Abstract
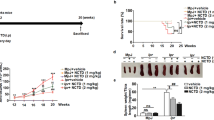
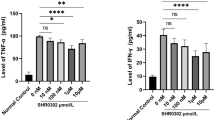
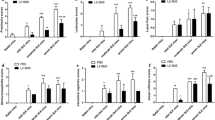
Jieduquyuziyin prescription (JP) is a traditional Chinese medicinal (TCM) formula which has been demonstrated to be effective for systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) treatment as an approved hospital prescription for many years in China. But its mechanism of action in combating this disease is largely unknown. Our previous studies showed that JP can slow disease progression without producing significant toxic side effects. We treated MRL/lpr mice with JP to ascertain if JP could improve SLE by the suppression of Ca2+/calmodulin-dependent protein kinase-4 (CaMK4) expression. We investigated the role of JP in a model of SLE in MRL/lpr mice, and identified the possible mechanism of action. Mice were divided randomly into four groups: control, model, and two treatment groups. Sections of renal tissue were stained with hematoxylin and eosin (H&E). Histopathologic changes in the kidney were evaluated by light microscopy. T-helper (Th)17 cells were analyzed by flow cytometry. mRNA levels of interleukin (IL)-17, CaMK4, and RORγt were measured by reverse transcription polymerase chain reaction (RT-PCR). CaMK4 expression was assessed by Western blotting. The results showed that the percentages of Th17, IL-17, and RORγt in mice treated with JP were decreased remarkably compared to the model group (p < 0.05). Interestingly, a high CaMK4 expression was observed in the SLE mice, which was inhibited by JP. These results suggest that CaMK4 activity was increased in T cells from MRL/lpr mice compared with the control group. Our findings support the conclusion that the effects of JP on MRL/lpr mice may involve the regulation of CaMK4 overexpression in MRL/lpr mice.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Tsokos GC (2011) Systemic lupus erythematosus. N Engl J Med 365:2110–2121
Skare T, da Silva Magalhães VD, Siqueira RE (2014) Systemic lupus erythematosus activity and depression. Rheumatol Int 34:445–446
Pan HF, Leng RX, Feng CC, Li XP, Chen GM, Li BZ, Xu WD, Zheng SG, Ye DQ (2013) Expression profiles of Th17 pathway related genes in human systemic lupus erythematosus. Mol Biol Rep 40:391–399
Chen XQ, Yu YC, Deng HH, Sun JZ, Dai Z, Wu YW, Yang M (2010) Plasma IL-17A is increased in new-onset SLE patients and associated with disease activity. J Clin Immunol 30:221–225
Henriques A, Inês L, Pais ML, da Silva JAP, Paiva AA (2012) Th17 cells in systemic lupus erythematosus share functional features with Th17 cells from normal bone marrow and peripheral tissues. Clin Rheumatol 31:483–491
Xing Q, Wang B, Su HH, Cui JJ, Li JH (2012) Elevated Th17 cells are accompanied by FoxP3+ Treg cells decrease in patients with lupus nephritis. Rheumatol Int 32:949–958
Zhu MY, Mo HY, Li D, Luo XH, Zhang LH (2013) Th17/Treg imbalance induced by increased incidence of atherosclerosis in patients with systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE). Clin Rheumatol 32:1045–1052
Sugimoto K, Itoh T, Takita M, Shimoda M, Chujo D, SoRelle JA, Naziruddin B, Levy MF, Shimada M, Matsumoto S (2014) Improving allogeneic islet transplantation by suppressing Th17 and enhancing Treg with histone deacetylase inhibitors. Transpl Int 27:408–415
Hedrich CM, Rauen T, Kis-Toth K, Kyttaris VC, Tsokos GC (2012) cAMP-responsive element modulator α (CREMα) suppresses IL-17F protein expression in T lymphocytes from patients with systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE). J Biol Chem 287:4715–4725
Rauen T, Hedrich CM, Juang YT, Tenbrock K, Tsokos GC (2011) cAMP-responsive element modulator (CREM)α protein induces interleukin 17A expression and mediates epigenetic alterations at the Interleukin-17A gene locus in patients with systemic lupus erythematosus. J Biol Chem 286:43437–43446
Ichinose K, Juang YT, Crispín JC, Kis-Toth K, Tsokos GC (2011) Suppression of autoimmunity and organ pathology in lupus-prone mice upon inhibition of calcium/calmodulin-dependent protein kinase type IV. Arthritis Rheum 63:523–529
Koga T, Ichinose K, Mizui M, Crispín JC, Tsokos GC (2012) Calcium/calmodulin-dependent protein kinase IV suppresses IL-2 production and regulatory T cell activity in lupus. J Immunol 189:3490–3496
