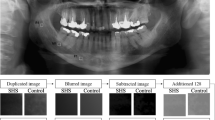
Abstract
Objectives
To assess the panoramic radiomorphometric indices and fractal dimension in women with celiac disease.
Methods
The sample consisted of 20 women with celiac disease and 20 healthy women (control group). The mandibular cortical index classification, panoramic mandibular index, mental index, and fractal dimension were evaluated on panoramic radiographs. One-way ANOVA with post hoc Tukey test was used for comparison of the linear measurements and fractal dimension between the celiac and control groups, adopting a significance level of 5%
Results
There was no significant difference in panoramic radiomorphometric indices or fractal dimension between the celiac and control groups.
Conclusions
Panoramic radiomorphometric indices and fractal dimension revealed no significant bone changes in women with celiac disease.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bianchi ML, Bardella M. Bone in celiac disease. Osteoporos Int. 2008;19:1705–16.
Schuppan D, Junker Y, Barisani D. Celiac disease: from pathogenesis to novel therapies. Gastroenterology. 2009;137:1912–33.
Bai JC, Fried M, Corazza GR, Schuppan D, Farthing M, Catassi C, et al. World Gastroenterology Organisation global guidelines on celiac disease. J Clin Gastroenterol. 2013;47:121–21616.
Bramatntini E, Ciccù M, Matacena G, Costa S, Magazzù G. Clinical evaluation of specific oral manifestations in pediatric patients with ascertained versus potential coeliac disease: a cross-sectional study. Gastroenterol Res Pract. 2014;52:1–9.
Blazina S, Bratanic N, Campa AS, Blagus R, Orel R. Bone mineral density and importance of strict gluten-free diet in children and adolescents with celiac disease. Bone. 2010;47:598–603.
Hujoel IA, Reilly NR, Rubio-Tapia A. Celiac disease: clinical features and diagnosis. Gastroenterol Clin North Am. 2019;48:19–37.
Roma E, Panayiotou J, Karantana H, Constantinidou C, Siakavellas S, Krini M, et al. Changing pattern in the clinical presentation of pediatric celiac disease: a 30-year study. Digestion. 2009;80:185–91.
Guandalini S, Assiri A. Celiac disease: a review. JAMA. Pediatr. 2014;168:272–8.
Queiroz AM, Arid J, de Carvalho FK, et al. Assessing the proposed association between DED and gluten-free diet introduction in celiac children. Spec Care Dent. 2017;37:194–8.
Souza-Souto D, Soares MEC, Rezende VS, Dantas PC, Galvão EL, Falci SGM. Association between developmental defects of enamel and celiac disease: a meta-analysis. Arch Oral Biol. 2018;87:180–90.
Gusso L, Simões MC, Skare TL, Nisihara R, Burkiewicz CC, Utiyama S. Celiac disease screening in Brazilian patients with osteoporosis. Arq Bras Endocrinol Metab. 2014;58:270–3.
Choudhary G, Gupta RK, Beniwal J. Bone mineral density in celiac disease. Indian J Pediatr. 2017;84:344–8.
Westerholm-ormio M, Garioch J, Ketola I, Savilahti E. Inflammatory cytokines in small intestinal mucosa of patients with potential coeliac disease. Clin Exp Immunol. 2002;128:94–101.
Rewers M. Epidemiology of celiac disease: what are the prevalence, incidence, and progression of celiac disease? Gastroenterol. 2005;128:47–51.
Lerner A, Shapira Y, Agmon-Levin N, Pacht A, Shor B, López HM. The clinical significance of 25OH-vitamin D status in celiac disease. Clinic Rev Allerg Immunol. 2012;42:322–30.
Benson BW, Prihoda TJ, Glass BJ. Variations in adult cortical bone mass as measured by a panoramic mandibular index. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol Oral Radiol. 1991;71:349–56.
Ledgerton D, Horner K, Devlin H, Worthington H. Panoramic mandibular index as a radiomorphometric tool: an assessment of precision. Dentomaxillofac Radiol. 1997;26:95–100.
Othman HI, Ouda SA. Mandibular radiomorphometric measurements as indicators of possible osteoporosis in celiac patients. JKAU Med Sci. 2010;17:21–35.
Carmo JZB, Medeiros SF. Mandibular inferior cortex erosion on dental panoramic radiograph as a sign of low bone mineral density in postmenopausal women. Rev Bras Ginecol Obstet. 2017;39:663–9.
