Abstract
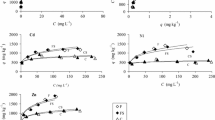
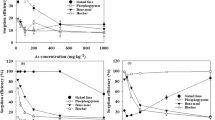
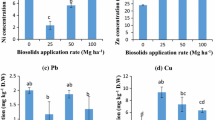
Soil contamination with anthropogenic metals resulting from biosolid application is widespread around the world. To better predict the environmental fate and mobility of contaminants, it is critical to study the capacity of biosolid-amended soils to retain and release metals. In this paper, nickel adsorption onto a calcareous soil, a lime-stabilized biosolid, and soil–biosolid mixtures (30, 75, and 150 t biosolid/ha) was studied in batch experiments. Sorption experiments showed that (1) Ni adsorption was higher onto the biosolid than the calcareous soil, and (2) biosolid acted as an adsorbent in the biosolid–soil mixtures by increasing Ni retention capacity. The sorption tests were complemented with the estimation of Ni adsorption reversibility by successive applications of extraction solutions with water, calcium (100 mg/L), and oxalic acid (equivalent to 100 mg carbon/L). It has been shown that Ni desorption rates in soil and biosolid-amended soils were lower than 30 % whatever the chemical reagent, indicating that Ni was strongly adsorbed on the different systems. This adsorption/desorption hysteresis effect was particularly significant at the highest biosolid concentration (150 t/ha). Finally, an adsorption empirical model was used to estimate the maximum permissible biosolid application rate using French national guideline. It has been shown that desorption effects should be quantitatively considered to estimate relevant biosolid loadings.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ahlberg G, Gustafsson O, Wedel P (2006) Leaching of metals from sewage sludge during one year and their relationship to particle size. Environ Pollut 144:545–553
Altin O, Özbelge HÖ, Doğu T (1998) Use of general purpose adsorption isotherms for heavy metal–clay mineral interactions. J Colloid Interf Sci 198:130–140
Alves S, Trancoso MA, Simões Gonçalves ML, Correia dos Santos MM (2012) A nickel availability study in serpentinised areas of Portugal. Geoderma 164:155–163
Antoniadis V, Alloway BJ (2002) The role of dissolved organic carbon in the mobility of Cd, Ni and Zn in sewage sludge-amended soils. Environ Pollut 117:515–521
Apul DS, Diaz ME, Gustafsson JP, Hundal LS (2010) Geochemical modeling of trace element release from biosolids. Environ Eng Sci 27:743–755
Ashworth DJ, Alloway BJ (2004) Soil mobility of sewage sludge-derived dissolved organic matter, copper, nickel and zinc. Environ Pollut 127:137–144
Barry GA, Chudek PJ, Best EK, Moody PW (1995) Estimating sludge application rates to land based on heavy metal and phosphorus sorption characteristics of soil. Water Res 29:2031–2034
Basso MC, Cerrella EG, Cukierman AL (2001) Activated carbons developed from a rapidly renewable biosource for removal of cadmium(II) and nickel(II) ions from dilute aqueous solutions. Ind Eng Chem Res 41:180–189
Bell PF, James BR, Chaney RL (1991) Heavy metal extractability in long-term sewage sludge and metal salt-amended soils. J Environ Qual 20:481–486
Bergkvist P, Berggren D, Jarvis N (2005) Cadmium solubility and sorption in a long-term sludge-amended arable soil. J Environ Qual 34:1530–1538
Burton ED, Hawker DW, Redding MR (2003) Estimating sludge loadings to land based on trace metal sorption in soil: effect of dissolved organo-metallic complexes. Water Res 37:1394–1400
Businelli D, Casciari F, Gigliotti G (2004) Sorption mechanisms determining Ni(II) retention by a calcareous soil. Soil Sci 169:355–362
Das B, Mondal NK (2011) Calcareous soil as a new adsorbent to remove lead from aqueous solution: equilibrium, kinetic and thermodynamic study. J Environ Res Technol 1:515–530
Debosz K, Petersen SO, Kure LK, Ambus P (2002) Evaluating effects of sewage sludge and household compost on soil physical, chemical and microbiological properties. Appl Soil Ecol 19:237–248
Frost HL, Ketchum LH Jr (2000) Trace metal concentration in durum wheat from application of sewage sludge and commercial fertilizer. Adv Environ Res 4:347–355
Gleyzes C, Tellier S, Astruc M (2002) Fractionation studies of trace elements in contaminated soils and sediments: a review of sequential extraction procedures. Trends Anal Chem 21:451–467
Hettiarachchi GM, Scheckel KG, Ryan JA, Sutton SR, Newville M (2006) μ-XANES and μ-XRF investigations of metal binding mechanisms in biosolids. J Environ Qual 35:342–351
Ho Y-S (2006) Review of second-order models for adsorption systems. J Hazard Mater 136:681–689
Ho YS, McKay G (1999) Pseudo-second order model for sorption processes. Process Biochem 34:451–465
Ho YS, Wase DAJ, Forster CF (1996) Kinetic studies of competitive heavy metal adsorption by sphagnum moss peat. Environ Technol 17:71–77
Kabata-Pendias A, Pendias H (1992) Trace elements in soils and plants. CRC Press, Boca Raton
Kaplan DI, Serkiz SM (2001) Quantification of thorium and uranium sorption to contaminated sediments. J Radioanal Nucl Chem 248:529–535
Karlik B (1995) Liming effect on dissolved organic matter leaching. Water, Air, Soil Pollut 85:949–954
