Abstract
Purpose
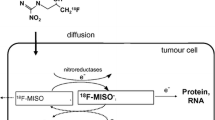
The high rates of failure in the radiotherapy target volume suggest that patients with stage II or III non-small-cell lung cancer (NSCLC) should receive an increased total dose of radiotherapy. 2-Deoxy-2-[18F]fluoro-d-glucose ([18F]FDG) and [18F]fluoromisonidazole ([18F]FMISO) (hypoxia) uptake on pre-radiotherapy positron emission tomography (PET)/X-ray computed tomography (CT) have been independently reported to identify intratumor subvolumes at higher risk of relapse after radiotherapy. We have compared the [18F]FDG and [18F]FMISO volumes defined by PET/CT in NSCLC patients included in a prospective study.
Procedures
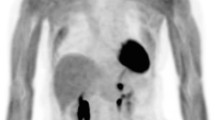
Thirty-four patients with non-resectable lung cancer underwent [18F]FDG and [18F]FMISO PET/CT before (pre-RT) and during radiotherapy (around 42 Gy, per-RT). The criteria were to delineate 40 % and 90 % SUVmax thresholds on [18F]FDG PET/CT (metabolic volumes), and SUV > 1.4 on pre-RT [18F]FMISO PET/CT (hypoxic volume). The functional volumes were delineated within the tumor volume as defined on co-registered CTs.
Results
The mean pre-RT and per-RT [18F]FDG volumes were not statistically different (30.4 cc vs 22.2; P = 0.12). The mean pre-RT SUVmax [18F]FDG was higher than per-RT SUVmax (12.7 vs 6.5; P < 0.0001). The mean [18F]FMISO SUVmax and volumes were 2.7 and 1.37 cc, respectively. Volume-based analysis showed good overlap between [18F]FDG and [18F]FMISO for all methods of segmentation but a poor correlation for Jaccard or Dice Indices (DI). The DI maximum was 0.45 for a threshold at 40 or 50 %.
Conclusion
The correlation between [18F]FDG and [18F]FMISO uptake is low in NSCLC, making it possible to envisage different management strategies as the studies in progress show.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Arriagada R, Le Chevalier T, Quoix E et al (1991) ASTRO (American Society for Therapeutic Radiology and Oncology) plenary: effect of chemotherapy on locally advanced non-small cell lung carcinoma: a randomized study of 353 patients. GETCB (Groupe d’Etude et Traitement des cancers Bronchiques), FNCLCC (Féderation Nationale des Centres de Lutte contre le Cancer) and the CEBI trialists. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 20:1183–1190
Wang YC, Tseng HL, Lin YH, Kao CH, Huang WC, Huang TC (2013) Improvement of internal tumor volumes of non-small cell lung cancer patients for radiation treatment planning using interpolated average CT in PET/CT. PLoS One 8:e64665
Garg S, Gielda BT, Kiel K, Turian JV, Fidler MJ, Batus M, Bonomi P, Sher DJ (2014) Patterns of locoregional failure in stage III non-small cell lung cancer treated with definitive chemoradiation therapy. Pract Radiat Oncol 4:342–348
Machtay M, Bae K, Movsas B, Paulus R, Gore EM, Komaki R, Albain K, Sause WT, Curran WJ (2012) Higher biologically effective dose of radiotherapy is associated with improved outcomes for locally advanced non-small cell lung carcinoma treated with chemoradiation: an analysis of the Radiation Therapy Oncology Group. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 82:425–434
Machtay M, Paulus R, Moughan J, Komaki R, Bradley J, Choy H, Albain K, Movsas B, Sause WT, Curran WJ (2012) Defining local-regional control and its importance in locally advanced non-small cell lung carcinoma. J Thorac Oncol 7:716–722
Bradley JD, Paulus R, Komaki R et al (2015) Standard-dose versus high-dose conformal radiotherapy with concurrent and consolidation carboplatin plus paclitaxel with or without cetuximab for patients with stage IIIA or IIIB non-small-cell lung cancer (RTOG 0617): a randomised, two-by-two factorial phase 3 study. Lancet Oncol 16:187–199
Vera P, Thureau S, Chaumet-Riffaud P, Modzelewski R, Bohn P, Vermandel M, Hapdey S, Pallardy A, Mahé MA, Lacombe M, Boisselier P, Guillemard S, Olivier P, Beckendorf V, Salem N, Charrier N, Chajon E, Devillers A, Aide N, Danhier S, Denis F, Muratet JP, Martin E, Riedinger AB, Kolesnikov-Gauthier H, Dansin E, Massabeau C, Courbon F, Farcy Jacquet MP, Kotzki PO, Houzard C, Mornex F, Vervueren L, Paumier A, Fernandez P, Salaun M, Dubray B (2017) Phase II study of a radiotherapy total dose increase in hypoxic lesions identified by 18F-misonidazole PET/CT in patients with non-small cell lung carcinoma (RTEP5 study). J Nucl Med 58:1045–1053