Klemetti E, Kolmakov S, Kroger H. Pantomography in assessment of the osteoporosis risk group. Scand J Dent Res. 1994;102:68–72.
Apolinário AC, Sindeaux R, de Souza-Figueiredo PT, Guimarães AT, Acevedo AC, Castro LC, et al. Dental panoramic indices and fractal dimension measurements in osteogenesis imperfecta children under pamidronate treatment. Dentomaxillofac Radiol. 2016;45:2–9.
Gumussoy I, Miroglu O, Cankaya E, Bayrakdar IS. Fractal properties of the trabecular pattern of the mandible in chronic renal failure. Dentomaxillofac Radiol. 2016;45:2–6.
Mansour AG, Ouda S, Saleh AE. Oral health in a group of patients with celiac disease: a clinical and radiographic study. Int J Clin Dent Sci. 2014;5:25–30.
Koh KJ, Park HN, Kim KA. Prediction of age-related osteoporosis using fractal analysis on panoramic radiographs. Imaging Sci Dent. 2012;42:231–5.
Demirbaş AK, Ergün S, Güneri P, Aktener BO, Boyacioğlu H. Mandibular bone changes in sickle cell anemia: fractal analysis. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol Oral Radiol Endod. 2008;106:41–8.
Camargo AJ, Côrtes ARG, Aoki EM, Baladi MG, Arita MS, Watanabe PCA. Analysis of bone quality on panoramic radiograph in osteoporosis research by fractal dimension. Appl Math. 2016;7:375–86.
White SC, Rudolph DJ. Alterations of the trabecular pattern of the jaws in patients with osteoporosis. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol Oral Radiol Endod. 1999;88:628–35.
Gaur B, Chaudhary A, Wanjari PV, Sunil MK, Basavaraj P. Evaluation of panoramic radiographs as a screening tool of osteoporosis in postmenopausal women: a cross sectional study. J Clin Diagn Res. 2013;7:2051–5.
Bhatnagar S, Krishnamurthy V, Pagare SS. Diagnostic efficacy of panoramic radiography in detection of osteoporosis in post-menopausal women with low bone mineral density. J Clin Imaging Sci. 2013;3:1–7.
Pallagatti S, Parnami P, Sheikh S, Gupta D. Efficacy of panoramic radiography in the detection of osteoporosis in post-menopausal women when compared to dual energy X-ray absorptiometry. Open Dent J. 2017;11:350–9.
Neves FS, Oliveira ISAF, Torres MGG, Toralles MBP, Silva MCBO, Campos MIG, et al. Evaluation of panoramic radiomorphometric indices related to low bone density in sickle cell disease. Osteoporos Int. 2012;23:2037–42.
Kurşun-Çakmak EŞ, Bayrak S. Comparison of fractal dimension analysis and panoramic-based radiomorphometric indices in the assessment of mandibular bone changes in patients with type 1 and type 2 diabetes mellitus. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol Oral Radiol. 2018;126:184–91.
Bayrak S, Göller-Bulut D, Orhan K, Sinanoğlu EA, Kurşun-Çakmak EŞ, Mısırlı M, Ankaralı H. Evaluation of osseous changes in dental panoramic radiography of thalassemia patients using mandibular indexes and fractal size analysis. Oral Radiol. 2019. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11282-019-00372-7. (Epub ahead of print).
Hernlund E, Svedbom A, Ivergard M, Compston J, Cooper C, Sternmark J, et al. Osteoporosis in the European Union: medical management, epidemiology and economic burden. Arch Osteoporos. 2013;8:136.
Hwang JJ, Lee JH, Kim YH, Jeong HG, Choi YJ, Han SS. Strut analyses for osteoporosis detection model using dental panoramic radiography. Dentomaxillofac Radiol. 2017;46:20170006.
Rabelink NM, Westgeest HM, Bravenboer N, Jacobs AJM. Bone pain and extremely low bone mineral density due to severe vitamin D deficiency in celiac disease. Arch Osteoporos. 2011;6:209–21.
Dutra V, Yang J, Devlin H, Susin C. Radiomorphometric indices and their relation to gender, age, and dental status. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol Oral Radiol Endod. 2005;99:479–84.
Alkurt MT, Peker I, Sanal O. Assessment of repeatability and reproducibility of mental and panoramic mandibular indices on digital panoramic images. Int Dent J. 2007;57:433–8.