Langmuir I (1918) The adsorption of gases on plane surfaces of glass, mica and platinum. Nat Geosci 40:1361–1403
Li Z, Ryan JA, Chen J-L, Al-Abed SR (2001) Adsorption of cadmium on biosolids-amended soils. J Environ Qual 30:903–911
Liao L, Selim HM (2010) Reactivity of nickel in soils: evidence of retention kinetics. J Environ Qual 39:1290–1297
Mamindy-Pajany Y, Hurel C, Marmier N, Roméo M (2011) Arsenic (V) adsorption from aqueous solution onto goethite, hematite, magnetite and zero-valent iron: effects of pH, concentration and reversibility. Desalination 281:93–99
Mamindy-Pajany Y, Sayen S, Guillon E (2013) Impact of sewage sludge spreading on nickel mobility in a calcareous soil: adsorption–desorption through column experiments. Environ Sci Pollut Res Int 20(7):4414-23
Massoura S, Echevarria G, Becquer T, Ghanbaja J, Leclerc-Cessac E, Morel JL (2006) Nickel bearing phases and availability in natural and anthropogenic soils. Geoderma 136:28–37
McBride MB (1989) Reactions controlling heavy metal solubility in soils. Adv Soil Sci 10:1–56
McBride MB (1995) Toxic metal accumulation from agricultural use of sludge: are USEPA regulations protective? J Environ Qual 24:5–18
McBride MB, Richards BK, Steenhuis T, Spiers G (1999) Long-term leaching of trace elements in a heavily sludge-amended silty clay loam soil. Soil Sci 164:613–623
Natal-da-Luz T, Ojeda G, Costa M, Pratas J, Lanno RP, Gestel CAM et al (2012) Short-term changes of metal availability in soil. Part I: comparing sludge-amended with metal-spiked soils. Arch Environ Con Tox 63:199–208
Oliveira EA, Montanher SF, Andrade AD, Nóbrega JA, Rollemberg MC (2005) Equilibrium studies for the sorption of chromium and nickel from aqueous solutions using raw rice bran. Process Biochem 40:3485–3490
Passuello A, Mari M, Nadal M, Schuhmacher M, Domingo JL (2010) POP accumulation in the food chain: integrated risk model for sewage sludge application in agricultural soils. Environ Int 36:577–583
Planquart P, Bonin G, Prone A, Massiani C (1999) Distribution, movement and plant availability of trace metals in soils amended with sewage sludge composts: application to low metal loadings. Sci Total Environ 241:161–179
Roig N, Sierra J, Martí E, Nadal M, Schuhmacher M, Domingo JL (2012) Long-term amendment of Spanish soils with sewage sludge: effects on soil functioning. Agric Ecosyst Environ 158:41–48
Römkens PFAM, Dolfing J (1998) Effect of Ca on the solubility and molecular size distribution of DOC and Cu binding in soil solution samples. Environ Sci Technol 32:363–369
Sastre J, Rauret G, Vidal M (2007) Sorption–desorption tests to assess the risk derived from metal contamination in mineral and organic soils. Environ Int 33:246–256
Shi Z, Peltier E, Sparks DL (2012) Kinetics of Ni sorption in soils: roles of soil organic matter and Ni precipitation. Environ Sci Technol 46:2212–2219
Sigua G, Adjei M, Rechcigl J (2005) Cumulative and residual effects of repeated sewage sludge applications: forage productivity and soil quality implications in South Florida, USA (9 pp). Environ Sci Pollut R 12:80–88
Singh AK, Pandeya SB (1998) Sorption and release of cadmium–fulvic acid complexes in sludge treated soils. Bioresource Technol 66:119–127
Stietiya MH, Wang JJ (2011) Effect of organic matter oxidation on the fractionation of copper, zinc, lead, and arsenic in sewage sludge and amended soils. J Environ Qual 40:1162–1171
Ström L, Owen AG, Godbold DL, Jones DL (2001) Organic acid behaviour in a calcareous soil: sorption reactions and biodegradation rates. Soil Biol Biochem 33:2125–2133
Tan IAW, Ahmad AL, Hameed BH (2009) Adsorption isotherms, kinetics, thermodynamics and desorption studies of 2,4,6-trichlorophenol on oil palm empty fruit bunch-based activated carbon. J Hazard Mater 164:473–482
Van Hullebusch ED, Zandvoort MH, Lens PNL (2004) Nickel and cobalt sorption on anaerobic granular sludges: kinetic and equilibrium studies. J Chem Technol Biot 79:1219–1227
Veeken AHM, Hamelers HVM (1999) Removal of heavy metals from sewage sludge by extraction with organic acids. Water Sci Technol 40:129–136
Weber WJ, Morris JC (1963) Kinetics of adsorption on carbon from solution. J Sanit Eng Div 89:31–60
Zanuzzi A, Arocena JM, van Mourik JM, Faz Cano A (2009) Amendments with organic and industrial wastes stimulate soil formation in mine tailings as revealed by micromorphology. Geoderma 154:69–75
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the EU ROUTES project (Contract No 265156, FP7 2007–2013, THEME [ENV.2010.3.1.1-2] Innovative system solutions for municipal sludge treatment and management).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Responsible editor: Zhihong Xu
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Mamindy-Pajany, Y., Sayen, S. & Guillon, E. Fate of nickel in a lime-stabilized biosolid, a calcareous soil and soil–biosolid mixtures. Environ Sci Pollut Res 21, 1638–1647 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-013-2043-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-013-2043-9