Vera P, Mihailescu SD, Lequesne J et al (2019) Radiotherapy boost in patients with hypoxic lesions identified by 18F-FMISO PET/CT in non-small-cell lung carcinoma: can we expect a better survival outcome without toxicity? [RTEP5 long-term follow-up]. Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging 46:1448–1456. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00259-019-04285-9
Bayman N, Blackhall F, McCloskey P, Taylor P, Faivre-Finn C (2014) How can we optimise concurrent chemoradiotherapy for inoperable stage III non-small cell lung cancer? Lung Cancer 83:117–125
Timmerman RD, Herman J, Cho LC (2014) Emergence of stereotactic body radiation therapy and its impact on current and future clinical practice. J Clin Oncol 32:2847–2854
Feddock J, Arnold SM, Shelton BJ, Sinha P, Conrad G, Chen L, Rinehart J, McGarry RC (2013) Stereotactic body radiation therapy can be used safely to boost residual disease in locally advanced non-small cell lung cancer: a prospective study. Int J Radiat Oncol 85:1325–1331
Abramyuk A, Tokalov S, Zöphel K et al (2009) Is pre-therapeutical FDG-PET/CT capable to detect high risk tumor subvolumes responsible for local failure in non-small cell lung cancer? Radiother Oncol 9:399–404
Aerts HJWL, van Baardwijk AAW, Petit SF, Offermann C, Loon J, Houben R, Dingemans AMC, Wanders R, Boersma L, Borger J, Bootsma G, Geraedts W, Pitz C, Simons J, Wouters BG, Oellers M, Lambin P, Bosmans G, Dekker ALAJ, Ruysscher DD (2009) Identification of residual metabolic-active areas within individual NSCLC tumours using a pre-radiotherapy 18fluorodeoxyglucose-PET-CT scan. Radiother Oncol 91:386–392
Aerts HJ, Bussink J, Oyen WJ et al (2012) Identification of residual metabolic-active areas within NSCLC tumours using a pre-radiotherapy FDG-PET-CT scan: a prospective validation. Lung Cancer 75:73–76
Shusharina N, Cho J, Sharp GC, Choi NC (2014) Correlation of 18F-FDG avid volumes on pre–radiation therapy and post–radiation therapy FDG PET scans in recurrent lung cancer. Int J Radiat Oncol 89:137–144
Calais J, Thureau S, Dubray B et al (2015) Areas of high correlation of 18F-FDG avid volumes on pre–radiation therapy and post–radiation therapy FDG PET scans in recurrent lung cancer F-FDG uptake on preradiotherapy PET/CT identify preferential sites of local relapse after chemoradiotherapy for non-small cell lung cancer. J Nucl Med 56:196–203
Qiu J, Lv B, Fu M, Wang X, Zheng X, Zhuo W (2017) 18F-Fluoromisonidazole positron emission tomography/CT-guided volumetric-modulated arc therapy-based dose escalation for hypoxic subvolume in nasopharyngeal carcinomas: a feasibility study. Head Neck 39:2519–2527
Pigorsch SU, Wilkens JJ, Kampfer S, Kehl V, Hapfelmeier A, Schläger C, Bier H, Schwaiger M, Combs SE (2017) Do selective radiation dose escalation and tumour hypoxia status impact the loco-regional tumour control after radio-chemotherapy of head & neck tumours? The ESCALOX protocol. Radiat Oncol 12:45
Thureau S, Dubray B, Modzelewski R, Bohn P, Hapdey S, Vincent S, Anger E, Gensanne D, Pirault N, Pierrick G, Vera P (2018) FDG and FMISO PET-guided dose escalation with intensity-modulated radiotherapy in lung cancer. Radiat Oncol 13:208
Rischin D, Hicks RJ, Fisher R et al (2006) Trans-Tasman Radiation Oncology Group Study 98.02. Prognostic significance of [18F]-misonidazole positron emission tomography-detected tumor hypoxia in patients with advanced head and neck cancer randomly assigned to chemoradiation with or without tirapazamine: a substudy of Trans-Tasman Radiation Oncology Group Study 98.02. J Clin Oncol 24:2098–2104