Bozdag G, Sener S. The evaluation of MCI, MI, PMI and GT on both genders with different age and dental status. Dentomaxillofac Radiol. 2015;44(9):20140435.
Poornima G, Poornima C. Radiomorphometric indices of the mandible—an indicator of osteoporosis. J Clin Diagn Res. 2014;8:195–8.
Devlin H, Horner K. Mandibular radiomorphometric indices in the diagnosis of reduced skeletal bone mineral density. Osteoporos Int. 2002;13:373–8.
Göller-Bulut D, Bayrak S, Uyeturk U, Ankarali H. Mandibular indexes and fractal properties on the panoramic radiographs of the patients using aromatase inhibitors. Br J Radiol. 2018;91:20180442.
Çankur B, Dagistan S, Sumbullu MA. No correlation between mandibular and non-mandibular measurements in osteoporotic men. Acta Radiol. 2010;51:789–92.
Damilakis J, Vlasiadis K. Have panoramic indices the power to identify women with low BMD at the axial skeleton? Phys Med. 2010;27:39–433.
Devlin H, Karayianni K, Mitsea A, et al. Diagnosing osteoporosis by using dental panoramic radiographs: the OSTEODENT project. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol Oral Radiol Endod. 2007;104:821–8.
Mahl CRW, Licks R, Fontanella VRC. Comparison of morphometric indices obtained from dental panoramic radiography for identifying individuals with osteoporosis/osteopenia. Radiol Bras. 2008;41:183–7.
Gulsahi A, Yuzugullu B, Imirzahoglu P, Genç Y. Assessment of panoramic radiomorphometric indices in Turkish patients of different age groups, gender and dental status. Dentomaxillofac Radiol. 2008;37:288–92.
Sindeaux R, Figueiredo PTS, Melo NS, Guimaraes ATB, Lazarte L, Pereira FB, et al. Fractal dimension and mandibular cortical width in normal and osteoporotic men and women. Maturitas. 2014;77:142–8.
Sanchez I, Uzcategui G. Fractals in dentistry. J Dent. 2011;39:273–92.
Kalinowski P, Rozylo-Kalinowska I. Mandibular inferior cortex width may serve as a prognostic osteoporosis index in Polish patients. Folia Morphol. 2011;70:272–81.
Gumussoy I, Miloglu O, Cankaya E, Bayrakdar IS. Fractal properties of the trabecular pattern of the mandible in chronic renal failure. Dentomaxillofac Radiol. 2016;45(5):20150389.
Demiralp KÖ, Kurşun-Çakmak EŞ, Bayrak S, Akbulut N, Atakan C, Orhan K. Trabecular structure designation using fractal analysis technique on panoramic radiographs of patients with bisphosphonate intake: a preliminary study. Oral Radiol. 2019;35:23–8.
McFarlane XA, Bhalla AK, Robertson DA. Effect of a gluten-free diet on osteopenia in adults with newly diagnosed celiac disease. Gut. 1996;39:180–4.
Kotze LMS, Skare T, Vinholi A, Jurkonis L, Nisihara R. Impact of a gluten-free diet on bone mineral density in celiac patients. Rev Esp Enferm Dig. 2016;108:84–8.
Zanchetta MB, Longobardi V, Costa F, Longarini G, Mazure RM, Moreno ML, et al. Impaired bone microarchitecture improves after 1 year on gluten-free diet: a prospective longitudinal HRpQCT study in women with celiac disease. J Bone Miner Res. 2017;32:135–42.
Krupa-Kozak U. Pathologic bone alterations in celiac disease: etiology, epidemiology, and treatment. Nutrition. 2014;30:16–24.
Acknowledgements
This study was financed by the Fundação de Amparo à Pesquisa do Estado da Bahia (FAPESB) and Coordenação de Aperfeiçoamento de Pessoal de Nível Superior - Brasil (CAPES)—Finance Code 001.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Human rights statements
All procedures followed were in accordance with the ethical standards of the responsible committee on human experimentation (institutional and national) and with the Helsinki Declaration of 1975, as revised in 2008 (5).
Informed consent
Informed consent was obtained from all patients for being included in the study.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Neves, F.S., Barros, A.S., Cerqueira, G.A. et al. Assessment of fractal dimension and panoramic radiomorphometric indices in women with celiac disease. Oral Radiol 36, 141–147 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11282-019-00388-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11282-019-00388-z