Tsokos GC, Thai TH (2012) Interleukin-2 in systemic autoimmunity hits the micro way. Arthritis Rheum 64:3494–3497
Koga T, Hedrich CM, Mizui M, Yoshida N, Otomo K, Lieberman LA, Rauen T, Crispín JC, Tsokos GC (2014) CaMK4-dependent activation of AKT/mTOR and CREM-α underlies autoimmunity-associated Th17 imbalance. J Clin Invest 124:2234–2245
Carli L, Tani C, Querci F, Della Rossa A, Vagnani S, Baldini C, Talarico R, d’Ascanio A, Neri R, Tavoni AG, Bombardieri S, Mosca M (2013) Analysis of the prevalence of cataracts and glaucoma in systemic lupus erythematosus and evaluation of the rheumatologists’ practice for the monitoring of glucocorticoid eye toxicity. Clin Rheumatol 32:1071–1073
Alexander T, Arnold R, Hiepe F (2009) Immunablation in Kombination mit autologer Stammzelltransplantation bei lupus. Z Rheumatol 68:205–213
Hu JB, Jiang FS, Gu HC, Ding ZS, Yao L, Fan YS, Ding XH (2013) Metabolomics study on the effects of jieduquyuziyin prescription on systemic lupus erythematosus mice by LC-Q-TOF/MS. Chromatographia 76:791–800
Ding XH, Hu JB, Wen CP, Ding ZS, Yao L, Fan YS (2014) Rapid resolution liquid chromatography coupled with quadrupole time-of-flight mass spectrometry-based metabolomics approach to study the effects of jieduquyuziyin prescription on systemic lupus erythematosus. PLoS One 9:e88223
Zhang F, Fuss IJ, Yang Z, Strober W (2014) Transcription of RORγt in developing Th17 cells is regulated by E-proteins. Mucosal Immunol 7:521–532
Axtell RC, Raman C, Steinman L (2013) Type I interferons: beneficial in Th1 and detrimental in Th17 autoimmunity. Clin Rev Allergy Immunol 44:114–120
Pappu R, Ramirez-Carrozzi V, Ota N, Ouyang WJ, Hu Y (2010) The IL-17 family cytokines in immunity and disease. J Clin Immunol 30:185–195
Fujie H, Niu K, Ohba M, Tomioka Y, Kitazawa H, Nagashima K, Ohrui T, Numasaki M (2012) A distinct regulatory role of Th17 cytokines IL-17A and IL-17F in chemokine secretion from lung microvascular endothelial cells. Inflammation 35:1119–1131
Korn T, Bettelli E, Oukka M, Kuchroo VK (2009) IL-17 and Th17 cells. Annu Rev Immunol 27:485–517
Dolff S, Quandt D, Wilde B, Feldkamp T, Hua F, Cai X, Specker C, Kribben A, Kallenberg CG, Witzke O (2010) Increased expression of costimulatory markers CD134 and CD80 on interleukin-17 producing T cells in patients with systemic lupus erythematosus. Arthritis Res Ther 12(4):R150
Brkic Z, Corneth OBJ, van Helden-Meeuwsen CG, Dolhain RJ, Maria NI, Paulissen SM, Davelaar N, van Hamburg JP, van Daele PL, Dalm VA, van Hagen PM, Hazes JM, Versnel MA, Lubberts E (2014) T-helper 17 cell cytokines and interferon type I: partners in crime in systemic lupus erythematosus. Arthritis Res Ther 16:R62
Racioppi L, Means AR (2008) Calcium/calmodulin-dependent kinase IV in immune and inflammatory responses: novel routes for an ancient traveller. Trends Immunol 29:600–607
Ichinose K, Rauen T, Juang YT, Kis-Toth K, Mizui M, Koga T, Tsokos GC (2011) Cutting edge: calcium/calmodulin-dependent protein kinase type IV is essential for mesangial cell proliferation and lupus nephritis. J Immunol 187:5500–5504
Ma HD, Deng YR, Tian ZG, Lian ZX (2013) Traditional Chinese medicine and immune regulation. Clin Rev Allergy Immunol 44:229–241
Acknowledgments
We thank the Zhejiang Chinese Medical University College of Basic Medical Science for their excellent technical assistance. We would also like to express our gratitude to Zhejiang Chinese Medical University College of Life Science. This study was supported by grants from the National Natural Science Foundation of China (no. 81001515) and the Natural Science Foundation of Zhejiang Province (no. LY14H270014).
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no competing financial interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Shui, B., Xia, W., Wen, C. et al. Jieduquyuziyin prescription suppresses IL-17 production and Th17 activity in MRL/lpr mice by inhibiting expression of Ca2+/calmodulin-dependent protein kinase-4. J Nat Med 69, 349–357 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11418-015-0900-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11418-015-0900-1