Thureau S, Chaumet-Riffaud P, Modzelewski R, Fernandez P, Tessonnier L, Vervueren L, Cachin F, Berriolo-Riedinger A, Olivier P, Kolesnikov-Gauthier H, Blagosklonov O, Bridji B, Devillers A, Collombier L, Courbon F, Gremillet E, Houzard C, Caignon JM, Roux J, Aide N, Brenot-Rossi I, Doyeux K, Dubray B, Vera P (2013) Interobserver agreement of qualitative analysis and tumor delineation of 18F-fluoromisonidazole and 3'-deoxy-3'-18F-fluorothymidine PET images in lung cancer. J Nucl Med 54:1543–1550
Wanet M, Delor A, Hanin FX, Ghaye B, van Maanen A, Remouchamps V, Clermont C, Goossens S, Lee JA, Janssens G, Bol A, Geets X (2017) An individualized radiation dose escalation trial in non-small cell lung cancer based on FDG-PET imaging. Strahlenther Onkol 193:812–822
Kerner GS, Bollineni VR, Hiltermann TJ, Groen HJ et al (2016) An exploratory study of volumetric analysis for assessing tumor response with 18F-FAZA PET/CT in patients with advanced non-small-cell lung cancer (NSCLC). EJNMMI Res 6:33
Minn H, Zasadny KR, Quint LE, Wahl RL (1995) Lung cancer: reproducibility of quantitative measurements for evaluating 2-[F-18]-fluoro-2-deoxy-D-glucose uptake at PET. Radiology 196:167–173
Grkovski M, Schwartz J, Rimner A, Schöder H, Carlin SD, Zanzonico PB, Humm JL, Nehmeh SA (2016) Reproducibility of 18F-fluoromisonidazole intratumour distribution in non-small cell lung cancer. EJNMMI Res 6:79
Holman BF, Cuplov V, Hutton BF, Groves AM, Thielemans K (2016) The effect of respiratory induced density variations on non-TOF PET quantitation in the lung. Phys Med Biol 61:3148–3163
Thomas HM, Kinahan PE, Samuel JJE, Bowen SR (2018) Impact of tumour motion compensation and delineation methods on FDG PET-based dose painting plan quality for NSCLC radiation therapy. J Med Imaging Radiat Oncol 62:81–90
Di Perri D, Lee JA, Bol A et al (2017) Correlation analysis of [18F]fluorodeoxyglucose and [18F]fluoroazomycin arabinoside uptake distributions in lung tumours during radiation therapy. Acta Oncol 56:1181–1188
Dehdashti F, Mintun MA, Lewis JS, Bradley J, Govindan R, Laforest R, Welch MJ, Siegel BA (2003) In vivo assessment of tumor hypoxia in lung cancer with 60Cu-ATSM. Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging 30:844–850
Kinoshita T, Fujii H, Hayashi Y, Kamiyama I, Ohtsuka T, Asamura H (2016) Prognostic significance of hypoxic PET using 18F-FAZA and 62Cu-ATSM in non-small-cell lung cancer. Lung Cancer 91:56–66
Cherk MH, Foo SS, Poon AM, Knight SR, Murone C, Papenfuss AT, Sachinidis JI, Saunder TH, O'Keefe GJ, Scott AM (2006) Lack of correlation of hypoxic cell fraction and angiogenesis with glucose metabolic rate in non-small cell lung cancer assessed by 18F-fluoromisonidazole and 18F-FDG PET. J Nucl Med 47:1921–1926
Bollineni VR, Kerner GS, Pruim J et al (2013) PET imaging of tumor hypoxia using 18F-fluoroazomycin arabinoside in stage III-IV non-small cell lung cancer patients. J Nucl Med 54:1175–1180
Sachpekidis C, Thieke C, Askoxylakis V et al (2015) Combined use of 18F-FDG and 18F-FMISO in unresectable non-small cell lung cancer patients planned for radiotherapy: a dynamic PET/CT study. Am J Nucl Med Mol Imaging 5:127–142
Zegers CM, van Elmpt W, Reymen B et al (2014) In vivo quantification of hypoxic and metabolic status of NSCLC tumors using [18F]HX4 and [18F]FDG-PET/CT imaging. Clin Cancer Res 20:6389–6397
Lelandais B, Ruan S, Denœux T, Vera P, Gardin I (2014) Fusion of multi-tracer PET images for dose painting. Med Image Anal 18:1247–1259
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Ethical Approval
All procedures performed in studies involving human participants were in accordance with the ethical standards of the institutional committee on human experimentation and with the Helsinki declaration of 1975, as revised in 1983.
Informed Consent
Informed consent was obtained from all individual participants included in the study.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Thureau, S., Modzelewski, R., Bohn, P. et al. Comparison of Hypermetabolic and Hypoxic Volumes Delineated on [18F]FDG and [18F]Fluoromisonidazole PET/CT in Non-small-cell Lung Cancer Patients. Mol Imaging Biol 22, 764–771 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11307-019-01422-6
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11307-019-01422-6