personal Higher Education, Brazil [CAPES—Finance Code 001].
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
There are no financial or other relations that could lead to a conflict of interest.
Ethical approval
This article does not contain any studies with human participants or animals performed by any of the authors.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Birk, L., Santos, S.O., Eller, S. et al. Determinations of new psychoactive substances in biological matrices with focus on microextraction techniques: a review of fundamentals and state-of-the-art extraction methods. Forensic Toxicol 39, 350–367 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11419-021-00582-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11419-021-00582-x